Tomcat 服务器
B/S 浏览器/服务器
C/S 客户端/服务器

URI:统一资源标识符 大 广
/项目名
URL:统一资源定位符 小
Http://localhost:8080/项目名/页面

conf文件下的文件介绍
Context.Xml文件
服务器监听项目中的WEB-INF文件夹下面的web.xml文件
<WatchedResource>WEB-INF/web.xml</WatchedResource>
配置 JNDI数据源
Web.xml文件中的
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> 设置优先级,大于0的整数!值越小优先级越大
设置会话的失效时间 默认是 30分钟
<session-config>
<session-timeout>30</session-timeout>
</session-config>
当用户请求服务器的时候,服务器默认的欢迎页面
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.html</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.htm</welcome-file>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
Server.xml文件
配置服务器的端口号 以及 设置 get方式请求时的编码格式
<Connector port="8080" protocol="HTTP/1.1"
connectionTimeout="20000"
redirectPort="8443" URIEncoding="UTF-8"/>

jsp的执行过程
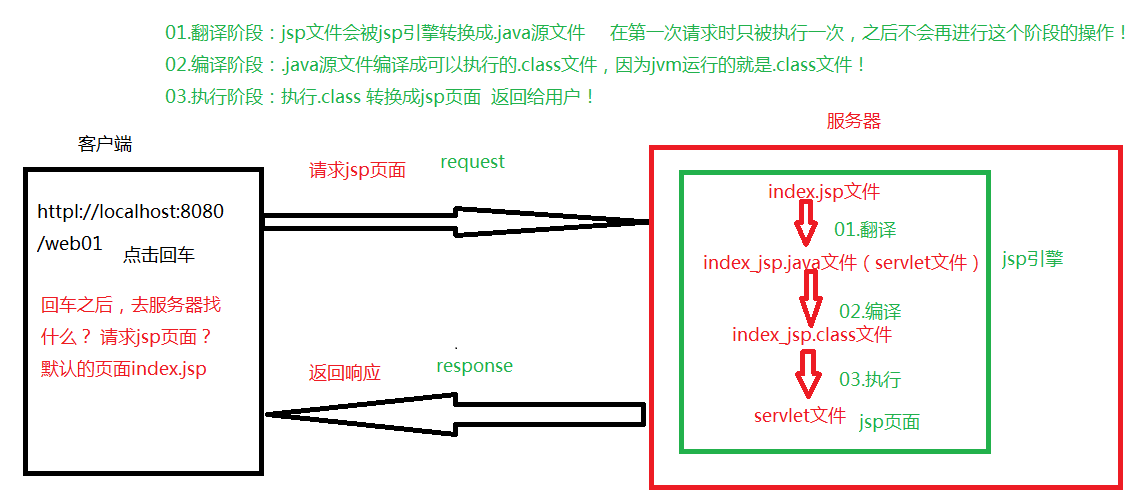
jsp的生命周期
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + path + "/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN"> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> </head> <body> <%!//全局变量 int initNum = 0; int serviceNum = 0; int destroyNum = 0; %> <%!//书写两个方法 public void jspInit() { initNum++; System.out.println("jspInit()初始化执行了" + initNum + "次"); } public void jspDestroy() { destroyNum++; System.out.println("jspdestroy()销毁执行了" + destroyNum + "次"); } %> <% //只要是没有! 所有的内容都会在service中 //service() serviceNum++; System.out.println("jspDestroy()销毁执行了" + destroyNum + "次"); String sayInit = "初始化次数" + initNum; String sayService = "执行次数" + serviceNum; String sayDestroy = "销毁次数" + destroyNum; %> <%=sayInit%><br/> <%=sayService%><br/> <%=sayDestroy%><br/> </body> </html>
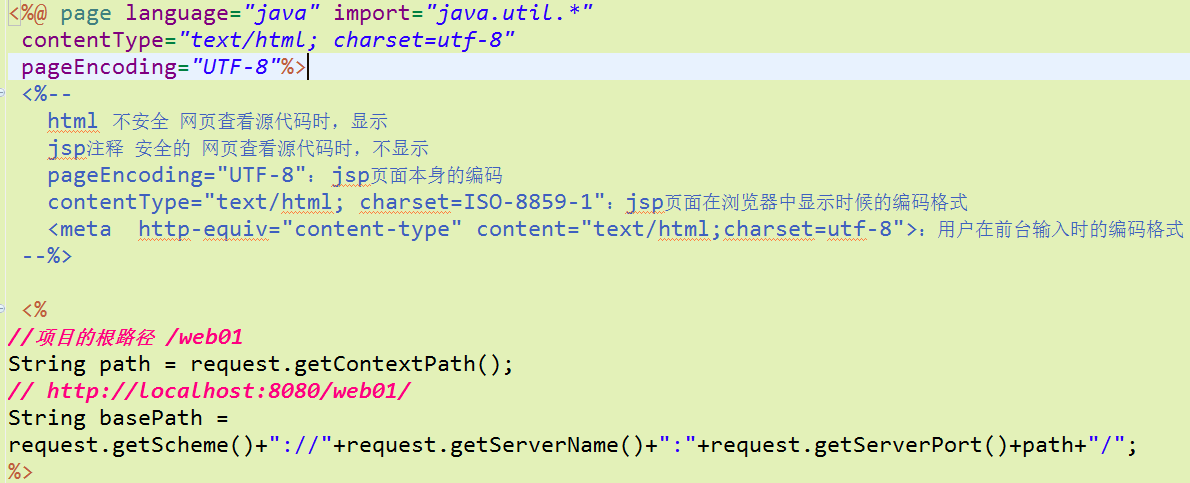
去掉jsp头部的预览界面

