新式类VS经典类
新式类:
class Fool(object)
pass
经典类:
class Fool:
pass
只有Python2中才分经典类和新式类,Python3中统一都是新式类
在Python2中,没有继承object类的类,以及该类的子类,都是经典类;继承object类的类,以及该类的子类,都是新式类
在Python3中,无论是否声明继承object,都默认继承object,即Python3中所有类均为新式类
查找方式:
Python2 中使用深度优先
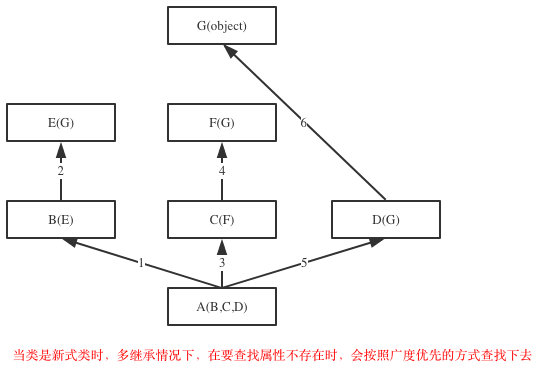
在Python3中使用广度优先查找
深度优先图例:
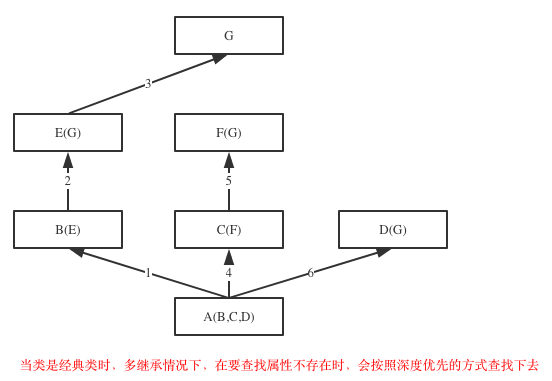
广度优先图例:
class A(object): def __init__(self): self.n='A' class B(A): pass # def __init__(self): # self.n='B' class C(A): pass def __init__(self): self.n='C' class D(B,C): pass # def __init__(self): # self.n='D' d=D() print(d.n)
一、isinstance(obj, cls)
检查是否obj是否是类 cls 的对象

class Foo(object): pass obj = Foo() isinstance(obj, Foo)
二、issubclass(sub, super)
检查sub类是否是 super 类的派生类

class Foo(object): pass class Bar(Foo): pass issubclass(Bar, Foo)
静态方法staticmethod,类方法classmethod,属性方法proerty
class Dog(object): age = 12 def __init__(self,name): self.name = name #@staticmethod #静态方法,将类方法变为普通方法,无法调用self,与类无关 def eat(self): print("%s is eatting %s"%(self.name,'ddd')) @classmethod #类方法,该方法只能使用类变量,无法使用实例的变量 def talk(self): print(self.name,) #1: 不能访问实例属性 print(self.age) #2:能访问类属性 d=Dog('aaa') #d.eat(d) #如果想使用对象的属性,需要自己手动将对象传入 d.talk() #1:AttributeError: type object 'Dog' has no attribute 'name' 无法使用实例的属性 #2:12 打印类属
class Dog(object): age = 12 def __init__(self,name): self.name = name @property #属性方法,将类方法变为属性,无法通过对象调用 def drink(self): print('drink ……',self.food) @drink.setter def drink(self,food): self.food = food d=Dog('aaa')
#d.drink() #不能通过加括号来调用 d.drink = 'water' #AttributeError: can't set attribute 不能设置参数,意味着不能像属性一样赋值,但可以通过 d.drink
class Dog(object): age = 12 def __init__(self,name): self.name = name #@staticmethod #静态方法,将类方法变为普通方法,无法调用self,与类无关 def eat(self): print("%s is eatting %s"%(self.name,'ddd')) @classmethod #类方法,该方法只能使用类变量,无法使用实例的变量 def talk(self): print(self.name,) #1: 不能访问实例属性 print(self.age) #2:能访问类属性 d=Dog('aaa') #d.eat(d) #如果想使用对象的属性,需要自己手动将对象传入 d.talk() #1:AttributeError: type object 'Dog' has no attribute 'name' 无法使用实例的属性 #2:12 打印类属性
