本文以 Elasticsearch 6.2.4为例。
经过前面的基础入门,我们对ES的基本操作也会了。现在来学习ES最强大的部分:全文检索。
准备工作
批量导入数据
先需要准备点数据,然后导入:
wget https://raw.githubusercontent.com/elastic/elasticsearch/master/docs/src/test/resources/accounts.json
curl -H "Content-Type: application/json" -XPOST "localhost:9200/bank/account/_bulk" --data-binary "@accounts.json"
这样我们就导入了1000条数据到ES。
注意:
accounts.json每行必须以换行。如果提示The bulk request must be terminated by a newline [ ],请检查最后一行是否以换行。
index是bank。我们可以查看现在有哪些index:
curl "localhost:9200/_cat/indices?format=json&pretty"
结果:
[
{
"health" : "yellow",
"status" : "open",
"index" : "bank",
"uuid" : "MDxR02uESgKSynX6k8B-og",
"pri" : "5",
"rep" : "1",
"docs.count" : "1000",
"docs.deleted" : "0",
"store.size" : "474.6kb",
"pri.store.size" : "474.6kb"
}
]
使用kibana可视化数据
该小节是可选的,如果不感兴趣,可以跳过。
该小节要求你已经搭建好了ElasticSearch + Kibana。
打开kibana web地址:http://127.0.0.1:5601,依次打开:Management
-> Kibana -> Index Patterns ,选择Create Index Pattern:
a. Index pattern 输入:bank ;
b. 点击Create。
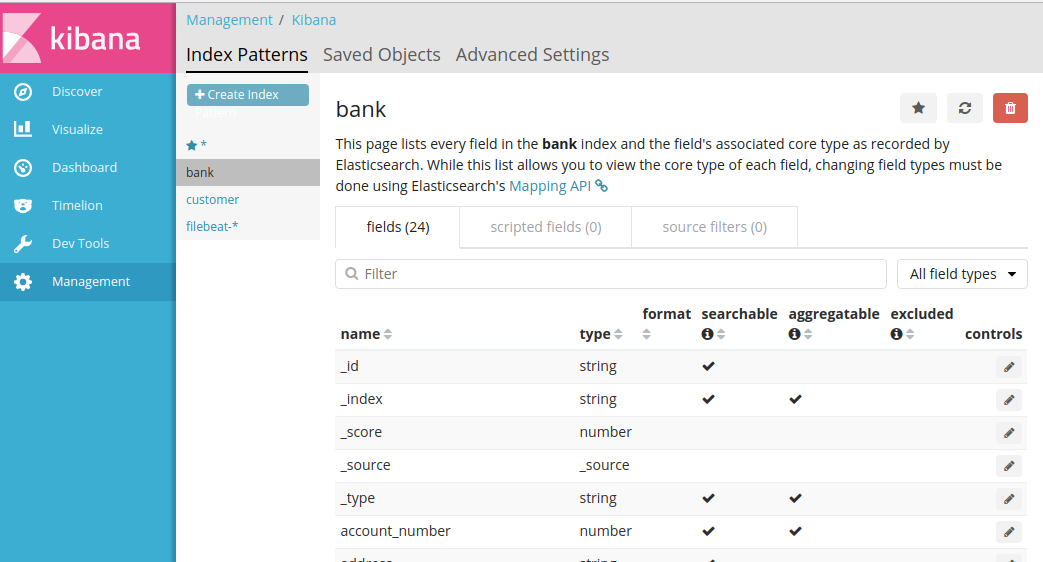
然后打开Discover,选择 bank 就能看到刚才导入的数据了。
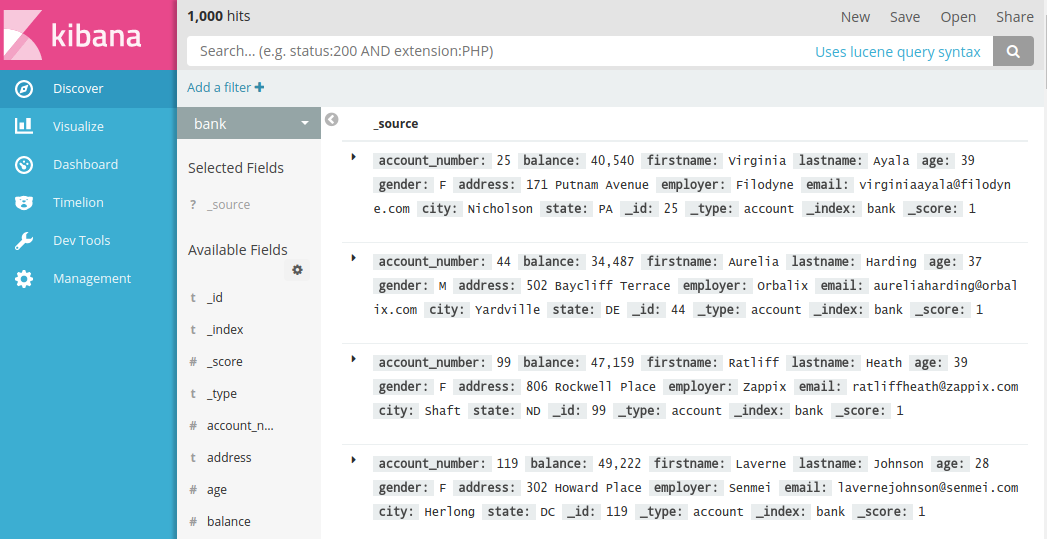
我们在可视化界面里检索数据:

是不是很酷!
接下来我们使用API来实现检索。
查询
URI检索
uri检索是通过提供请求参数纯粹使用URI来执行搜索请求。
GET /bank/_search?q=Virginia&pretty
GET /bank/_search?q=firstname:Virginia
curl:
curl -XGET "localhost:9200/bank/_search?q=Virginia&pretty"
curl -XGET "localhost:9200/bank/_search?q=firstname:Virginia&pretty"
解释:检索关键字为"Virginia"的结果。结果示例:
{
"took": 4,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 2,
"max_score": 4.631368,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bank",
"_type": "account",
"_id": "298",
"_score": 4.631368,
"_source": {
"account_number": 298,
"balance": 34334,
"firstname": "Bullock",
"lastname": "Marsh",
"age": 20,
"gender": "M",
"address": "589 Virginia Place",
"employer": "Renovize",
"email": "bullockmarsh@renovize.com",
"city": "Coinjock",
"state": "UT"
}
},
{
"_index": "bank",
"_type": "account",
"_id": "25",
"_score": 4.6146765,
"_source": {
"account_number": 25,
"balance": 40540,
"firstname": "Virginia",
"lastname": "Ayala",
"age": 39,
"gender": "F",
"address": "171 Putnam Avenue",
"employer": "Filodyne",
"email": "virginiaayala@filodyne.com",
"city": "Nicholson",
"state": "PA"
}
}
]
}
}
返回字段含义:
- took – Elasticsearch执行搜索的时间(以毫秒为单位)
- timed_out – 搜索是否超时
- _shards – 搜索了多少个分片,以及搜索成功/失败分片的计数
- hits – 搜索结果,是个对象
- hits.total – 符合我们搜索条件的文档总数
- hits.hits – 实际的搜索结果数组(默认为前10个文档)
- hits.sort - 对结果进行排序(如果按score排序则没有该字段)
- hits._score、max_score - 暂时忽略这些字段
参数:
- q 查询字符串(映射到query_string查询)
- df 在查询中未定义字段前缀时使用的默认字段。
- analyzer 分析查询字符串时要使用的分析器名称。
