在学习c++基础总结了笔记,并分享出来。有问题请及时联系博主:Alliswell_WP,转载请注明出处。
04-c++day04
目录:
一、类和对象
1、静态成员变量
2、静态成员函数
3、单例模式
练习1:——主席案例
练习2:打印机案例
4、C++面向对象模型初探
5、this指针
6、空指针访问成员函数
7、常函数与常对象
8、全局函数做友元函数
9、整个类做友元类
10、类模板的分文件编写问题及解决
11、成员函数做友元函数
二、总结
一、类和对象
1、静态成员变量
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Person 6 { 7 public: 8 9 static int m_Age;//加入static就是静态成员变量,会共享数据 10 //静态成员变量,在类内声明,类外进行初始化 11 12 //静态成员变量,也是有权限的 13 private: 14 static int m_other;//私有权限,在类外不能访问 15 }; 16 int Person::m_Age = 0;//类外初始化实现 17 int Person::m_other = 10; 18 19 void test01() 20 { 21 //1.通过对象访问属性 22 Person p1; 23 p1.m_Age = 10; 24 25 Person p2; 26 p2.m_Age = 20; 27 28 cout << "p1 = " << p1.m_Age << endl;//10或者20?20 29 cout << "p2 = " << p2.m_Age << endl;//20 30 //共享数据 31 32 //2.通过类名访问属性 33 cout << "通过类名访问Age" << Person::m_Age << endl; 34 //cout << "other = " << Person::m_other << endl;//私有权限在类外无法访问 35 36 } 37 38 int main() 39 { 40 test01(); 41 42 system("pause"); 43 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 44 }
2、静态成员函数
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Person 6 { 7 public: 8 9 static int m_Age;//加入static就是静态成员变量,会共享数据 10 //静态成员变量,在类内声明,类外进行初始化 11 12 //静态成员变量,也是有权限的 13 int m_A; 14 15 //静态成员函数 16 //不可以访问普通成员变量 17 //可以访问静态成员变量 18 static void func(); 19 { 20 //m_A = 10; 21 m_Age = 100; 22 cout << "func调用" << endl; 23 } 24 25 //普通成员函数,可以访问普通成员变量,也可以访问静态成员变量 26 void myFunc() 27 { 28 m_A = 100; 29 m_Age = 100; 30 } 31 32 private: 33 static int m_other;//私有权限,在类外不能访问 34 35 static void func2() 36 { 37 cout << "func调用" << endl; 38 } 39 }; 40 int Person::m_Age = 0;//类外初始化实现 41 int Person::m_other = 10; 42 43 void test01() 44 { 45 //1.通过对象访问属性 46 Person p1; 47 p1.m_Age = 10; 48 49 Person p2; 50 p2.m_Age = 20; 51 52 cout << "p1 = " << p1.m_Age << endl;//10或者20?20 53 cout << "p2 = " << p2.m_Age << endl;//20 54 //共享数据 55 56 //2.通过类名访问属性 57 cout << "通过类名访问Age" << Person::m_Age << endl; 58 //cout << "other = " << Person::m_other << endl;//私有权限在类外无法访问 59 60 //静态成员函数调用 61 p1.func(); 62 p2.func(); 63 Person::func(); 64 65 //静态成员函数也是有权限的 66 //Person::func2(); 67 68 69 } 70 71 int main() 72 { 73 test01(); 74 75 system("pause"); 76 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 77 }
3、单例模式
单例模式是一种常用的软件设计模式。在它的核心结构中只包含一个被称为单例的特殊类。通过单例模式可以保证系统中一个类只有一个实例而且该实例易于外界访问,从而方便对实例个数的控制并节约系统资源。如果希望在系统中某个类的对象只能存在一个,单例模式是最好的解决方案。
Singleton(单例):在单例类的内部实现只生成一个实例,同时它提供一个静态的getInstance()工厂方法,让客户可以访问它的唯一实例;为了防止在外部对其实例化,将其默认构造函数和拷贝构造函数设计为私有;在单例类内部定义了一个Singleton类型的静态对象,作为外部共享的唯一实例。
练习1:——主席案例
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //创建主席类 6 //需求:单例模式,为了创建类中的对象,并且保证只有一个对象实例 7 class ChairMan 8 { 9 10 //1.构造函数进行私有化 11 private: 12 ChairMan() 13 { 14 cout << "创建国家主席" << endl; 15 } 16 //拷贝构造私有化 17 ChairMan(const ChairMan &c) 18 { 19 20 } 21 22 23 public: 24 //提供get方法,访问主席 25 static ChairMan* getInstance() 26 { 27 return singleMan; 28 } 29 30 private: 31 static ChairMan* singleMan; 32 33 }; 34 ChairMan* ChairMan::singleMan = new ChairMan; 35 36 void test01() 37 { 38 /* 39 ChairMan c1; 40 ChairMan* c2 = new ChairMan; 41 */ 42 43 /* 44 ChairMan* cm = ChairMan::singleMan; 45 ChairMan* cm2 = ChairMan::singleMan; 46 */ 47 48 //ChairMan::singleMan = NULL; 49 50 51 ChairMan* cm1 = ChairMan::getInstance(); 52 ChairMan* cm2 = ChairMan::getInstance(); 53 if(cm1 == cm2) 54 { 55 cout << "cm1与cm2相同" << endl; 56 } 57 else 58 { 59 cout << "cm1与cm2不相同" << endl; 60 } 61 62 /* 63 ChairMan* cm3 = new ChairMan(*cm2);//拷贝构造私有化可解决 64 if(cm3 == cm2) 65 { 66 cout << "cm3与cm2相同" << endl; 67 } 68 else 69 { 70 cout << "cm3与cm2不相同" << endl; 71 } 72 */ 73 } 74 75 int main() 76 { 77 cout << "main调用" << endl;//主席创建先于main调用 78 test01(); 79 80 system("pause"); 81 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 82 }
练习2:打印机案例(提供打印功能、打印次数功能)
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Printer 7 { 8 private: 9 Printer() 10 { 11 m_Count = 0; 12 } 13 Printer(const Printer &p); 14 15 public: 16 static Printer* getInstance() 17 { 18 return singlePrinter; 19 } 20 21 void printText(string text) 22 { 23 cout << text << endl; 24 m_Count++; 25 cout << "打印机使用了次数为:" << m_Count << endl; 26 } 27 28 29 private: 30 static Printer* singlePrinter; 31 int m_Count; 32 }; 33 Printer* singlePrinter::singlePrinter = new Printer; 34 35 void test01() 36 { 37 //拿到打印机 38 Printer* printer = Printer::getInstance(); 39 40 printer->printText("离职报告"); 41 printer->printText("入职报告"); 42 printer->printText("加薪申请"); 43 printer->printText("升级申请"); 44 printer->printText("退休申请"); 45 } 46 47 int main() 48 { 49 test01(); 50 51 system("pause"); 52 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 53 }
4、C++面向对象模型初探
成员变量和函数的存储
在c语言中,“分开来声明的,也就是说,语言本身并没有支持“数据”和“函数”之间的关联性我们把这种程序方法称为“程序性的”,由一组“分布在各个以功能为导航的函数中”的算法驱动,它们处理的是共同的外部数据。
c++实现了“封装”,那么数据(成员属性)和操作(成员函数)是什么样的呢?
“数据”和“处理数据的操作(函数)”是分开存储的。
1)c++中的非静态数据成员直接内含在类对象中,就像c struct一样。
2)成员函数(member function)虽然内含在class声明之内,却不出现在对象中。
3)每一个非内联成员函数(non-inline member function)只会诞生一份函数实例.
成员变量和成员函数分开处理
1.成员变量和成员函数是分开存储的
2.空类的大小:1
3.只有非静态成员才属于对象身上
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Person 6 { 7 public: 8 int m_A;//非静态成员变量,属于对象身上 9 void func(){}//非静态成员函数,不属于对象身上 10 static int m_B;//静态成员变量,不属于对象身上 11 static void func2(){}//静态成员函数,不属于对象身上 12 double m_C;//12错误,16正确(增加#pragma pack(1)按1个字节对齐,为12) 13 } 14 15 //结论:非静态成员变量,才属于对象身上 16 17 void test01() 18 { 19 cout << "size of (Person)" << sizeof(Person) << endl; 20 //空类的大小为:1,每个实例的对象,都有独一无二的地址,char维护这个地址 21 //例如Person p[10],数组也是需要区分的 22 23 } 24 25 int main() 26 { 27 test01(); 28 29 system("pause"); 30 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 31 }
5、this指针
this指针工作原理
通过上例我们知道,c++的数据和操作也是分开存储,并且每一个非内联成员函数(non-inline member function)只会诞生一份函数实例,也就是说多个同类型的对象会共用一块代码
那么问题是:这一块代码是如何区分那个对象调用自己的呢?