类的特殊成员方法
class A(object): ''' 这个是类的注释,可以通过__doc__打印 ''' def __init__(self,name): self.name=name self.data = {} def __call__(self): print('__call__是通过实例加括号调用的') def __str__(self): return self.name def __setitem__(self, key, value): print("__setitem__",key,value) self.data[key]=value def __getitem__(self, key): print("__getitem__",key) print(self.data.get(key)) def __delitem__(self, key): print("__delitem__",key) a=A('zyp') print(a.__doc__) #__doc__ #这个是类的注释,可以通过__doc__打印 a() # __call__ 通过加括号调用 #__call__是通过实例加括号调用的 print("通过__str__打印实例的返回值:",a) a['age']=12 # 调用__setitem__ age 12 print(a['age']) #打印了三个结果 1, __getitem__ age 2,12 3,None 有返回值 print(a.data) #打印{'age': 12} del a['aaa'] #调用__delitem__ aaa 只是执行没有触发删除
#aa.py __author__ = 'zyp' class A(object): def a(self): print("这是一个类") #bb.py __author__ = 'zyp' from day8.aa import A C=A() C.a() print(C.__module__) #打印对象所属的模块 #day7.aa print(C.__class__) #打印对象所属的类 #<class 'day7.aa.A'>
__new__ __metaclass__
a = 2 def talk(self): print("hello %s"%self.name) def __init__(self,name): self.name = name Foo = type("Foo",(object,),{"a":a,"tal":talk,"__init__":__init__}) #"Foo" 类名 #object 继承的基类,注意逗号, #{ 字典 }类中的方法和属性,key可以是任意,值必须是类的方法和属性名 a = Foo("aaa") print(type(Foo)) #<class 'type'> print(type(a)) # <class '__main__.Foo'> a.tal() # hello aaa print(a.a)
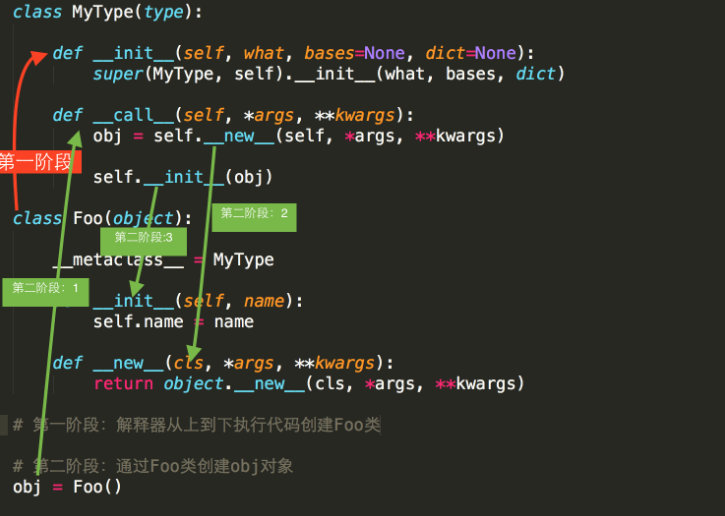
类 是由 type 类实例化产生
类中有一个属性 __metaclass__,其用来表示该类由 谁 来实例化创建,所以,我们可以为 __metaclass__ 设置一个type类的派生类,从而查看 类 创建的过程。

class MyType(type): def __init__(self,*args,**kwargs): print("Mytype __init__",*args,**kwargs) def __call__(self, *args, **kwargs): print("Mytype __call__", *args, **kwargs) obj = self.__new__(self) print("obj ",obj,*args, **kwargs) print(self) self.__init__(obj,*args, **kwargs) return obj def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): print("Mytype __new__",*args,**kwargs) return type.