先说一些注解:
@EnableAutoConfiguration 可以帮助SpringBoot应用将所有符合条件的@Configuration配置都加载到当前SpringBoot创建并使用的IoC容器。
@ComponentScan 扫包
@Configuration 用于定义配置类,可替换xml配置文件
使用以上是三个注解 则可以实现 springboot 的启动类的功能,不过每次 写的太得 所以 可以使用@SpringBootApplication 代替三个注解,实现启动类功能
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = {
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication
@SringBootApplication只能作用于同级目录之下,其余目录之下无法扫描不起作用
使用springboot搭建mybatis
第一步:导入 mybatis 所需要的依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-mybatis-demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-mybatis-demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- 添加 mybatis所需要的依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入数据库连接 注意版本,版本低了 执行的时候 报错 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.46</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
第二步:创建数据库表
CREATE TABLE `users` (
`name` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(50) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
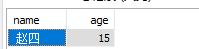
创建一个名为users的表,有两个字段name和age
第三步:编写mapper类 创建一个 名为com.example.mapper的包,并创建 UserMapper接口
package com.example.mpper;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
@Mapper//如果不用mapper注解 则需要在启动类中配置@MapperScan(basePackages = { "包名" })
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("SELECT * FROM USERS WHERE NAME = #{name}")
List<com.example.entity.User> findByName(@Param("name") String name);
@Insert("INSERT INTO USERS(NAME, AGE) VALUES(#{name}, #{age})")
int insert(@Param("name") String name, @Param("age") Integer age);
@Delete("DELETE FROM USERS WHERE AGE=#{age}")
void delete(@Param("age") int age);
@Update("UPDATE USERS SET AGE=#{age} WHERE NAME=#{name}")
void update(@Param("name") String name, @Param("age") int age);
}
@Mapper注解:mybatis的注解,不用像以前那样配置 xml文件,然后在xml文件里面 写 sql语句了
第四步:创建 UserService类,
package com.example.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import com.example.entity.User;
import com.example.mpper.UserMapper;
@Controller
public class UserService {
@Autowired
public UserMapper mapper;
public List<User> findUser(String name) {
return mapper.findByName(name);
}
public void insertUser(String name, int age) {
mapper.insert(name, age);
}
public void delet(int age) {
mapper.delete(age);
}
public void update(String name, int age) {
mapper.update(name, age);
}
}
第五步: 编写 controller类
package com.example.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.example.entity.User;
import com.example.service.UserService;
@Controller
public class UserController {
@Autowired
public UserService service;
@RequestMapping("/selectUser")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> selectUser(String name) {
List<User> users = service.findUser(name);
return users;
}
@RequestMapping("/insertUser")
public String insertUser(String name, int age) {
service.insertUser(name, age);
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping("/deletUser")
@ResponseBody
public String deletUser(int age) {
service.delet(age);
return "success";
}
@RequestMapping("/updateUser")
@ResponseBody
public String updateUser(String name, int age) {
service.update(name, age);
return "success";
}
}
第六步:编写启动类
编写启动类的时候 选择用的是@SpringBootApplication注解启动,所以 要保证所有的都再同一目录结构
package com.example;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootMybatisDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootMybatisDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
完整项目包结构:
如果只是这样,启动的时候会报错,找不到 数据源,所以我们还需要配置数据源
第七步:配置 数据源 springboot 的配置文件 有两种 一种是properties文件 一种 是yml文件,原来一直用的是properties文件,没有yml文件好用。可读性,编写的时候都要方便些
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
这里如果 使用yml文件没有自动提示 或者补全的话 可以升级或者安装sts插件,在抛出一个问题 如果有多个数据源的时候springboot如何处理多个数据源,按照上面步骤就可以简单的完成一个 spring boot+mybatis的crud
如果哪里有问题的,有人到了这个文章 则留言 改正...........