修改jsp页面的默认编码格式
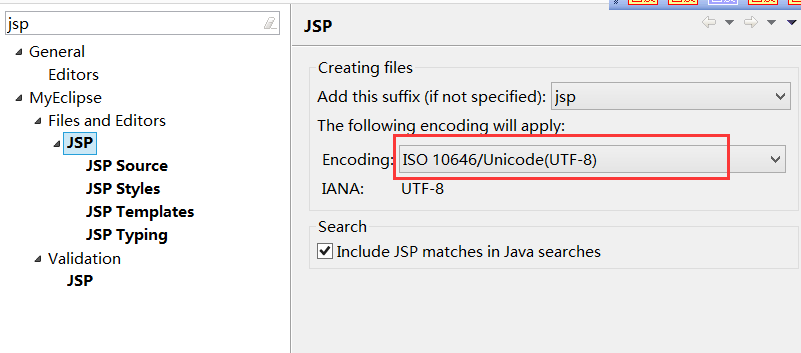
jsp页面中几种编码格式的区别:

jsp九大内置对象

在jsp页面中书写java代码
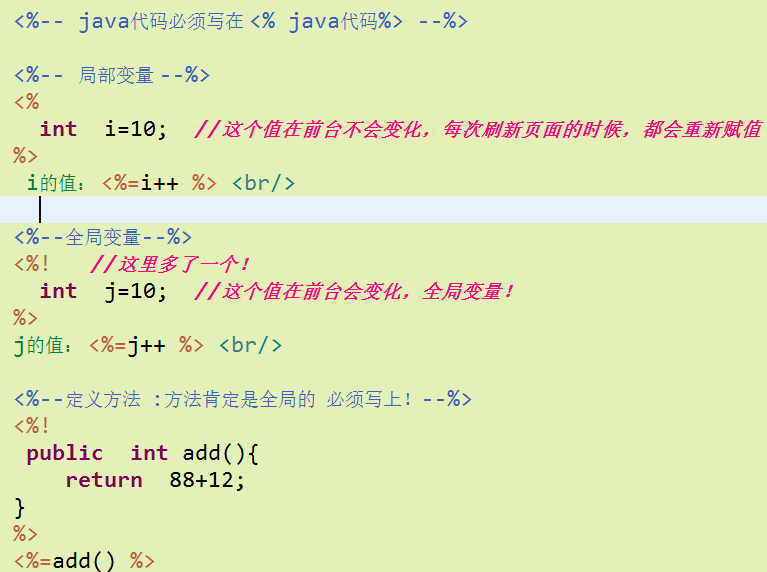
找到项目在tomcat中的位置,之后找到对应java源文件查看!


jsp页面输出 双引号(“”)

<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="UTF-8" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" %> <%-- language:指定了jsp页面中使用的脚本语言 import:引入使用的脚本语言所需要的类文件 pageEncoding:当前页面的编码格式 contentType:制定页面中的 MIME 类型,以及编码格式(在浏览器中显示的编码) --%> <% String path = request.getContextPath(); String basePath = request.getScheme() + "://" + request.getServerName() + ":" + request.getServerPort() + path + "/"; %> <!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <base href="<%=basePath%>"> <title>My JSP 'index.jsp' starting page</title> <meta http-equiv="pragma" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="cache-control" content="no-cache"> <meta http-equiv="expires" content="0"> <meta http-equiv="keywords" content="keyword1,keyword2,keyword3"> <meta http-equiv="description" content="This is my page"> </head> <body> <%-- 什么是内置对象? 不需要声明和创建,就可以在jsp页面直接使用的成员变量! 九大内置对象 对应java中的类 out 输出对象 JspWriter request 请求对象 HttpServletRequest response 响应对象 HttpServletResponse page 页面对象 this pageContext 页面的上下文对象 PageContext session 会话对象 HttpSession application 应用程序对象 ServletContext config 配置对象 ServletConfig exception 异常对象 Throwable --%> <% //局部变量 如果没有使用 在service中是不显示的 //都在service方法中 int a=5; int b=15; %> <%=a %> <%=b %> <%! //全局变量 private int num1=10; private int num2=10; public int add(){ return num1+num2; } //单行注释 /* 多行注释*/ %> <!-- html注释 可以看到 --> <%-- jsp注释 用户在前台源码中看不到 --%> <% out.print(add()); %> <%=add() %> <br/> <%-- 转义符 --%> <%=""哈哈"" %> </body> </html>