C语言编程练习
双向链表添加节点
根据数据添加到双向链表中的位置不同,可细分为以下 3 种情况:
添加至表头
将新数据元素添加到表头,只需要将该元素与表头元素建立双层逻辑关系即可。
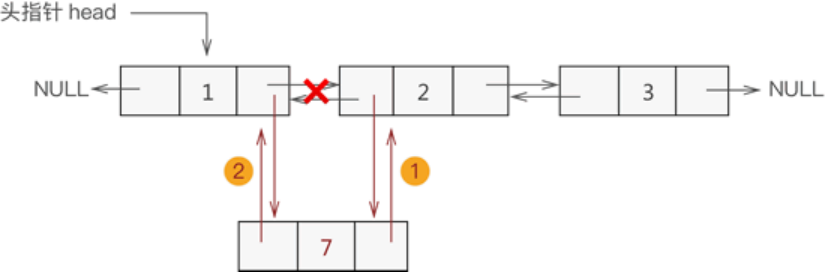
换句话说,假设新元素节点为 temp,表头节点为 head,则需要做以下 2 步操作即可:
temp->next=head; head->prior=temp;
将 head 移至 temp,重新指向新的表头;
例如,将新元素 7 添加至双链表的表头

中间位置添加节点
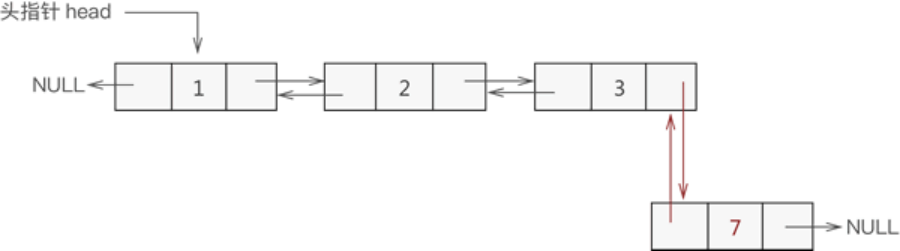
添加到表尾
实现代码:
head.h
#ifndef _head_h_
#define _head_h_
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct line{
struct line * prior;
int data;
struct line * next;
}line;
//双链表的创建
line* initLine(line * head);
//双链表插入元素,add表示插入位置
line * insertLine(line * head,int data,int add);
//双链表删除指定元素
line * delLine(line * head,int data);
//双链表中查找指定元素
int selectElem(line * head,int elem);
//双链表中更改指定位置节点中存储的数据,add表示更改位置
line *amendElem(line * p,int add,int newElem);
//输出双链表的实现函数
void display(line * head);
#endif
main.c
#include head.h
int main() {
line * head=NULL;
//创建双链表
head=initLine(head);
display(head);
//在表中第 3 的位置插入元素 7
head=insertLine(head, 7, 3);
display(head);
//表中删除元素 2
head=delLine(head, 2);
display(head);
printf("元素 3 的位置是:%d
",selectElem(head,3));
//表中第 3 个节点中的数据改为存储 6
head = amendElem(head,3,6);
display(head);
return 0;
}
line.c
#include head.h
line* initLine(line * head){
head=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
head->prior=NULL;
head->next=NULL;
head->data=1;
line * list=head;
for (int i=2; i<=5; i++) {
line * body=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
body->prior=NULL;
body->next=NULL;
body->data=i;
list->next=body;
body->prior=list;
list=list->next;
}
return head;
}
line * insertLine(line * head,int data,int add){
//新建数据域为data的结点
line * temp=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
