KDL(Kinematics and Dynamics Library)中定义了一个树来代表机器人的运动学和动力学参数,ROS中的kdl_parser提供了工具能将机器人描述文件URDF转换为KDL tree.
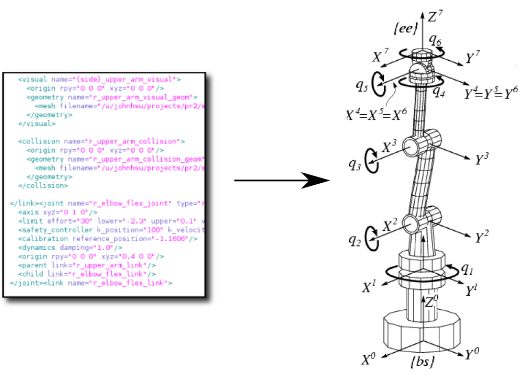
Kinematic Trees: 链或树形结构。已经有多种方式来定义机构的运动学结构,KDL使用图论中的术语来定义:
- A closed-loop mechanism is a graph, 闭链机构是一幅图
- an open-loop mechanism is a tree, 开链机构是一棵树
- an unbranched tree is a chain. 没有分支的树是一个运动链
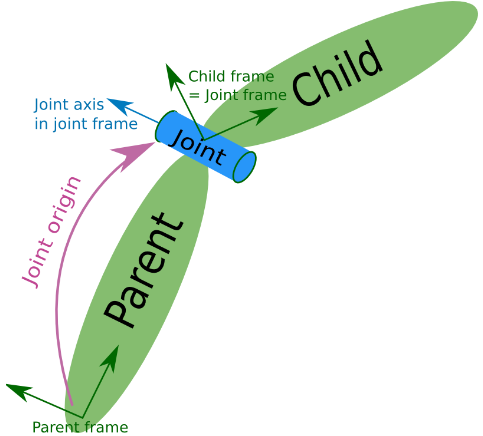
KDL Chain和KDL Tree都由最基本的KDL Segments元素串接而成,Segment可以理解为机构运动链上的一个运动部件。如下图所示KDL Segment包含关节KDL Joint 以及部件的质量/惯性属性KDL RigidBodyInertia,并且定义了一个参考坐标系Freference和末端坐标系Ftip
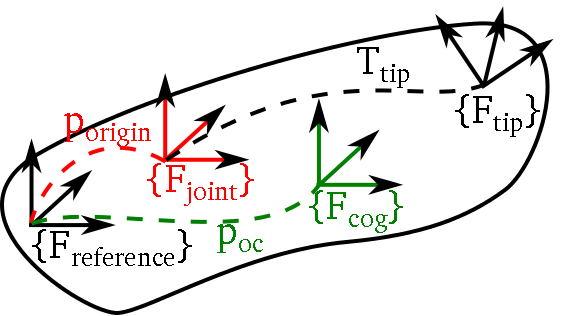
KDL segment
末端到关节坐标系的转换由Ttip描述。在一个运动链或树中,子部件会被添加到父部件的末端,因此上一个部件的Ftip就是下一个部件的参考坐标系Freference (tip frame of parent = reference frame of the child). 通常Fjoint和Freference是重合的,但是也可以存在偏移。
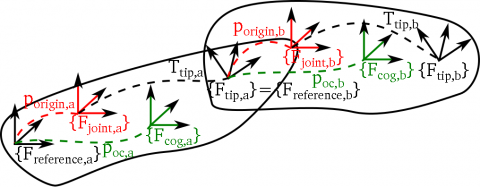
KDL chain
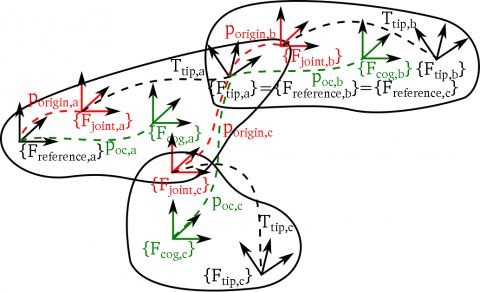
KDL tree
KDL中的定义与URDF中的定义基本是一样的:
也可以参考MATLAB Robotics System Toolbox中的对Rigid Body Tree Robot Model的描述:

Python中创建KDL tree
参考pykdl_utils,pykdl_utils中包含了kdl_parser.py(用于解析URDF文件并将其转换为KDL tree或chain),kdl_kinematics.py(封装了KDL kinematics的一系列函数,使得用Python调用更方便)等实用程序。下面先安装urdfdom_py(Python implementation of the URDF parser):
sudo apt-get install ros-indigo-urdfdom-py
然后在github上下载pykdl_utils的源代码,使用catkin_make进行编译。
convert URDF objects into PyKDL.Tree
首先通过urdf_parser_py来解析URDF文件,有下面几种使用方式:通过xml字符串解析、xml文件解析,以及从ROS 参数服务器获取robot_description字符串信息。
#! /usr/bin/env python # Load the urdf_parser_py manifest, you use your own package # name on the condition but in this case, you need to depend on # urdf_parser_py. import roslib; roslib.load_manifest('urdfdom_py') import rospy # Import the module from urdf_parser_py.urdf import URDF # 1. Parse a string containing the robot description in URDF. # Pro: no need to have a roscore running. # Cons: n/a # Note: it is rare to receive the robot model as a string. robot = URDF.from_xml_string("<robot name='myrobot'></robot>") # - OR - # 2. Load the module from a file. # Pro: no need to have a roscore running. # Cons: using hardcoded file location is not portable. robot = URDF.from_xml_file() # - OR - # 3. Load the module from the parameter server. # Pro: automatic, no arguments are needed, consistent # with other ROS nodes. # Cons: need roscore to be running and the parameter to # to be set beforehand (through a roslaunch file for # instance). robot = URDF.from_parameter_server() # Print the robot print(robot)
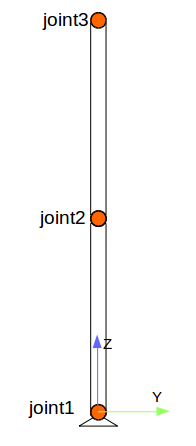
下面编写一个简单的robot.urdf文件,创建一个连杆机器人。joint1为与基座link0相连的基关节,joint3为末端关节。

<robot name="test_robot"> <link name="link0" /> <link name="link1" /> <link name="link2" /> <link name="link3" /> <joint name="joint1" type="continuous"> <parent link="link0"/> <child link="link1"/> <origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0" /> <axis xyz="1 0 0" /> </joint> <joint name="joint2" type="continuous"> <parent link="link1"/> <child link="link2"/> <origin xyz="0 0 1" rpy="0 0 0" /> <axis xyz="1 0 0" /> </joint> <joint name="joint3" type="continuous"> <parent link="link2"/> <child link="link3"/> <origin xyz="0 0 1" rpy="0 0 0" /> <axis xyz="1 0 0" /> </joint> </robot>
pykdl_utils中还提供了下列几个指令用于测试分析我们的机器人,如果ROS参数服务器中加载了/robot_description则命令行中的xml文件可以省略:
rosrun pykdl_utils kdl_parser.py [robot.xml]
rosrun pykdl_utils kdl_kinematics.py [robot.xml]
rosrun pykdl_utils joint_kinematics.py [robot.xml]
