Netty如何处理连接事件
上文讲了Netty如何绑定端口,现在我们来阅读下netty如何处理connect事件。上文我们说了NioEventLoop启动后不断去调用select的事件,当客户端连接时候,回触发processSelectedKeys方法,然后调用 processSelectedKey方法
| SelectKey | 说明 |
|---|---|
| OP_READ | 读 1 |
| OP_WRITE | 写 4 |
| OP_CONNECT | 客户端connect 8 |
| OP_ACCEPT | 连接 16 |
private void processSelectedKey(SelectionKey k, AbstractNioChannel ch) {
// 省略。。。
try {
// 16 是连接事件
int readyOps = k.readyOps();
// We first need to call finishConnect() before try to trigger a read(...) or write(...) as otherwise
// the NIO JDK channel implementation may throw a NotYetConnectedException.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT) != 0) {
// remove OP_CONNECT as otherwise Selector.select(..) will always return without blocking
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/924
int ops = k.interestOps();
ops &= ~SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT;
k.interestOps(ops);
unsafe.finishConnect();
}
// Process OP_WRITE first as we may be able to write some queued buffers and so free memory.
if ((readyOps & SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) != 0) {
// Call forceFlush which will also take care of clear the OP_WRITE once there is nothing left to write
ch.unsafe().forceFlush();
}
// Also check for readOps of 0 to workaround possible JDK bug which may otherwise lead
if ((readyOps & (SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)) != 0 || readyOps == 0) {
// 调用NioMessageUnsafe的read方法
unsafe.read();
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ignored) {
unsafe.close(unsafe.voidPromise());
}
}
通过代码我们知道调用的是NioMessageUnsafe的read方法,进入方法我们源码,我门发现其调用了NioServerSocketChannel的doReadMessages方法,
try {
do {
// 调用NioServerSocketChannel的doReadMessages方法
int localRead = doReadMessages(readBuf);
if (localRead == 0) {
break;
}
if (localRead < 0) {
closed = true;
break;
}
allocHandle.incMessagesRead(localRead);
} while (continueReading(allocHandle));
} catch (Throwable t) {
exception = t;
}
int size = readBuf.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i ++) {
readPending = false;
// 触发fireChannelRead事件
pipeline.fireChannelRead(readBuf.get(i));
}
@Override
protected int doReadMessages(List<Object> buf) throws Exception {
//这里处理java的accpet事件
SocketChannel ch = SocketUtils.accept(javaChannel());
try {
if (ch != null) {
// 丢到buf里 然后触发channelRead事件
buf.add(new NioSocketChannel(this, ch));
return 1;
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn("Failed to create a new channel from an accepted socket.", t);
try {
ch.close();
} catch (Throwable t2) {
logger.warn("Failed to close a socket.", t2);
}
}
return 0;
}
之前文章我门在绑定端口时候,pipiline中添加了一个ServerBootstrapAcceptor类,我门看下其channelRead方法的实现
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
// 这个其实就是上面的NioSocketChannel
final Channel child = (Channel) msg;
// 我们启动设置的ChannelInitializer
child.pipeline().addLast(childHandler);
//设置 options
setChannelOptions(child, childOptions, logger); //设置 attributes
setAttributes(child, childAttrs);
try {
// 注册child?