temp->data=data;
temp->prior=NULL;
temp->next=NULL;
//插入到链表头,要特殊考虑
if (add==1) {
temp->next=head;
head->prior=temp;
head=temp;
}else{
line * body=head;
//找到要插入位置的前一个结点
for (int i=1; i<add-1; i++) {
body=body->next;
}
//判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾
if (body->next==NULL) {
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}else{
body->next->prior=temp;
temp->next=body->next;
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}
}
return head;
}
line * delLine(line * head,int data){
line * temp=head;
//遍历链表
while (temp) {
//判断当前结点中数据域和data是否相等,若相等,摘除该结点
if (temp->data==data) {
temp->prior->next=temp->next;
temp->next->prior=temp->prior;
free(temp);
return head;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("链表中无该数据元素");
return head;
}
//head为原双链表,elem表示被查找元素
int selectElem(line * head,int elem){
//新建一个指针t,初始化为头指针 head
line * t=head;
int i=1;
while (t) {
if (t->data==elem) {
return i;
}
i++;
t=t->next;
}
//程序执行至此处,表示查找失败
return -1;
}
//更新函数,其中,add 表示更改结点在双链表中的位置,newElem 为新数据的值
line *amendElem(line * p,int add,int newElem){
line * temp=p;
//遍历到被删除结点
for (int i=1; i<add; i++) {
temp=temp->next;
}
temp->data=newElem;
return p;
}
display.c
#include “head.h”
void display(line * head){
line * temp=head;
while (temp) {
if (temp->next==NULL) {
printf("%d
",temp->data);
}else{
printf("%d->",temp->data);
}
temp=temp->next;
}
}
建立自己的项目目录
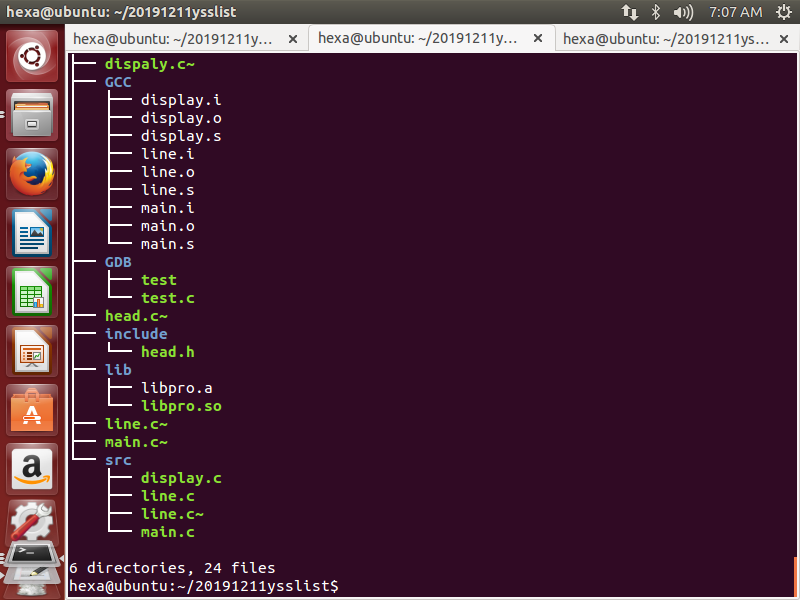
新建三个标签,分别用于基本命令、编译文件和调试文件,GCC测试生成文件转移到GCC中,源文件转移到src中,库文件转移到lib中等等。生成的tree目录如上所示。
GCC练习
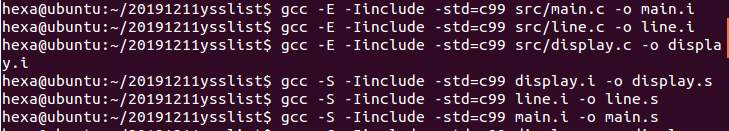

编译过程
1、编译预处理:c文件到c文件
2、编译:c文件到asm文件(就是汇编语言)
3、汇编:asm到code
4、链接:将生成的目标文件链接起来
Gcc+文件名.c:编译,会得到a.out文件
