假设,要你在控制台输出1到100,这个时候怎么输出,emmmmm我可以写100个输出语句。干得漂亮!
for循环:
for循环的结构:
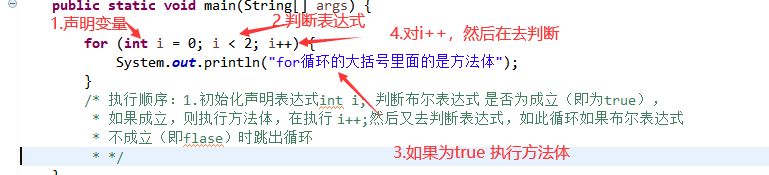
for循环练习:
01:打印1到100的累加和:
public static void main(String[] args) { /* 打印1到100的累加和 */ int num = 0 ; //初始化num变量来算累加和 for (int i = 1; i <=100; i++) { //开始循环从1开始到100 num = num + i; //每循环一次都把i与num相加一遍 } System.out.println(num); //输出累加和num 结果为5050。 }
01:打印九九乘法表:
public static void main(String[] args) { /* * 打印九九乘法表 例如1 x 1 = 1 * 我把前面的1看做是i, 把后面的看做是j * */ for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) { //定义i循环九次 for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) { //定义j内部循环的次数等于 i System.out.print(i+"x"+j+"="+i*j+" "); //一次打印出乘法口诀表 } System.out.println(" ");//当内部循环执行完时,进行换行 } }
for循环的变换:
public static void main(String[] args) { /* for循环的变换以九九乘法表为例 */ int i =1; //将变量i放在对应for循环外 for (; i <= 9;) { int j = 1;//将变量j放在对应for循环外 for (; j <= i;) { System.out.print(i+"x"+j+"="+i*j+" "); j++; //将j++放在对应的for循环的方法体内 } i++; //将i++放在对应的for循环的方法体内 System.out.println(" ");//当内部循环执行完时,进行换行 } /*注:无论放在括号里面还是放在外面,for循环括号中的分号不能少必须是两个,且是英文*/ }
while循环:
while循环可以说和for循环如出一辙没有太大的区别
while循环结构:
public static void main(String[] args) { int a =1; //声明变量表达式a 并赋初始值为1 while (a<2) { //布尔表达式a是否小于2 如果为true则执行方法体 ,如果为flase则跳出循环 System.out.println(a); //方法体 } }
while循环练习:
01.打印1到100内所有偶数:
public static void main(String[] args) { /* 使用while循环输出1到100以内所有的偶数; */ int i = 1; //初始化i while (i < 100) { //表达式小于100 if (i % 2 == 0) { //判断i对2取余是否为0 System.out.println(i); //输出i } i++; //i进行加加 } }
do...while循环:
do...while结构:
public static void main(String[] args) { int x =1; //声明变量表达式 do { System.out.println(x); //括号里面是循环体 x++; } while (x<10); //布尔表达式 }
do...while特点:
do...while循环的特点:无条件执行一次循环体,即使我们将循环条件直接写成false,也依然会循环一次。
三大循环之间的区别:
- 首先结构上的不同,就是写法不一样;
- for循环可以变换着写,while,do...while不可以
- for循环和while循环先判断布尔表达式是否成立在执行方法体,do...while先执行方法体再执行布尔表达式
- for循环运用在循环次数已知的情况下,while,do...while运用在循环次数 未知的情况下
- 建议使用的顺序:for,while,do-while
三大循环对应的死循环:
- for: for( ; ; ){}
- while: while(true){}
- do...while: do{ }while(true);
例子如下:
public static void main(String[] args) { // 三大死循环; for (;;) { System.out.println("我是for死循环"); } while (true) { System.out.println("我是while死循环"); } do { System.out.println("我是do...while死循环"); } while (true); }
注:这三给死循环不能同时出现,一次只能出现一种。
Random随机数:
Random是java API提供是一个类,它可以向我们提供一个随机数。
语法格式:
package com.code_test01; import java.util.Random; //导包 public class Dome08 { public static void main(String[] args) { Random random = new Random();//实例化Random类 /*调用nextInt方法,默认为int类型范围之间的随机数*/ int nextInt = random.nextInt();//调用random类里面的nextInt方法 System.out.println(nextInt); //输出nextInt int nextInt2 = random.nextInt(100); //随机产生一个0到99的随机整数,包含零不包含100 System.out.println(nextInt2); } }
随机数没有深入的去了解,好像其他的有些数据类型不能正常方法的使用。
综合练习01:
public static void main(String[] args) { /* * 猜拳游戏 规则 :你和电脑猜拳,1代表石头,2代表剪刀 ,3代表布 电脑随机出1~3,你键盘录入, */ Random random = new Random(); Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); int randInt = random.nextInt(3) + 1; System.out.println(randInt); System.out.println("电脑已就位,请出拳"); int nextInt2 = sc.nextInt(); //方式1 if (randInt == nextInt2) { System.out.println("你们平局"); } else if (randInt == 1 & nextInt2 == 2 || randInt == 2 & nextInt2 == 3 || randInt == 3 & nextInt2 == 1) { System.out.println("抱歉,你输给了电脑,真没用"); } else if (randInt == 2 & nextInt2 == 1 || randInt == 3 & nextInt2 == 2 || randInt == 1 & nextInt2 == 3) { System.out.println("恭喜你,你赢了电脑,真棒"); } else { System.out.println("叫你输入1 2 3,输错了懂不懂?重新输去"); main(args); } //方式2 if(nextInt2 - randInt ==0) { System.out.println("你们为平局"); }else if (nextInt2 - randInt == 1) { System.out.println("抱歉,你输给了电脑,真没用"); }else if (nextInt2 - randInt == -1) { System.out.println("恭喜你,你赢了电脑,真棒"); }else if (nextInt2 - randInt == -2) { System.out.println("抱歉,你输给了电脑,真没用"); }else { System.out.println("叫你输入1 2 3,输错了懂不懂?重新输去"); main(args); } }
//这有两个方式,记得注释掉一个
综合案例02:
public static void main(String[] args) { /* * 利用随机数生成1~100的数,用户来猜大小 */ Random random = new Random(); int ranInt = random.nextInt(100)+1; try (Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in)) { while (true) { System.out.println("请输入你猜的数:"); int nextInt = sc.nextInt(); if (nextInt > ranInt) { System.out.println("不好意思,你猜的数大了,请重新猜一下哦"); } if (nextInt < ranInt) { System.out.println("不好意思,你猜的数小了,请重新猜一下哦"); } if (nextInt == ranInt) { System.out.println("恭喜你,猜的刚刚好"); break; } } } }
综合案例03:
public static void main(String[] args) { //练习一: 打印金字塔 int tem = 10; for (int i = 1; i <= tem; i++) { for (int j2 = 1; j2 <= tem - i; j2++) { System.out.print(" "); } for (int j = 1; j <= i * 2 - 1; j++) { System.out.print("*"); } System.out.println(); } //练习2 个数如果恰好等于它的因子之和,这个数就称为 "完数 "。例如6=1+2+3,找出1000以内的所有完数。 for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i++) { int temp = 0; for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) { if (i % j == 0) { temp = temp + j; } } if (temp == i) { System.out.println(i); } } }
个人学习,内容简略。