childGroup.register(child).addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture future) throws Exception {
if (!future.isSuccess()) {
forceClose(child, future.cause());
}
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
forceClose(child, t);
}
}
接下来我们继续看下childGroup.register(child)如何注册channel的。逻辑就是调用EveentLoopGrpoup的next方法分配SingleThreadEventLoop,调用其register方法
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(Channel channel) {
return register(new DefaultChannelPromise(channel, this));
}
@Override
public ChannelFuture register(final ChannelPromise promise) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(promise, "promise");
// 最终走到NioSocketChannel的unsafe对象,registry这个方法在Abstract&AbstractUnsafe对象里实现
promise.channel().unsafe().register(this, promise);
return promise;
}
我们看下register方法实现,我们发现这个其实跟NioServerSocketChannel的注册是一样的,绑定EventLoop,并且开启EventLoop,然后调用其
@Override
public final void register(EventLoop eventLoop, final ChannelPromise promise) {
ObjectUtil.checkNotNull(eventLoop, "eventLoop");
if (isRegistered()) {
promise.setFailure(new IllegalStateException("registered to an event loop already"));
return;
}
if (!isCompatible(eventLoop)) {
promise.setFailure(
new IllegalStateException("incompatible event loop type: " + eventLoop.getClass().getName()));
return;
}
// 绑定当前的EventLoop
AbstractChannel.this.eventLoop = eventLoop;
if (eventLoop.inEventLoop()) {
register0(promise);
} else {
try {
// 第一次提交Runnable会启动EventLoop线程去启动事件,具体之前Netty绑定端口文章我写过。如何去启动的
eventLoop.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
register0(promise);
}
});
} catch (Throwable t) {
logger.warn(
"Force-closing a channel whose registration task was not accepted by an event loop: {}",
AbstractChannel.this, t);
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
}
继续看下register0方法
private void register0(ChannelPromise promise) {
try {
// check if the channel is still open as it could be closed in the mean time when the register
// call was outside of the eventLoop
if (!promise.setUncancellable() || !ensureOpen(promise)) {
return;
}
boolean firstRegistration = neverRegistered;
// 开始注册绑定selectKey
doRegister();
neverRegistered = false;
registered = true;
// Ensure we call handlerAdded(...) before we actually notify the promise. This is needed as the
// user may already fire events through the pipeline in the ChannelFutureListener.
pipeline.invokeHandlerAddedIfNeeded();
safeSetSuccess(promise);
pipeline.fireChannelRegistered();
// Only fire a channelActive if the channel has never been registered. This prevents firing
// multiple channel actives if the channel is deregistered and re-registered.
if (isActive()) {
//第一次注册时候会调用HeadContext的channelActive完成读事件的注册
if (firstRegistration) {
pipeline.fireChannelActive();
} else if (config().isAutoRead()) {
// This channel was registered before and autoRead() is set. This means we need to begin read
// again so that we process inbound data.
//
// See https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/4805
beginRead();
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// Close the channel directly to avoid FD leak.
closeForcibly();
closeFuture.setClosed();
safeSetFailure(promise, t);
}
}
这边如何调用链路比较长 我这边以断点形式给大家展示一下
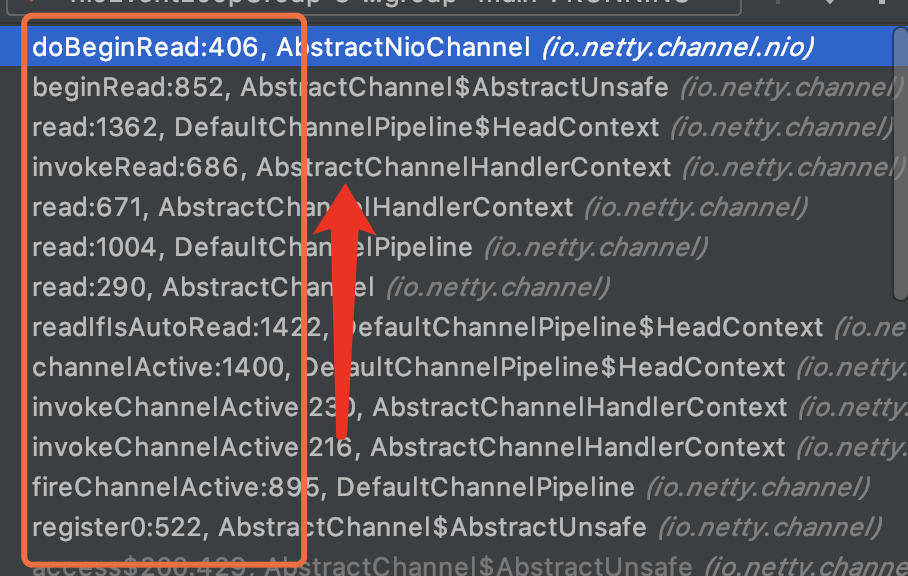
至此netty完成了处理客户端的连接,绑定EventLoop,并且开启EventLoop,完成读事件的注册,
结束
❝识别下方二维码!回复: 「
❞入群」 ,扫码加入我们交流群!