Gcc+文件名.c+ -o+文件名 :一步到位的编译指令
./文件名:执行编译后的文件
对应编译过程的命令(记忆:ESC)
1、gcc -E + xx.c -o + xx.i
或者 gcc -E +xx.c
2、gcc -S + xx.i -o + xx.s
3、gcc -C + xx.s -o + xx.o
4、gcc xx.o -o + xx
-Iinclude选项是用来寻找头文件的,-std=c99选项用于将编译指令换成c99标准。这是因为在gcc中直接在for循环中初始化了增量:
for(int i=0; i<len; i++)
{}
这语法在gcc中是错误的,必须先先定义i变量:
int i;
for(i=0;i<len;i++){}
这是因为gcc基于c89标准,换成C99标准就可以在for循环内定义i变量了。
注意:ESc选项中的大小写要区分清
静态库,动态库制作和调用
静态库

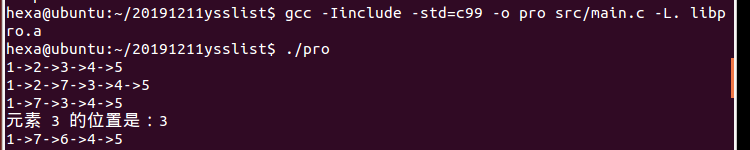
动态库
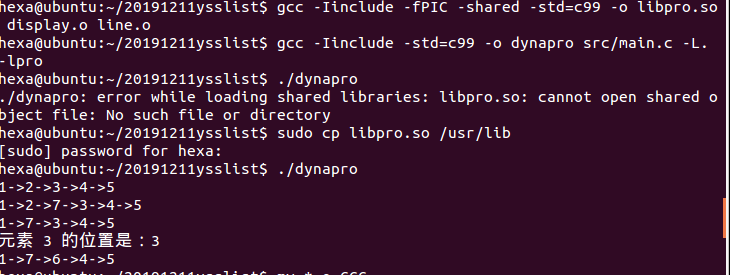
gdb练习(四种断点)
实验代码:
#include<stdio.h>
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
int num = 1;
while(num<100)
{
num *= 2;
}
printf("num=%d",num);
return 0;
}
1、b location
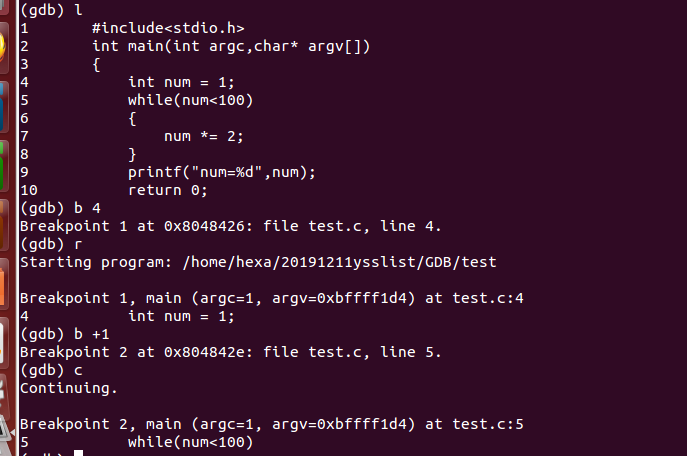
b 4和b +1,分别在第四行和第五行打上断点
2、b .. if condition
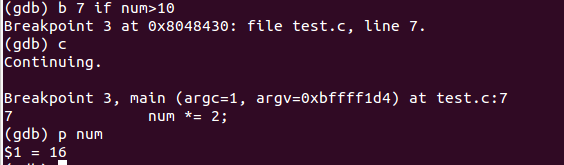
条件断点,当num>10时在第7行打上断点
此时打印num得到值为16,结果正确
3、tbreak
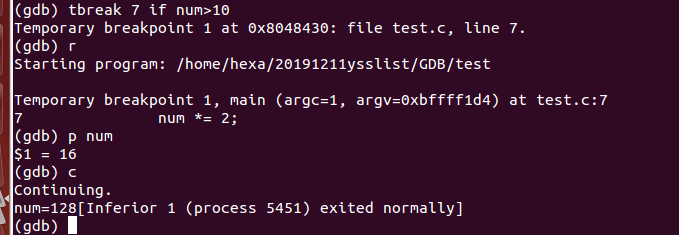
和条件断点类似,但可以看到在continue之后,num还是大于10,程序理应在第7行的断点停下,可由于tbreak的作用,它只在这个断点停了一次
4、rbreak
对源程序进行修改,添加一个函数
#include<stdio.h>
void rb_one(){
printf("rb_one
");
}
void rb_second(){
printf("rb_second");
}
int main(int argc,char* argv[])
{
rb_one();
rb_second();
return 0;
}
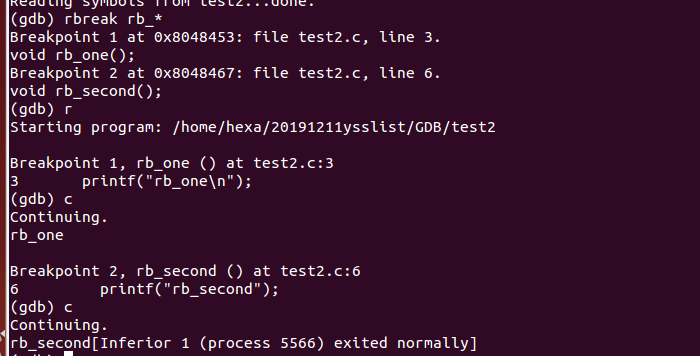
rbreak是针对函数设置的断点
rbreak 命令的使用语法格式为:
(gdb) rbreak regex
其中 regex 为一个正则表达式,程序中函数的函数名只要满足 regex 条件,rbreak 命令就会其内部的开头位置打断点。值得一提的是,rbreak 命令打的断点和 break 命令打断点的效果是一样的,会一直存在,不会自动消失。
我们可以对rb开头的函数设置断点,得到结果如下所示
makefile
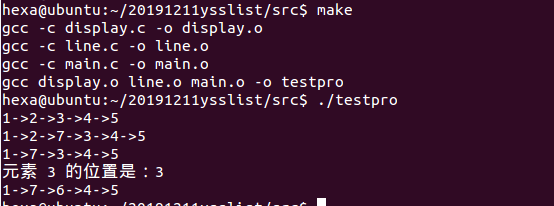
内容:
testpro:display.o line.o main.o
gcc display.o line.o main.o -o testpro
display.o:display.c head.h
gcc -c display.c -o display.o
line.o:line.c head.h
gcc -c line.c -o line.o
main.o:main.c head.h
gcc -c main.c -o main.o