- sort 排序。可以是
fieldName或fieldName:asc/的形式fieldName:desc。fieldName可以是文档中的实际字段,也可以是特殊_score名称,表示基于分数的排序。可以有几个sort参数(顺序很重要)。 - timeout 搜索超时。默认为无超时。
- from 从命中的索引开始返回。默认为0。
- size 要返回的点击次数。默认为10。
- default_operator 要使用的默认运算符可以是AND或 OR。默认为OR。
详见: https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.2/search-uri-request.html
示例:
GET /bank/_search?q=*&sort=account_number:asc&pretty
解释:所有结果通过account_number字段升序排列。默认只返回前10条。
下面的查询与上面的含义一致:
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match" : {
"query" : "Virginia",
"fields" : ["_all"]
}
}
}
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"sort": [
{ "account_number": "asc" }
]
}
通常我们会采用传JSON方式查询。Elasticsearch提供了一种JSON样式的特定于域的语言,可用于执行查询。这被称为查询DSL。
注意:上述的查询里面我们仅指定了index,并没有指定type,那么ES将不会区分type。如果想区分,请在URI后面追加type。示例:
GET /bank/account/_search。
match查询
GET /bank/_search
{
"query" : {
"match" : { "address" : "Avenue" }
}
}
curl:
curl -XGET -H "Content-Type: application/json" "localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty" -d '{"query":{"match":{"address":"Avenue"}}}'
上述查询返回结果是address含有Avenue的结果。
term查询
GET /bank/_search
{
"query" : {
"term" : { "address" : "Avenue" }
}
}
curl:
curl -XGET -H "Content-Type: application/json" "localhost:9200/bank/_search?pretty" -d '{"query":{"term":{"address":"Avenue"}}}'
上述查询返回结果是address等于Avenue的结果。
注:如果一个字段既需要分词搜索,又需要精准匹配,最好是一开始设置mapping的时候就设置正确。例如:通过增加
.keyword字段来支持精准匹配:
{
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
这样相当于有
address和address.keyword两个字段。这个后面mapping章节再讲解。
分页(from/size)
分页使用关键字from、size,分别表示偏移量、分页大小。
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"from": 0,
"size": 2
}
from默认是0,size默认是10。
注意:ES的from、size分页不是真正的分页,称之为浅分页。from+ size不能超过
index.max_result_window默认为10,000的索引设置。有关 更有效的深度滚动方法,请参阅 Scroll或 Search After API。
排序(sort)
字段排序关键字是sort。支持升序(asc)、降序(desc)。默认是对_score字段进行排序。
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"sort": [
{ "account_number": "asc" }
],
"from":0,
"size":10
}
多个字段排序:
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"sort": [
{ "account_number": "asc" },
{ "_score": "asc" }
],
"from":0,
"size":10
}
先按照account_number排序,再按照_score排序。
按脚本排序
允许基于自定义脚本进行排序,这是一个示例:
GET bank/account/_search
{
"query": { "range": { "age": {"gt": 20} }},
"sort" : {
"_script" : {
"type" : "number",
"script" : {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "doc['account_number'].value * params.factor",
"params" : {
"factor" : 1.1
}
},
"order" : "asc"
}
}
}
上述查询是使用脚本进行排序:按 account_number*1.1 的结果进行升序。其中lang指的是使用的脚本语言类型为painless。painless支持Math.log函数。
上述例子仅仅是演示使用方法,没有实际含义。
过滤字段
默认情况下,ES返回所有字段。这被称为源(_source搜索命中中的字段)。如果我们不希望返回所有字段,我们可以只请求返回源中的几个字段。
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": { "match_all": {} },
"_source": ["account_number", "balance"]
}
通过_source关键字可以实现字段过滤。
返回脚本字段
可以通过脚本动态返回新定义字段。示例:
GET bank/account/_search
{
"query" : {
"match_all": {}
},
"size":2,
"script_fields" : {
"age2" : {
"script" : {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "doc['age'].value * 2"
}
},
"age3" : {
"script" : {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "params['_source']['age'] * params.factor",
"params" : {
"factor" : 2.0
}
}
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took": 2,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1000,
"max_score": 1,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bank",
"_type": "account",
"_id": "25",
"_score": 1,
"fields": {
"age3": [
78
],
"age2": [
78
]
}
},
{
"_index": "bank",
"_type": "account",
"_id": "44",
"_score": 1,
"fields": {
"age3": [
74
],
"age2": [
74
]
}
}
]
}
}
注意:使用
doc['my_field_name'].value比使用params['_source']['my_field_name']更快更效率,推荐使用。
AND查询
如果我们想同时查询符合A和B字段的结果,该怎么查呢?可以使用must关键字组合。
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "address": "mill" } },
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } }
]
}
}
}
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "account_number":136 } },
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } },
{ "match": { "city": "Urie" } }
]
}
}
}
must也等价于:
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "address": "mill" } }
],
"must": [
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } }
]
}
}
}
这种相当于先查询A再查询B,而上面的则是同时查询符合A和B,但结果是一样的,执行效率可能有差异。有知道原因的朋友可以告知。
OR查询
ES使用should关键字来实现OR查询。
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{ "match": { "account_number":136 } },
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } },
{ "match": { "city": "Urie" } }
]
}
}
}
AND取反查
must_not关键字实现了既不包含A也不包含B的查询。
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{ "match": { "address": "mill" } },
{ "match": { "address": "lane" } }
]
}
}
}
表示 address 字段需要符合既不包含 mill 也不包含 lane。
布尔组合查询
我们可以组合 must 、should 、must_not、filter 进行复杂的查询。
- A AND NOT B
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "age": 40 } }
],
"must_not": [
{ "match": { "state": "ID" } }
]
}
}
}
相当于SQL:
select * from bank where age=40 and state!= "ID";
- A AND (B OR C)
GET /bank/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":[
{"match":{"age":39}},
{"bool":{"should":[
{"match":{"city":"Nicholson"}},
{"match":{"city":"Yardville"}}
]}
}
]
}
}
}
相当于SQL:
select * from bank where age=39 and (city="Nicholson" or city="Yardville");
范围查询
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "match_all": {} },
"filter": {
"range": {
"balance": {
"gte": 20000,
"lte": 30000
}
}
}
}
}
}
- A AND (B OR C) AND (D BETWEEN E, F)
GET /bank/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"must":[
{"match":{"age":39}},
{"bool":{"should":[
{"match":{"city":"Nicholson"}},
{"match":{"city":"Yardville"}}
]}
},
{"bool":{"filter": {"range": {
"balance": {
"gte": 20000,
"lte": 30000
}}}
}
}
]
}
}
}
相当于SQL:
select * from bank where age=39 and (city="Nicholson" or city="Yardville") and (balance between 20000 and 30000);
如果仅仅是单字段范围查询,也可以直接省略 must、filter等关键字:
GET /bank/_search
{
"query":{
"range":{
"balance":{
"gte":20000,
"lte":30000
}
}
}
}
相当于SQL:
select * from bank where balance between 20000 and 30000;
多字段范围查询:
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "match_all": {} },
"filter": {
"bool":{
"must":[
{"range": {"balance": {"gte": 20000,"lte": 30000}}},
{"range": {"age": {"gte": 30}}}
]
}
}
}
}
}
查询字段不存在或者为0的值
GET /bank/doc/_search
{
"query":{
"bool":{
"should":[
{
"term":{"age":0}
},
{
"bool":{
"must_not":[{"exists":{"field":"age"}}]
}
}
]
}
}
}
高亮结果
ES可以高亮返回结果里的关键字,使用html标记标出。
GET bank/account/_search
{
"query" : {
"match": { "address": "Avenue" }
},
"from": 0,
"size": 1,
"highlight" : {
"require_field_match": false,
"fields": {
"*" : { }
}
}
}
输出:
{
"took": 10,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 214,
"max_score": 1.5814995,
"hits": [
{
"_index": "bank",
"_type": "account",
"_id": "102",
"_score": 1.5814995,
"_source": {
"account_number": 102,
"balance": 29712,
"firstname": "Dena",
"lastname": "Olson",
"age": 27,
"gender": "F",
"address": "759 Newkirk Avenue",
"employer": "Hinway",
"email": "denaolson@hinway.com",
"city": "Choctaw",
"state": "NJ"
},
"highlight": {
"address": [
"759 Newkirk <em>Avenue</em>"
]
}
}
]
}
}
返回结果里的highlight部分就是高亮结果,默认使用<em>标出。如果需要修改,可以使用pre_tags设置修改:
"fields": {
"*" : { "pre_tags" : ["<strong>"], "post_tags" : ["</strong>"] }
}
*代表所有字段都高亮,也可以只高亮具体的字段,直接用具体字段替换*即可。
require_field_match:默认情况下,仅突出显示包含查询匹配的字段。设置require_field_match为false突出显示所有字段。默认为true。详见:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.2/search-request-highlighting.html
聚合查询
GET /bank/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_state": {
"terms": {
"field": "state.keyword"
}
}
}
}
结果:
{
"took": 29,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 1000,
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"group_by_state" : {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 20,
