几种常见的运算符重载
运算符重载,就是对现有的运算符重新进行定义,赋予其另一种功能,以适应不同的数据类型。
形式如下:
1 (返回类型)operator运算符(参数列表) 2 { 3 ....... 4 }
(1)左移(<<) 和右移(>>)运算符
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class Person 4 { 5 public: 6 int age; 7 }; 8 ostream& operator<<(ostream &cout,Person &p) 9 { 10 cout<<p.age; 11 return cout; 12 } 13 void operator>>(istream &cin,Person &p) 14 { 15 cout<<"请输入年龄:"<<endl; 16 cin>>p.age; 17 } 18 void test01() 19 { 20 Person p1; 21 cin>>p1; 22 cout<<"年龄是:"; 23 cout<<p1<<endl; 24 } 25 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 26 { 27 test01(); 28 return 0; 29 }
运行结果:
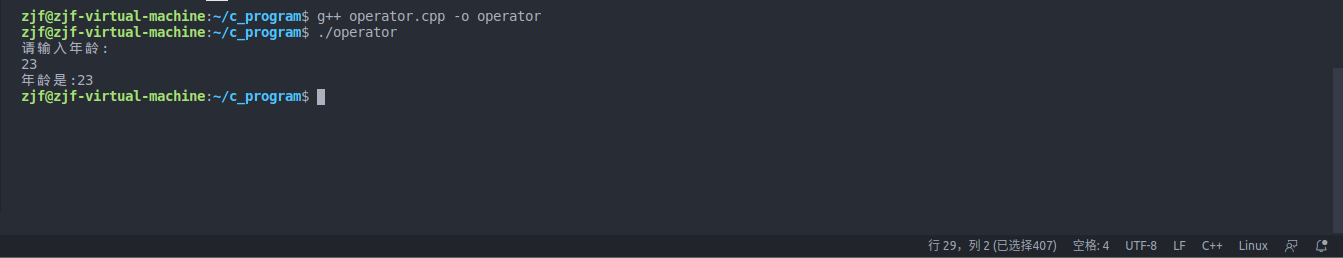
在21行和23行的代码中,我们可以看到左移和右移操作符都是对p1进行的,但是我们的输入输出实际上只能对内置的数据类型,进行操作,因此我们必须要对运算符惊醒重载,包括我们接下来要写的几种运算符也都是这样。
(2)前置++和后置++运算符
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<string.h> 4 class Myint 5 { 6 public: 7 int myint; 8 Myint(){} 9 Myint(int myint) 10 { 11 this->myint = myint; 12 } 13 Myint& operator++() 14 { 15 this->myint = this->myint + 1; 16 return *this; 17 } 18 Myint operator++(int) 19 { 20 Myint tmp = (*this); 21 this->myint = this->myint + 1; 22 return tmp; 23 } 24 }; 25 ostream& operator<<(ostream &cout,Myint &m) 26 { 27 cout<<m.myint; 28 return cout; 29 } 30 void test01() 31 { 32 Myint m1(20); 33 cout<<++m1<<endl; 34 m1++; 35 cout<<m1<<endl; 36 } 37 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 38 { 39 test01(); 40 return 0; 41 }
运行结果:

(3)=运算符
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 #include<string.h> 4 class Person 5 { 6 public: 7 Person(){} 8 Person(int age,char* name) 9 { 10 this->age = age; 11 this->name = new char[strlen(name)+1]; 12 strcpy(this->name,name); 13 } 14 ~Person() 15 { 16 cout<<"析构"<<endl; 17 delete []name; 18 } 19 void show(); 20 Person& operator=(Person &p1) 21 { 22 this->age = p1.age; 23 this->name = new char[strlen(p1.name)+1]; 24 strcpy(this->name,p1.name); 25 return *this; 26 } 27 int age; 28 char *name; 29 }; 30 void Person::show() 31 { 32 cout<<this->age<<" "<<this->name<<endl; 33 } 34 void test01() 35 { 36 Person p1(20,"bob"); 37 p1.show(); 38 Person p2; 39 p2 = p1; 40 p2.show(); 41 } 42 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 43 { 44 test01(); 45 return 0; 46 }
运行结果:

(4)==和!=运算符
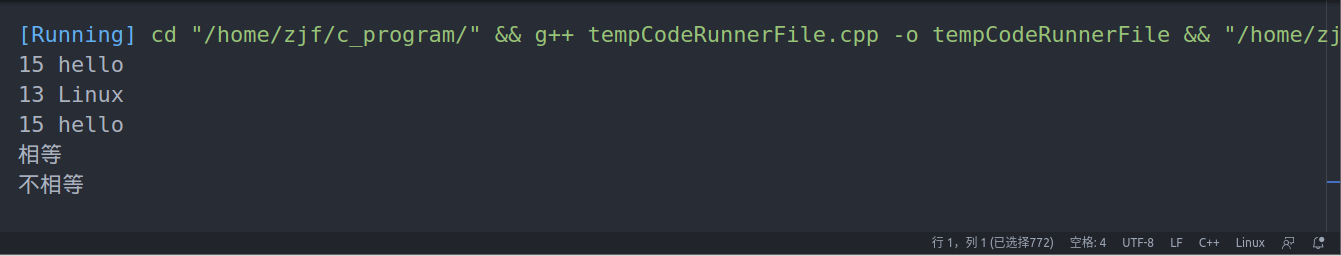
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 class Person 4 { 5 public: 6 int age; 7 string name; 8 Person(int age,string name) 9 { 10 this->age = age; 11 this->name =name; 12 } 13 void show() 14 { 15 cout<<age<<" "<<name<<endl; 16 } 17 int operator==(Person &p) 18 { 19 return this->age==p.age&&this->name==p.name; 20 } 21 int operator!=(Person &p) 22 { 23 return this->age!=p.age||this->name!=p.name; 24 } 25 }; 26 void test01() 27 { 28 Person p1(15,"hello"); 29 Person p2(13,"Linux"); 30 Person p3(15,"hello"); 31 p1.show(); 32 p2.show(); 33 p3.show(); 34 if(p1 == p3) 35 { 36 cout<<"相等"<<endl; 37 } 38 if(p1 != p2) 39 { 40 cout<<"不相等"<<endl; 41 } 42 43 } 44 int main(int argc, char const *argv[]) 45 { 46 test01(); 47 return 0; 48 }
运行结果: