实验七 继承附加实验实验时间 2018-10-11
1、实验目的与要求
(1)进一步理解4个成员访问权限修饰符的用途;
Public 该类或非该类均可访问
Private 只有该类可以访问
Protected 该类及其子类的成员可以访问,同一个包中的类也可访问
默认(friendly) 相同包中的类可以访问
(2)掌握Object类的常用API用法;
Object类是java中所有类的祖先,每一个类都有他扩展而来。在不给出超类的情况下,java会自动把Object作为要定义类的超类。
A: equals方法用于测试某个对象是否同另一个对象相等。它在Object类中实现的是判断两个对象是否具有相同的引用。如果两个对象具有相同的引用,它们一定是相等的。
定义子类的equals方法时,可调用子类的equals方法。
Super.equals(otherObject)
B:hashCode方法可导出某个对象的散列码。散列码是任意整数。表示对象的存储地址。两个相等对象的散列码相等。
C:toString方法返回一个代表该对象域值的字符串。一个字符串与对象名通过操作符“+”连接起来就会自动调用toString方法。
(3)掌握ArrayList类用法与常用API;
ArrayList是一个采用类型参数的泛类型。为指定数组列表保存元素的对象类型,需要一对尖括号将数组对象类名括起来加在后面。
ArrayList<Employee>staff = new ArrayList<Employee>();
没有<>的ArrayList将被认为是一个删去了类型参数的“原始”类型。
A:添加元素 boolean add(T obj) 吧元素的obj追加到数组列表的结尾
staff.add(new Employee(...));
B:统计个数 int size() 返回列表当前元
staff.add()
C:调整大小 void trimToSize() 把数组列表的存储空间调整到当前大小
E: 访问 void set(int index,T obj) 将obj放入列表index位置,将覆盖这个位置的原有内容
T get(int index)获得指定位置index的元素值。
(4)掌握枚举类使用方法;
声明枚举类
public enum Grade{A,B,C,D,E}
它包括一个关键字enum,一个新枚举类型的名字Grade以及为Grade定义的一组值,这里的值既非整型,亦非字符型。
枚举值隐含都是由public、static、final修饰的,无须自己几添加这些修饰符
(5)结合本章知识,理解继承与多态性两个面向对象程序设计特征,并体会其优点;


(6)熟练掌握Java语言中基于类、继承技术构造程序的语法知识(ch1-ch5);
(7)利用已掌握Java语言程序设计知识,学习设计开发含有1个主类、2个以上用户自定义类的应用程序。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1 补充以下程序中主类内main方法体,以验证四种权限修饰符的用法。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TEST2 test2 = new TEST2();
test2.demo1();
test2.demo3();
test2.demo4();
test2.tese2();
test2.tese3();
test2.tese4();
System.out.println( test2.t2);
System.out.println( test2.t3);
System.out.println( test2.t4);
System.out.println( test2.e2);
System.out.println( test2.e3);
System.out.println( test2.e4);
/*在下面分别调用 demo1 demo2 demo3 demo4 test1 test2 test3 test4方法
和t1 t2 t3 t3 e1 e2 e3 e4属性,好好理解继承和权限修饰符的用法与区别*/
}
}
public class TEST1 { private String t1 = "这是TEST1的私有属性"; public String t2 = "这是TEST1的公有属性"; protected String t3 = "这是TEST1受保护的属性"; String t4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性"; private void tese1() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } public void tese2() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void tese3() { System.out.println("我是TEST1用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void tese4() { System.out.println("我是TEST1无修饰符修饰的方法"); } }
public class TEST2 extends TEST1{ private String e1 = "这是TEST1的私有属性"; public String e2 = "这是TEST1的公有属性"; protected String e3 = "这是TEST1受保护的属性"; String e4 = "这是TEST1的默认属性"; public void demo1() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用public修饰符修饰的方法"); } private void demo2() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用private修饰符修饰的方法"); } protected void demo3() { System.out.println("我是TEST2用protected修饰符修饰的方法"); } void demo4() { System.out.println("我是TEST2无修饰符修饰的方法"); } }

实验2 第五章测试程序反思,继承知识总结。
测试程序1:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-8、5-9、5-10(教材174页-177页);
Ÿ 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Object类的定义及用法;
package equals; import java.time.*; import java.util.Objects; public class Employee//用户自定义类 { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name;//this指代当前对象 this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) //Objects类中的equals方法用于检测一个对象是否等于另外一个对象 { // a quick test to see if the objects are identical if (this == otherObject) return true; // must return false if the explicit parameter is null 如果显示参数为空,则返回false if (otherObject == null) return false; // if the classes don't match, they can't be equal if (getClass() != otherObject.getClass()) return false; //getClass方法将返回一个对象所属的类 // now we know otherObject is a non-null Employee Employee other = (Employee) otherObject; // test whether the fields have identical values 测试字段是否有相同的值 return Objects.equals(name, other.name) && salary == other.salary && Objects.equals(hireDay, other.hireDay); } public int hashCode() { return Objects.hash(name, salary, hireDay); //Objects.hash() 这个类用于操作对象的静态实用方法这些工具包括用于计算对象的哈希代码的空安全或空容错方法,返回一个对象的字符串,并比较两个对象 //Object类中的hashCode方法导出某个对象的散列码。散列码世人以整数,表示对象的存储地址 //两个相等对象的散列码相等 } public String toString() //toString() 方法返回一个代表该对象域值的字符串 { return getClass().getName() + "[name=" + name + ",salary=" + salary + ",hireDay=" + hireDay + "]"; } }
package equals; /** * This program demonstrates the equals method. * @version 1.12 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EqualsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Employee alice1 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); Employee alice2 = alice1; Employee alice3 = new Employee("Alice Adams", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); Employee bob = new Employee("Bob Brandson", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); System.out.println("alice1 == alice2: " + (alice1 == alice2)); System.out.println("alice1 == alice3: " + (alice1 == alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(alice3): " + alice1.equals(alice3)); System.out.println("alice1.equals(bob): " + alice1.equals(bob)); System.out.println("bob.toString(): " + bob); Manager carl = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); Manager boss = new Manager("Carl Cracker", 80000, 1987, 12, 15); boss.setBonus(5000);//调用更改器 将bonus的值由初值0改为5000 System.out.println("boss.toString(): " + boss); System.out.println("carl.equals(boss): " + carl.equals(boss)); System.out.println("alice1.hashCode(): " + alice1.hashCode()); System.out.println("alice3.hashCode(): " + alice3.hashCode()); System.out.println("bob.hashCode(): " + bob.hashCode()); System.out.println("carl.hashCode(): " + carl.hashCode()); } }
package equals; public class Manager extends Employee { private double bonus; public Manager(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { super(name, salary, year, month, day); bonus = 0; } public double getSalary() { double baseSalary = super.getSalary(); return baseSalary + bonus; } public void setBonus(double bonus) { this.bonus = bonus; } public boolean equals(Object otherObject) { if (!super.equals(otherObject)) return false; //在子类中定义equals 方法时,首先调用超类的equals,如果检测失败,对象就不可能像等,如果超类中的域都相等,就需要比较子类中的实例域 Manager other = (Manager) otherObject; // super.equals checked that this and other belong to the same class return bonus == other.bonus; } public int hashCode() { return java.util.Objects.hash(super.hashCode(), bonus); } public String toString()//toString方法,返回一个字符串 { return super.toString() + "[bonus=" + bonus + "]"; } }
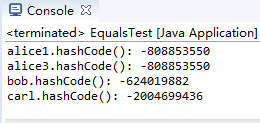
测试程序2:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行教材程序5-11(教材182页);
Ÿ 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握ArrayList类的定义及用法;
package arrayList; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates the ArrayList class. * @version 1.11 2012-01-26 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ArrayListTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // fill the staff array list with three Employee objects ArrayList<Employee> staff = new ArrayList<>();//动态数组 构建一个空数组列表 staff.add(new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15));//向数组添加新元素 staff.add(new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1)); staff.add(new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15)); // raise everyone's salary by 5% for (Employee e : staff) /* 使用for each 循环遍历数组列表 for(<类型><变量><数组>) {...} */ e.raiseSalary(5); // print out information about all Employee objects for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); } }
package arrayList; import java.time.*; public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
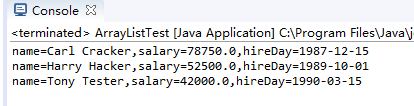
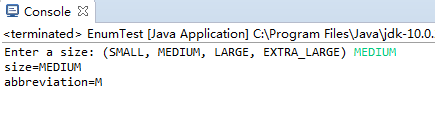
测试程序3:
Ÿ 编辑、编译、调试运行程序5-12(教材189页);
Ÿ 结合运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握枚举类的定义及用法;
package enums; import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates enumerated types. * @version 1.0 2004-05-24 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EnumTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("Enter a size: (SMALL, MEDIUM, LARGE, EXTRA_LARGE) "); String input = in.next().toUpperCase(); Size size = Enum.valueOf(Size.class, input); //valueOf方法用于返回相关Number对象持有传递的参数的值,该参数可以是基本数据类型,字符串等等 System.out.println("size=" + size); System.out.println("abbreviation=" + size.getAbbreviation()); if (size == Size.EXTRA_LARGE) System.out.println("Good job--you paid attention to the _."); } } enum Size { SMALL("S"), MEDIUM("M"), LARGE("L"), EXTRA_LARGE("XL"); private Size(String abbreviation) { this.abbreviation = abbreviation; }//构造枚举常量 public String getAbbreviation() { return abbreviation; } private String abbreviation; }
总结:本周实验内容主要是复习和回顾继承方面的知识,个人认为比较重要的内容是继承和toString方法,抽象类。继承时,子类不能继承父类的private属性,因为private只对该类可见。