"sum_other_doc_count": 770,
"buckets" : [ {
"key" : "ID",
"doc_count" : 27
}, {
"key" : "TX",
"doc_count" : 27
}, {
"key" : "AL",
"doc_count" : 25
}, {
"key" : "MD",
"doc_count" : 25
}, {
"key" : "TN",
"doc_count" : 23
}, {
"key" : "MA",
"doc_count" : 21
}, {
"key" : "NC",
"doc_count" : 21
}, {
"key" : "ND",
"doc_count" : 21
}, {
"key" : "ME",
"doc_count" : 20
}, {
"key" : "MO",
"doc_count" : 20
} ]
}
}
}
查询结果返回了ID州(Idaho)有27个账户,TX州(Texas)有27个账户。
相当于SQL:
SELECT state, COUNT(*) FROM bank GROUP BY state ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC
该查询意思是按照字段state分组,返回前10个聚合结果。
其中size设置为0意思是不返回文档内容,仅返回聚合结果。state.keyword表示字段精确匹配,因为使用模糊匹配性能很低,所以不支持。
如果需要聚合的时候对某个字段去重,使用cardinality关键字即可:
GET /bank/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_state": {
"cardinality": {
"field": "state.keyword"
}
}
}
}
多重聚合
我们可以在聚合的基础上再进行聚合,例如求和、求平均值等等。
GET /bank/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_state": {
"terms": {
"field": "state.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"average_balance": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
}
}
上述查询实现了在前一个聚合的基础上,按州计算平均帐户余额(同样仅针对按降序排序的前10个州)。
我们可以在聚合中任意嵌套聚合,以从数据中提取所需的统计数据。
在前一个聚合的基础上,我们现在按降序排列平均余额:
GET /bank/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_state": {
"terms": {
"field": "state.keyword",
"order": {
"average_balance": "desc"
}
},
"aggs": {
"average_balance": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
}
}
这里基于第二个聚合结果进行倒序排列。其实上一个例子隐藏了默认排序,也就是默认按照_sort(分值)倒序:
GET /bank/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_state": {
"terms": {
"field": "state.keyword",
"order": {
"_sort": "desc"
}
},
"aggs": {
"average_balance": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
}
}
此示例演示了我们如何按年龄段(20-29岁,30-39岁和40-49岁)进行分组,然后按性别分组,最后得到每个年龄段的平均帐户余额:
GET /bank/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"group_by_age": {
"range": {
"field": "age",
"ranges": [
{
"from": 20,
"to": 30
},
{
"from": 30,
"to": 40
},
{
"from": 40,
"to": 50
}
]
},
"aggs": {
"group_by_gender": {
"terms": {
"field": "gender.keyword"
},
"aggs": {
"average_balance": {
"avg": {
"field": "balance"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
这个结果就复杂了,属于嵌套分组,结果也是嵌套的:
{
"took": 5,
"timed_out": false,
"_shards": {
"total": 5,
"successful": 5,
"skipped": 0,
"failed": 0
},
"hits": {
"total": 1000,
"max_score": 0,
"hits": []
},
"aggregations": {
"group_by_age": {
"buckets": [
{
"key": "20.0-30.0",
"from": 20,
"to": 30,
"doc_count": 451,
"group_by_gender": {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
"sum_other_doc_count": 0,
"buckets": [
{
"key": "M",
"doc_count": 232,
"average_balance": {
"value": 27374.05172413793
}
},
{
"key": "F",
"doc_count": 219,
"average_balance": {
"value": 25341.260273972603
}
}
]
}
},
{
"key": "30.0-40.0",
"from": 30,
"to": 40,
"doc_count": 504,
"group_by_gender": {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
"sum_other_doc_count": 0,
"buckets": [
{
"key": "F",
"doc_count": 253,
"average_balance": {
"value": 25670.869565217392
}
},
{
"key": "M",
"doc_count": 251,
"average_balance": {
"value": 24288.239043824702
}
}
]
}
},
{
"key": "40.0-50.0",
"from": 40,
"to": 50,
"doc_count": 45,
"group_by_gender": {
"doc_count_error_upper_bound": 0,
"sum_other_doc_count": 0,
"buckets": [
{
"key": "M",
"doc_count": 24,
"average_balance": {
"value": 26474.958333333332
}
},
{
"key": "F",
"doc_count": 21,
"average_balance": {
"value": 27992.571428571428
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
term与match查询
首先大家看下面的例子有什么区别:
已知条件:ES里address为171 Putnam Avenue的数据有1条;address为Putnam的数据有0条。index为bank,type为account,文档ID为25。
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match" : {
"address" : "Putnam"
}
}
}
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"match" : {
"address.keyword" : "Putnam"
}
}
}
GET /bank/_search
{
"query": {
"term" : {
"address" : "Putnam"
}
}
}
结果:
1、第一个能匹配到数据,因为会分词查询。
2、第二个不能匹配到数据,因为不分词的话没有该条数据。
3、结果不确定。需要看实际是怎么分词的。
我们通过下列查询可以知晓该条数据字段address的分词情况:
GET /bank/account/25/_termvectors?fields=address
结果:
{
"_index": "bank",
"_type": "account",
"_id": "25",
"_version": 1,
"found": true,
"took": 0,
"term_vectors": {
"address": {
"field_statistics": {
"sum_doc_freq": 591,
"doc_count": 197,
"sum_ttf": 591
},
"terms": {
"171": {
"term_freq": 1,
"tokens": [
{
"position": 0,
"start_offset": 0,
"end_offset": 3
}
]
},
"avenue": {
"term_freq": 1,
"tokens": [
{
"position": 2,
"start_offset": 11,
"end_offset": 17
}
]
},
"putnam": {
"term_freq": 1,
"tokens": [
{
"position": 1,
"start_offset": 4,
"end_offset": 10
}
]
}
}
}
}
}
可以看出该条数据字段address一共分了3个词:
171
avenue
putnam
现在可以得出第三个查询的答案:匹配不到!但值改成小写的putnam又能匹配到了!
原因是:
- term query 查询的是倒排索引中确切的term
- match query 会对filed进行分词操作,然后再查询
由于Putnam不在分词里(大小写敏感),所以匹配不到。match query先对filed进行分词,也就是分成putnam,再去匹配倒排索引中的term,所以能匹配到。
standardanalyzer 分词器分词默认会将大写字母全部转为小写字母。
参考
1、Getting Started | Elasticsearch Reference [6.2] | Elastic
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/6.2/getting-started.html
2、Elasticsearch 5.x 关于term query和match query的认识 - wangchuanfu - 博客园
https://www.cnblogs.com/wangchuanfu/p/7444253.html