__new__(cls, *args, **kwargs) print('here...') class Foo(object,metaclass=MyType): def __init__(self,name): self.name = name print("Foo __init__") def __new__(cls, *args, **kwargs): print("Foo __new__",cls, *args, **kwargs) return object.__new__(cls) f = Foo("Alex") print("f",f) print("fname",f.name)
类的生成 调用 顺序依次是 __new__ --> __init__ --> __call__
反射
python面向对象中的反射:通过字符串的形式操作对象相关的属性。python中的一切事物都是对象(都可以使用反射)
def eat(self): print("将类外面的方法装配到类里面",self.name) class Eg(object): name='zyp' age=12 def eg(self): print('name',getattr(self,'name')) return hasattr(self,'name') e=Eg() e.eg() print(hasattr(e,'id')) #False setattr(e,'id',1234) #添加没有的属性 print(hasattr(e,'id')) #True print(e.id) # 1234 打印对象新添加的属性 setattr(e,'talk',eat) #talk为类中创建的方法名,创建类中不存在的方法。这样创建的是静态方法 e.talk(e) #调用的时候使用talk,而不是eat,需要手动将对象传入 delattr(e,'talk') e.talk(e) #AttributeError: 'Eg' object has no attribute 'talk' 此时已经删除了talk方法
socket编程
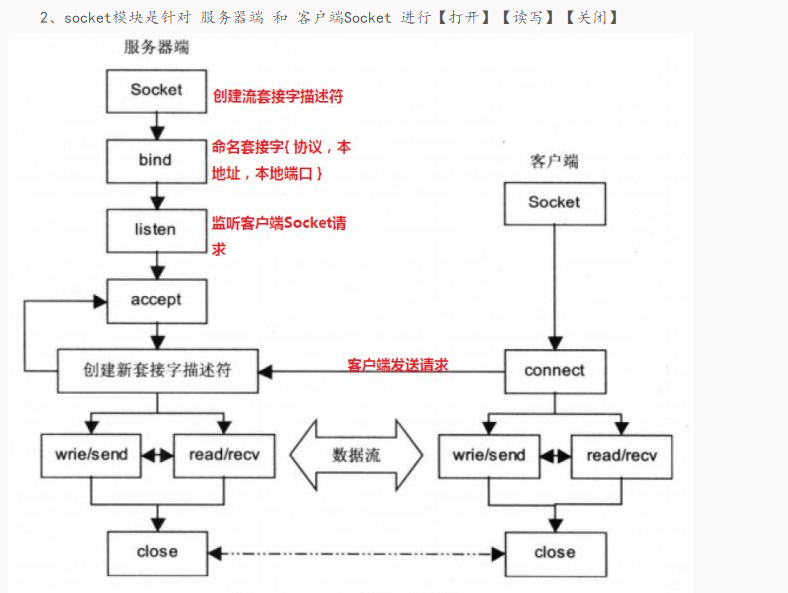
socket通常也称作"套接字",用于描述IP地址和端口,是一个通信链的句柄,应用程序通常通过"套接字"向网络发出请求或者应答网络请求。
socket和file的区别:
- file模块是针对某个指定文件进行【打开】【读写】【关闭】
- socket模块是针对 服务器端 和 客户端Socket 进行【打开】【读写】【关闭】
网络七层协议
应用层 上层用户可操作的应用
表示层 数据加密,压缩等
会话层 建立、管理和终止会话
传输层 TCP/IP(三次握手,四次断开)
网络层 基于IP地址
数据链路层 基于MAC地址
物理层
实例
#服务器端 __author__ = 'zyp' #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- import socket import os server = socket.socket() server.bind(('localhost',6969)) server.listen(5) while True: print("我在等电话") conn,addr=server.accept() print("电话来了") while True: data = conn.recv(1024) print('recv:',data.decode()) if not data : print("输入为空!") break res = os.popen(data.decode()).read() conn.send(res.encode()) server.close() #客户端 __author__ = 'zyp' import socket client = socket.socket() client.connect(('localhost',6969)) while True: mag = input("用户输入").strip() if len(mag) == 0: print("输入为空") continue if mag == 'q': exit() client.send(mag.encode("utf-8")) data = client.recv(1024) print(data.decode()) client.close()
