在学习c++基础总结了笔记,并分享出来。有问题请及时联系博主:Alliswell_WP,转载请注明出处。
04-c++day01
目录:
一、C++概述
1、C++简介
2、可移植性和标准
二、C++初识
1、练习1:hello world
2、面向对象
3、面向对象三大特性
练习2:双冒号作用域运算符
练习3:namespace命名空间
练习4:using声明和using编译指令
三、C++对C扩展
1、C++对C语言增强
2、C++对C语言增强——const
3、const分配内存情况
4、尽量以const替换#define
四、引用
1、引用的基本语法以及注意事项
2、参数的传递方式
3、引用的注意事项
4、引用的本质
5、指针的引用
6、常量引用
五、总结

C++程序模板
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 void test()
{
} 6 7 int main() 8 { 9 test(); 10 11 system("pause"); 12 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 13 }
一、C++概述
1、C++简介
“c++”中的++来自于c语言中的递增运算符++,该运算符将变量加1。c++起初也叫”c with clsss”.通过名称表明,c++是对C的扩展,因此c++是c语言的超集,这意味着任何有效的c程序都是有效的c++程序。c++程序可以使用已有的c程序库。
库是编程模块的集合,可以在程序中调用它们。库对很多常见的编程问题提供了可靠的解决方法,因此可以节省程序员大量的时间和工作量。
c++语言在c语言的基础上添加了面向对象编程和泛型编程的支持。
c语言和c++语言的关系:
c++语言是在C语言的基础上,添加了面向对象、模板等现代程序设计语言的特性而发展起来的。两者无论是从语法规则上,还是从运算符的数量和使用上,都非常相似,所以我们常常将这两门语言统称为“C/C++”。
C语言和C++并不是对立的竞争关系:
1)C++是C语言的加强,是一种更好的C语言。
2)C++是以C语言为基础的,并且完全兼容C语言的特性。
c语言和C++语言的学习是可以相互促进。学好C语言,可以为我们将来进一步地学习C++语言打好基础,而C++语言的学习,也会促进我们对于C语言的理解,从而更好地运用C语言。
2、可移植性和标准
c++98——>(修订)c++98/c++2003——>c++11
二、C++初识
1、练习1:hello world
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
//#include<iostream>标准输入输出流 in输入 out 输出 2 using namespace std;//使用命名空间std 打开一个叫std房间 3 4 //函数入口地址 5 int main() 6 { 7 //cout标准的输出 8 // << 左移运算符 9 //endl 结束换行 10 cout << "hello world" << endl; 11 12 system("pause");//阻塞功能 13 return EXIT_SUCCESS;//返回正常退出 14 }
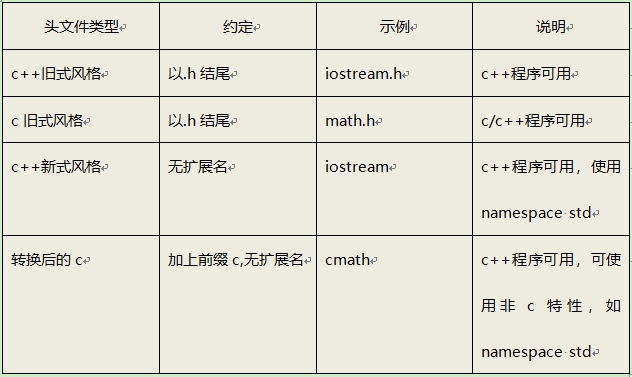
问题1:c++头文件为什么没有.h?
在c语言中头文件使用扩展名.h,将其作为一种通过名称标识文件类型的简单方式。但是c++得用法改变了,c++头文件没有扩展名。但是有些c语言的头文件被转换为c++的头文件,这些文件被重新命名,丢掉了扩展名.h(使之成为c++风格头文件),并在文件名称前面加上前缀c(表明来自c语言)。例如c++版本的math.h为cmath.
由于C使用不同的扩展名来表示不同文件类型,因此用一些特殊的扩展名(如hpp或hxx)表示c++的头文件也是可以的,ANSI/IOS标准委员会也认为是可以的,但是关键问题是用哪个比较好,最后一致同意不适用任何扩展名。
问题2:using namespace std 是什么?
namespace是指标识符的各种可见范围。命名空间用关键字namespace 来定义。命名空间是C++的一种机制,用来把单个标识符下的大量有逻辑联系的程序实体组合到一起。此标识符作为此组群的名字。
问题3:cout 、endl 是什么?
cout是c++中的标准输出流,endl是输出换行并刷新缓冲区。
2、面向对象
面向对象编程(Object-Oriented Programming)简称 OOP 技术,是开发计算机应用程序的一种新方法、新思想。过去的面向过程编程常常会导致所有的代码都包含在几个模块中,使程序难以阅读和维护。在做一些修改时常常牵一动百,使以后的开发和维护难以为继。而使用 OOP 技术,常常要使用许多代码模块,每个模块都只提供特定的功能,它们是彼此独立的,这样就增大了代码重用的几率,更加有利于软件的开发、维护和升级。
在面向对象中,算法与数据结构被看做是一个整体,称作对象,现实世界中任何类的对象都具有一定的属性和操作,也总能用数据结构与算法两者合一地来描述,所以可以用下面的等式来定义对象和程序:
对象 = 算法 + 数据结构
程序 = 对象 + 对象 + ……
3、面向对象三大特性
》封装
把客观事物封装成抽象的类,并且类可以把自己的数据和方法只让可信的类或者对象操作,对不可信的进行信息隐藏。
类将成员变量和成员函数封装在类的内部,根据需要设置访问权限,通过成员函数管理内部状态。
》 继承
继承所表达的是类之间相关的关系,这种关系使得对象可以继承另外一类对象的特征和能力。
继承的作用:避免公用代码的重复开发,减少代码和数据冗余。
》多态
多态性可以简单地概括为“一个接口,多种方法”,字面意思为多种形态。程序在运行时才决定调用的函数,它是面向对象编程领域的核心概念。
练习2:双冒号作用域运算符
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 int atk = 200; 6 void test01() 7 { 8 int atk = 100; 9 10 cout << "攻击力为:" << atk << endl; 11 //双冒号 作用域运算符 ::全局作用域 12 cout << "全局攻击力为:" << ::atk << endl; 13 } 14 15 16 int main() 17 { 18 test01(); 19 20 system("pause"); 21 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 22 }
练习3:namespace命名空间
namespace的使用.cpp
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include"game1.h" 4 #include"game2.h" 5 6 using namespace std; 7 8 //namespace命名空间主要用途 用来解决命名冲突的问题 9 void test01() 10 { 11 LOL::goAtk(); 12 KingGlory::goAtk(); 13 } 14 15 //1.命名空间下 可以放函数、变量、结构体、类 16 namespace A 17 { 18 void func(); 19 int m_A = 20; 20 struct Person 21 { 22 }; 23 class Animal{}; 24 namespace B 25 { 26 int m_A = 10; 27 } 28 } 29 //2.命名空间必须定义在全局作用域下 30 //3.命名空间可以嵌套命名空间 31 32 void test02() 33 { 34 cout << "作用域B下的m_A为:" << A::B::m_A << endl; 35 } 36 37 //4.命名空间是开放的,可以随时在原先的命名空间添加内容 38 namespace A //此A命名空间会和上面的命名空间A进行合并 39 { 40 int m_B = 1000; 41 } 42 43 void test03() 44 { 45 cout << "A::下的m_A为:" << A::m_A << "m_B为:" << A::m_B << endl; 46 } 47 48 //5.无名/匿名命名空间 49 namespace 50 { 51 int m_C = 0; 52 int m_D = 0; 53 } 54 //当写了无名命名空间,相当于写了static int m_C,static int m_D(即只能在当前文件中使用) 55 56 //6.命名空间可以起别名 57 namespace veryLongName 58 { 59 int m_A = 0; 60 } 61 void test04() 62 { 63 //起别名 64 namespace veryShortName = veryLongName; 65 cout << veryLongName::m_A << endl; 66 cout << veryShortName::m_A << endl; 67 } 68 69 70 int main() 71 { 72 test01(); 73 74 system("pause"); 75 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 76 }
game1.h
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 namespace LOL 5 { 6 void goAtk(); 7 }
game1.c
1 #include "game1.h" 2 3 void LOL::goAtk() 4 { 5 cout << "LOL攻击实现" << endl; 6 }
game2.h
1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 namespace KingGlory 5 { 6 void goAtk(); 7 }
game2.c
1 #include"game2.h" 2 3 void KingGlory::goAtk() 4 { 5 cout << "王者农药攻击实现" << endl; 6 }
练习4:using声明和using编译指令
using声明和using编译指令.cpp
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 namespace KingGlory 6 { 7 int sunwukongId = 10; 8 } 9 10 void test01() 11 { 12 int sunwukongId = 20; 13 14 //using声明 15 //写了using声明后,下面这行代码说明以后看到的sunwukongId是用KingGlory下的 16 //但是 编译器又有就近原则 17 //二义性 18 //using KingGlory::sunwukongId; 19 20 cout << sunwukongId << endl; 21 } 22 23 //using编译指令 24 namespace LOL 25 { 26 int sunwukongId = 30; 27 } 28 29 30 void test02() 31 { 32 //int sunwukongId = 20; 33 //using编译指令 34 using namespace KingGlory;//打开王者荣耀房间 35 using namespace LOL;//打开LOL房间 36 //如果打开多个房间,也要避免二义性问题 37 cout << sunwukongId << endl; 38 } 39 40 int main() 41 { 42 test01(); 43 44 system("pause"); 45 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 46 }
三、C++对C扩展
1、C++对C语言增强
C语言代码——C++对C语言的增强C语言.c
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 6 //1.全局变量检测增强 7 int a; 8 int a = 10; 9 10 //2.函数检测增强 11 int getRectS(w, h) 12 { 13 } 14 void test02() 15 { 16 getRectS(10, 10, 10); 17 } 18 19 //3.类型转换检测增强 20 void test03() 21 { 22 char* p = malloc(sizeof(64));//malloc返回值是void* 23 } 24 25 //4.struct增强 26 struct Person 27 { 28 int m_Age; 29 //void plusAge();//C语言中struct不可以加函数 30 }; 31 void test04() 32 { 33 struct Person p1;//C语言使用时候必须加入struct关键字 34 } 35 36 //5.bool类型增强 C语言中没有bool类型 37 //bool flag; 38 39 //6.三目运算符增强 40 void test06() 41 { 42 int a = 10; 43 int b = 20; 44 45 printf("ret = %d ", a > b ? a : b); 46 47 //a > b ? a : b = 100;//相当于20=100,C语言返回的是值 48 49 //C语言中想模仿C++写 50 *(a > b ? &a : &b) = 100; 51 printf("a = %d,b = %d ", a, b); 52 } 53
//7.const增强
const int m_A = 10;//全局只读区,受到保护,不可以修改
void test07()
{
//m_A = 100;
const int m_B = 20;//伪常量
//m_B = 100;
int* p = (int*)&m_B;
*p = 200;
printf("*p = %d, m_B = %d ", *p, m_B);
//int arr[m_B];不可以初始化数组
} 54 55 int main(){ 56 57 test02(); 58 59 system("pause"); 60 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 61 }
C++代码——C++对C语言的增强C++语言.cpp
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //1.全局变量检测增强 6 //int a; 7 int a = 10; 8 9 //2.函数检测增强,参数类型增强,返回值检测增强,函数调用参数检测增强 10 int getRectS(int w, int h) 11 { 12 return w*h; 13 } 14 15 void test02() 16 { 17 getRectS(10, 10); 18 } 19 20 //3.类型转换检测增强 21 void test03() 22 { 23 char* p = (char*)malloc(sizeof(64));//malloc返回值是void* 24 } 25 26 //4.struct增强 27 struct Person 28 { 29 int m_Age; 30 void plusAge(){m_Age++;};//C++中struct可以加函数 31 }; 32 void test04() 33 { 34 Person p1;//C++使用时候可以不加struct关键字 35 p1.m_Age = 10; 36 p1.plusAge(); 37 cout << p1.m_Age << endl; 38 } 39 40 41 //5.bool类型增强 C++中有bool类型 42 bool flag = true;//只有真或假 true代表真(非0) false代表假(0) 43 void test05() 44 { 45 cout << sizeof(bool) << endl;//1个字节 46 47 flag = 100; 48 //bool类型 非0转为1,0就转为0 49 cout << flag << endl; 50 } 51 52 //6.三目运算符增强 53 void test06() 54 { 55 int a = 10; 56 int b = 20; 57 58 cout << "ret = " << (a > b ? a : b) << endl; 59 60 (a > b ? a : b) = 100;//b = 100,C++中返回的是变量 61 62 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 63 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 64 } 65
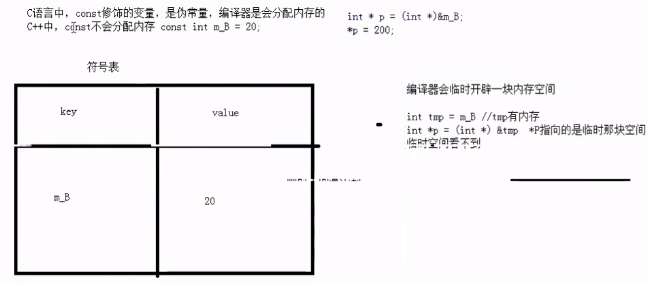
//7.const增强
const int m_A = 10;//全局只读区,受到保护,不可以修改
void test07()
{
//m_A = 100;
const int m_B = 20;//真正常量
//m_B = 100;
int* p = (int*)&m_B;
*p = 200;
cout << "*p = " << *p << endl;
cout << "m_B = " << m_B << endl;
int arr[m_B];//可以初始化数组
} 66 67 int main() 68 { 69 test02(); 70 71 system("pause"); 72 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 73 }
解释(7.const增强)
2、C++对C语言增强——const
C语言中const默认外部链接,C++默认内部链接
C语言代码——test.c
1 const int a = 10;//C语言中默认是外部链接
C语言代码——C语言const默认是外部链接.c
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<stdio.h> 3 #include<string.h> 4 #include<stdlib.h> 5 6 7 int main(){ 8 9 extern const int a;//告诉编译器a在外部 10 printf("a = %d ", a); 11 12 system("pause"); 13 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 14 }
C++代码——test.cpp
1 extern const int a = 10;//C++中默认是内部链接,extern提高作用域
C++代码——C++const默认是内部链接.cpp
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 6 int main() 7 { 8 extern const int a; 9 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 10 11 system("pause"); 12 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 13 }
3、const分配内存情况
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //1.const分配内存 取地址会分配临时内存 7 //2.extern编译器也会给const变量分配内存 8 void test01() 9 { 10 const int m_A = 10; 11 int* p = (int*)&m_A;//会分配临时内存 12 } 13 14 //3.用普通变量初始化const的变量 15 void test02() 16 { 17 int a = 10; 18 const int b = a;//会分配内存 19 20 int* p = (int*)&b; 21 *p = 1000; 22 23 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 24 } 25 26 //4.自定义数据类型,加const也会分配内存 27 struct Person 28 { 29 string m_Name;//姓名 30 int m_Age; 31 } 32 void test03() 33 { 34 const Person p1; 35 //p1.m_Name = "aaa"; 36 37 Person* p = (Person*)&p1; 38 p->m_Name = "德玛西亚"; 39 (*p).m_Age = 18; 40 41 cout << "姓名:" << p1.m_Name << "年龄:" << p1.m_Age << endl; 42 } 43 44 45 int main() 46 { 47 test01(); 48 49 system("pause"); 50 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 51 }
4、尽量以const替换#define
在旧版本C中,如果想建立一个常量,必须使用预处理器”
#define MAX 1024;
我们定义的宏MAX从未被编译器看到过,因为在预处理阶段,所有的MAX已经被替换为了1024,于是MAX并没有将其加入到符号表中。但我们使用这个常量获得一个编译错误信息时,可能会带来一些困惑,因为这个信息可能会提到1024,但是并没有提到MAX.如果MAX被定义在一个不是你写的头文件中,你可能并不知道1024代表什么,也许解决这个问题要花费很长时间。
解决办法就是用一个常量替换上面的宏。
const int max= 1024;
const和#define区别总结:
1)const有类型,可进行编译器类型安全检查。#define无类型,不可进行类型检查.
2)const有作用域,而#define不重视作用域,默认定义处到文件结尾.如果定义在指定作用域下有效的常量,那么#define就不能用。
四、引用
1、引用的基本语法以及注意事项
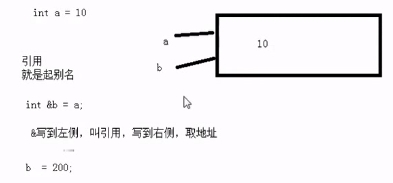
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //1.引用基本语法 Type &别名 = 原名 6 void test01() 7 { 8 int a = 10; 9 int &b = a; 10 11 b = 20; 12 13 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 14 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 15 } 16 17 //2.引用必须初始化 18 void test02() 19 { 20 //int &a;//必须初始化 21 int a = 10; 22 int &b = a;//引用初始化后不可以修改了 23 int c = 20; 24 25 b = c;//赋值!!! 26 } 27 28 //3.对数组建立引用 29 void test03() 30 { 31 int arr[10]; 32 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 33 { 34 arr[i] = i; 35 } 36 37 //给数组起别名 38 int(&pArr)[10] = arr; 39 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 40 { 41 cout << pArr[i] << ""; 42 } 43 cout << endl; 44 45 //第二种方式 起别名 46 47 typedef int(ARRAYREF)[10];//一个具有10个元素的int类型的数组 48 ARRAYREF &pArr2 = arr; 49 for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) 50 { 51 cout << pArr2[i] << ""; 52 } 53 } 54 55 int main() 56 { 57 test01(); 58 59 system("pause"); 60 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 61 }
2、参数的传递方式
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4
//值传递 5 void mySwap(int a, int b) 6 { 7 int temp = a; 8 a = b; 9 b = temp; 10 11 cout << "mySwap:a = " << a << endl; 12 cout << "mySwap:b = " << b << endl; 13 } 14 15 void test01() 16 { 17 int a = 10; 18 int b = 20; 19 mySwap(a, b);//值传递 20 21 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 22 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 23 } 24 25 //地址传递 26 void mySwap2(int* a, int* b) 27 { 28 int temp = *a; 29 *a = *b; 30 *b = temp; 31 } 32 void test02() 33 { 34 int a = 10; 35 int b = 20; 36 mySwap2(&a, &b);//地址传递 37 38 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 39 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 40 } 41 42 //引用传递,类似传地址 43 void mySwap3(int &a, int &b)//&a = a, &b = b 44 { 45 int temp = a; 46 a = b; 47 b = temp; 48 } 49 void test02() 50 { 51 int a = 10; 52 int b = 20; 53 mySwap3(a, b); 54 55 cout << "a = " << a << endl; 56 cout << "b = " << b << endl; 57 } 58 59 int main() 60 { 61 test01(); 62 63 system("pause"); 64 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 65 }
3、引用的注意事项
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //引用的注意事项 6 //1.引用必须引一块合法的内存空间 7 //2.不要返回局部变量的引用 8 int& doWork() 9 { 10 int a = 10; 11 return a; 12 } 13 void test01() 14 { 15 //int &a = 10;//引用必须引一块合法的内存空间 16 17 int &ret = doWork(); 18 cout << "ret = " << ret << endl;//第一次10是编译器做了优化 19 cout << "ret = " << ret << endl; 20 cout << "ret = " << ret << endl; 21 cout << "ret = " << ret << endl; 22 cout << "ret = " << ret << endl; 23 } 24 25 int& doWork2() 26 { 27 static int a = 10; 28 return a; 29 } 30 void test01() 31 { 32 int &ret = doWork2(); 33 34 //如果函数的返回值是引用,那么这个函数可以作为左值 35 doWork2() = 1000;//相当于写了a = 1000 36 } 37 38 39 int main() 40 { 41 test01(); 42 43 system("pause"); 44 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 45 }
4、引用的本质
引用的本质在c++内部实现是一个指针常量。
1 Type& ref = val; // Type* const ref = &val;
c++编译器在编译过程中使用常指针作为引用的内部实现,因此引用所占用的空间大小与指针相同,只是这个过程是编译器内部实现,用户不可见。
1 //发现是引用,转换为 int* const ref = &a; 2 void testFunc(int& ref){ 3 ref = 100; // ref是引用,转换为*ref = 100 4 } 5 int main(){ 6 int a = 10; 7 int& aRef = a; //自动转换为 int* const aRef = &a;这也能说明引用为什么必须初始化 8 aRef = 20; //内部发现aRef是引用,自动帮我们转换为: *aRef = 20; 9 cout << "a:" << a << endl; 10 cout << "aRef:" << aRef << endl; 11 testFunc(a); 12 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 13 }
5、指针的引用
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 struct Person 6 { 7 int m_Age; 8 }; 9 10 void allocateMemory(Person** p)//**p 具体的Person对象 *p对象的指针 p指针的指针 11 { 12 *p = (Person*)malloc(sizeof(Person)); 13 14 (*p)->m_Age = 100; 15 } 16 17 void test01() 18 { 19 Person* p = NULL; 20 allocateMemory(&p); 21 cout << "p的年龄:" << p->m_Age << endl; 22 } 23 24 //利用指针引用开辟空间 25 void allocateMemoryByRef(Person* &p) 26 { 27 p = (Person*)malloc(sizeof(Person)); 28 p->m_Age = 1000; 29 } 30 31 void test02() 32 { 33 Person* p = NULL; 34 allocateMemoryByRef(p); 35 cout << "p的年龄:" << p->m_Age << endl; 36 } 37 38 39 int main() 40 { 41 test01(); 42 43 system("pause"); 44 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 45 }
6、常量引用
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 6 void test01() 7 { 8 //int &ref = 10;//引用了不合法的内存,不可以 9 const int &ref = 10;//加入const后,编译器内部处理方式为:int tmp = 10; const int &ref = tmp; 10 11 //ref = 20;//不可以直接改 12 13 int* p = (int*)&ref; 14 *p = 1000; 15 16 cout << "ref = " << ref << endl; 17 18 } 19 20 //常量引用使用场景,用来修饰形参 21 void showValue(const int &val) 22 { 23 //val += 1000;//如果只是想显示内容,而不修改内容,那么就用const修饰这个形参 24 cout << "val = " << val << endl; 25 } 26 void test02() 27 { 28 int a = 10; 29 showValue(a); 30 } 31 32 33 int main() 34 { 35 test01(); 36 37 system("pause"); 38 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 39 }
[const引用使用场景]
常量引用主要用在函数的形参,尤其是类的拷贝/复制构造函数。
将函数的形参定义为常量引用的好处:
>引用不产生新的变量,减少形参与实参传递时的开销。
>由于引用可能导致实参随形参改变而改变,将其定义为常量引用可以消除这种副作用。
如果希望实参随着形参的改变而改变,那么使用一般的引用,如果不希望实参随着形参改变,那么使用常引用。
五、总结
1 #include <iostream>
1.1 using namespace std;
1.2 cout << “hello ..” << endl;
1.3 system(“pause”)
1.4 retrun 0
2 ::双冒号作用域运算符
2.1 全局作用域 直接加::
3 namespace 命名空间
3.1 用途 解决名称冲突问题
3.2 必须在全局作用域下声明
3.3 命名空间下可以放入 函数、变量、结构体、类…
3.4 命名空间可以嵌套命名空间
3.5 命名空间是开放的,可以随时加入新的成员
3.6 匿名命名空间 static
3.7 可以起别名
4 using声明和using编译指令
4.1 using LOL:: sunwukongID;
4.2 如果局部范围内还有 sunwukongID,会出现二义性问题,要注意避免
4.3 编译指令
4.4 using namespace LOL
4.5 如果局部范围内还有 sunwukongID ,使用局部的ID
4.6 如果打开多个房间,那么也要注意二义性问题
5 C++对C语言增强
5.1 全局变量检测增强
5.2 函数检测增强
5.2.1 参数类型检测
5.2.2 返回值检测
5.2.3 传参个数检测
5.3 类型转换检测增强
5.3.1 malloc返回void* ,C中可以不用强转,C++必须强转
5.4 struct增强
5.4.1 C中不许有函数 C++可以
5.4.2 使用C必须加关键字 struct ,C++可以不加
5.5 bool数据类型增强
5.5.1 C没有 C++有
5.5.2 true 真 false假
5.5.3 sizeof 1
5.6 三目运算符增强
5.6.1 C中返回的是值
5.6.2 C++中返回的是变量
5.7 const增强
5.7.1 C语言中const是伪常量,可以通过指针修改
5.7.2 C++中const会放入到符号表中
5.7.3 C语言中const默认是外部链接,C++中const默认是内部链接
5.7.4 const分配内存情况
5.7.4.1 对变量取地址,会分配临时内存
5.7.4.2 extern关键字下的const会分配内存
5.7.4.3 用普通变量初始化const变量
5.7.4.4 自定义数据类型会分配内存
5.7.5 尽量用const代替define
5.7.5.1 define宏没有作用域概念
5.7.5.2 define宏常量没有类型
6 引用基本语法
6.1.1 用途起别名
6.1.2 Type &别名 = 原名
6.1.3 引用必须初始化
6.1.4 一旦初始化后 不能修改
6.1.5 对数组建立引用
6.2 参数3种传递方式
6.2.1 值传递
6.2.2 地址传递
6.2.3 引用传递
6.3 注意事项,不要返回局部变量的引用
6.4 如果函数返回值是引用,那么函数的调用可以作为左值
6.5 引用的本质 就是一个指针常量
7 指针的引用
7.1 用一级指针引用 可以代替二级指针
8 常量引用
8.1 使用场景 修饰形参为只读
8.2 const int &a = 10;会分配内存
在学习c++基础总结了笔记,并分享出来。有问题请及时联系博主:Alliswell_WP,转载请注明出处。