对于我们上面编写的robot.urdf文件,可以用下面命令进行测试:
rosrun pykdl_utils kdl_parser.py `rospack find test`/robot.urdf
下面是KDL运动学一些基本的用法,相关函数可以参考:KDLKinematics Class Reference
#! /usr/bin/env python # Import the module from urdf_parser_py.urdf import URDF from pykdl_utils.kdl_parser import kdl_tree_from_urdf_model from pykdl_utils.kdl_kinematics import KDLKinematics robot = URDF.from_xml_file("/home/sc/catkin_ws/src/test/robot.urdf") tree = kdl_tree_from_urdf_model(robot) print tree.getNrOfSegments() chain = tree.getChain("link0", "link3") print chain.getNrOfJoints() # forwawrd kinematics kdl_kin = KDLKinematics(robot, "link0", "link3") q = [0, 0, 0] pose = kdl_kin.forward(q) # forward kinematics (returns homogeneous 4x4 matrix) print pose q_ik = kdl_kin.inverse(pose) # inverse kinematics print q_ik if q_ik is not None: pose_sol = kdl_kin.forward(q_ik) # should equal pose print pose_sol J = kdl_kin.jacobian(q) print 'J:', J
我们将URDF文件转换为KDL tree以后可以获取机构运动链/树的相关信息。KDLKinematics的构造函数根据urdf文件,以及机器人的基座base_link和末端end_link就可以创建出运动链:
def pykdl_utils.kdl_kinematics.KDLKinematics.__init__ (self, urdf, base_link, end_link, kdl_tree = None) # Parameters: # urdf URDF object of robot. # base_link Name of the root link of the kinematic chain. # end_link Name of the end link of the kinematic chain. # kdl_tree Optional KDL.Tree object to use. If None, one will be generated from the URDF.
正运动学的计算函数forward参数就是关节角度;逆运动学计算函数inverse的参数为末端位姿矩阵,因为是数值解,还可以指定初始值,以及关节角的范围。
# Inverse kinematics for a given pose, returning the joint angles required to obtain the target pose. def pykdl_utils.kdl_kinematics.KDLKinematics.inverse(self, pose, q_guess = None, min_joints = None, max_joints = None )
# Parameters: # pose Pose-like object represeting the target pose of the end effector. # q_guess List of joint angles to seed the IK search. # min_joints List of joint angles to lower bound the angles on the IK search. If None, the safety limits are used. # max_joints List of joint angles to upper bound the angles on the IK search. If None, the safety limits are used.
C++中创建KDL tree
为了使用KDL parser需要在package.xml中添加相关依赖项:
<package> ... <build_depend package="kdl_parser" /> ... <run_depend package="kdl_parser" /> ... </package>
另外还需要在C++程序中加入相关的头文件:
#include <kdl_parser/kdl_parser.hpp>
下面有多种从urdf创建KDL tree的方式:
1. From a file
KDL::Tree my_tree; if (!kdl_parser::treeFromFile("filename", my_tree)){ ROS_ERROR("Failed to construct kdl tree"); return false; }
2. From the parameter server
KDL::Tree my_tree; ros::NodeHandle node; std::string robot_desc_string; node.param("robot_description", robot_desc_string, std::string()); if (!kdl_parser::treeFromString(robot_desc_string, my_tree)){ ROS_ERROR("Failed to construct kdl tree"); return false; }
3. From an xml element
KDL::Tree my_tree; TiXmlDocument xml_doc; xml_doc.Parse(xml_string.c_str()); xml_root = xml_doc.FirstChildElement("robot"); if (!xml_root){ ROS_ERROR("Failed to get robot from xml document"); return false; } if (!kdl_parser::treeFromXml(xml_root, my_tree)){ ROS_ERROR("Failed to construct kdl tree"); return false; }
4. From a URDF model
KDL::Tree my_tree; urdf::Model my_model; if (!my_model.initXml(....)){ ROS_ERROR("Failed to parse urdf robot model"); return false; } if (!kdl_parser::treeFromUrdfModel(my_model, my_tree)){ ROS_ERROR("Failed to construct kdl tree"); return false; }
参考:
