一.定义
策略模式(Strategy Pattern):定义一系列算法,将每一个算法封装起来,并让它们可以相互替换。策略模式让算法独立于使用它的客户而变化,也称为政策模式(Policy)。策略模式是一种对象行为型模式。
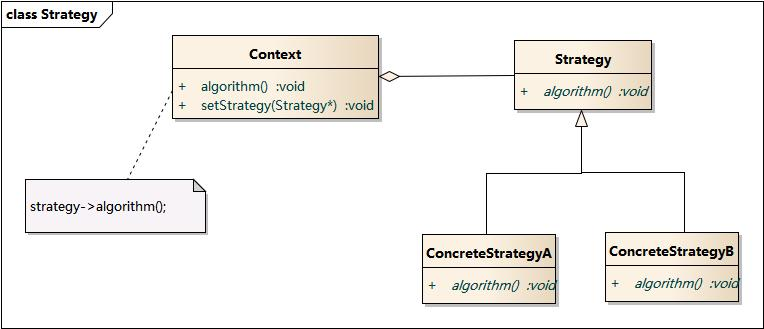
二、模式结构成员构成
• Context: 环境类
• Strategy: 抽象策略类
• ConcreteStrategy: 具体策略类
三.代码示例

1 /** 2 * Strategy 3 * 抽象策略类 4 * 抽象折扣类 5 */ 6 public interface MemberStrategy { 7 /** 8 * 计算图书的价格 9 * @param booksPrice 图书的原价 10 * @return 计算出打折后的价格 11 */ 12 public double calcPrice(double booksPrice); 13 } 14 15 /** 16 * ConcreteStrategy 17 * 具体策略类 18 * 初级会员折扣类 19 */ 20 public class PrimaryMemberStrategy implements MemberStrategy { 21 22 @Override 23 public double calcPrice(double booksPrice) { 24 25 System.out.println("对于初级会员的没有折扣"); 26 return booksPrice; 27 } 28 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * ConcreteStrategy 33 * 具体策略类 34 * 中级会员折扣类 35 */ 36 public class IntermediateMemberStrategy implements MemberStrategy { 37 38 @Override 39 public double calcPrice(double booksPrice) { 40 41 System.out.println("对于中级会员的折扣为10%"); 42 return booksPrice * 0.9; 43 } 44 45 } 46 47 /** 48 * ConcreteStrategy 49 * 具体策略类 50 * 高级会员折扣类 51 */ 52 public class AdvancedMemberStrategy implements MemberStrategy { 53 54 @Override 55 public double calcPrice(double booksPrice) { 56 57 System.out.println("对于高级会员的折扣为20%"); 58 return booksPrice * 0.8; 59 } 60 } 61 62 /** 63 * Context 64 * 环境类 65 * 价格类 66 */ 67 public class Price { 68 //持有一个具体的策略对象 69 private MemberStrategy strategy; 70 /** 71 * 构造函数,传入一个具体的策略对象 72 * @param strategy 具体的策略对象 73 */ 74 public Price(MemberStrategy strategy){ 75 this.strategy = strategy; 76 } 77 78 /** 79 * 计算图书的价格 80 * @param booksPrice 图书的原价 81 * @return 计算出打折后的价格 82 */ 83 public double quote(double booksPrice){ 84 return this.strategy.calcPrice(booksPrice); 85 } 86 } 87 88 /** 89 * client 90 * 客户端 91 * 92 * 从示例可以看出,策略模式仅仅封装算法,提供新的算法插入到已有系统中, 93 * 以及老算法从系统中“退休”的方法,策略模式并不决定在何时使用何种算法。在什么情况下使用什么算法是由客户端决定的。 94 */ 95 public class Client { 96 97 public static void main(String[] args) { 98 //选择并创建需要使用的策略对象 99 MemberStrategy strategy = new AdvancedMemberStrategy(); 100 //创建环境 101 Price price = new Price(strategy); 102 //计算价格 103 double quote = price.quote(300); 104 System.out.println("图书的最终价格为:" + quote); 105 } 106 107 }
四.优点和缺点分析
优点:
>策略模式提供了对“开闭原则”的完美支持,用户可以在不修改原有系统的基础上选择算法或行为,也可以灵活地增加新的算法或行为。
>策略模式提供了管理相关的算法族的办法。
>策略模式提供了可以替换继承关系的办法。
>使用策略模式可以避免使用多重条件转移语句。
缺点:
>客户端必须知道所有的策略类,并自行决定使用哪一个策略类。
>策略模式将造成产生很多策略类,可以通过使用享元模式在一定程度上减少对象的数量。
五.应用场景
>如果在一个系统里面有许多类,它们之间的区别仅在于它们的行为,那么使用策略模式可以动态地让一个对象在许多行为中选择一种行为。
>一个系统需要动态地在几种算法中选择一种。
>如果一个对象有很多的行为,如果不用恰当的模式,这些行为就只好使用多重的条件选择语句来实现。
>不希望客户端知道复杂的、与算法相关的数据结构,在具体策略类中封装算法和相关的数据结构,提高算法的保密性与安全性。