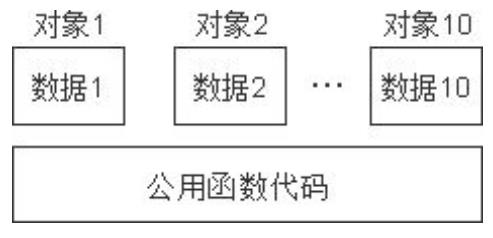
c++通过提供特殊的对象指针,this指针,解决上述问题。This指针指向被调用的成员函数所属的对象。
c++规定,this指针是隐含在对象成员函数内的一种指针。当一个对象被创建后,它的每一个成员函数都含有一个系统自动生成的隐含指针this,用以保存这个对象的地址,也就是说虽然我们没有写上this指针,编译器在编译的时候也是会加上的。因此this也称为“指向本对象的指针”,this指针并不是对象的一部分,不会影响sizeof(对象)的结果。
this指针是C++实现封装的一种机制,它将对象和该对象调用的成员函数连接在一起,在外部看来,每一个对象都拥有自己的函数成员。一般情况下,并不写this,而是让系统进行默认设置。
this指针永远指向当前对象。
成员函数通过this指针即可知道操作的是那个对象的数据。This指针是一种隐含指针,它隐含于每个类的非静态成员函数中。This指针无需定义,直接使用即可。
注意:静态成员函数内部没有this指针,静态成员函数不能操作非静态成员变量。
说明:
1 void test02() 2 { 3 //this指针指向被调用的成员函数所属的对象 4 Person p1; 5 p1.func();//编译器会偷偷加入一个this指针Person* this 6 7 Person p2; 8 p2.func(); 9 10 11 12 }
练习:
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 //this可以解决命名冲突 6 class Person 7 { 8 public: 9 Person(int age)//p1调用时候默认把Person* this传入 10 { 11 this->age = age;//此处不可以写age = age; 12 } 13 14 //对比年龄 15 void compareAge(Person &p) 16 { 17 if(this->age == p.age)//此处可以写age == p.age 18 { 19 cout << "年龄相等" << endl; 20 } 21 else 22 { 23 cout << "年龄不相等" << endl; 24 } 25 } 26 27 //年龄相加 28 Person& PlusAge(Person& p) 29 { 30 this->age += p.age; 31 return *this;//*this指向对象本体 32 } 33 34 int age; 35 }; 36 37 38 void test01() 39 { 40 Person p1(10); 41 42 cout << "p1的年龄" << p1.age << endl; 43 44 Person p2(10); 45 46 p1.compareAge(p2); 47 48 p1.PlusAge(p2).PlusAge(p2);//链式编程! 49 cout << "p1的年龄" << p1.age << endl; 50 } 51 52 int main() 53 { 54 test01(); 55 56 system("pause"); 57 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 58 }
注意:非静态的成员函数才有this指针!
6、空指针访问成员函数
1)如果成员函数没有用到this,那么空指针可以直接访问
2)如果成员函数用的this指针,就要注意,可以加if判断,如果if为空,就return。
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Person 6 { 7 public: 8 void show() 9 { 10 cout << "Person show" << endl; 11 } 12 void showAge() 13 { 14 if(this == NULL)//用途:防止空指针调用成员 15 { 16 return; 17 } 18 19 cout << m_Age << endl;//NULL->m_Age 20 } 21 22 int m_Age; 23 }; 24 25 26 void test01() 27 { 28 Person* p = NULL; 29 p->show(); 30 //p->showAge(); 31 32 33 } 34 35 int main() 36 { 37 test01(); 38 39 system("pause"); 40 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 41 }
7、常函数与常对象
const修饰成员函数
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 5 class Person 6 { 7 public: 8 Person() 9 { 10 //构造中修改属性 11 //this指针永远指向本体 12 //Person* const this 13 this->m_A = 0; 14 this->m_B = 0; 15 } 16 17 void showInfo() const//常函数,不允许修改指针指向的值 18 { 19 //this->m_A = 1000; 20 this->m_B = 1000; 21 cout << "m_A = " << this->m_A << endl; 22 cout << "m_B = " << this->m_B << endl; 23 } 24 25 void show2() const 26 { 27 //m_A = 100; 28 } 29 30 int m_A; 31 mutable int m_B;//就算是常函数,我还是执意要修改 32 }; 33 34 void test01() 35 { 36 Person p1; 37 p1.showInfo(); 38 39 //常对象,不允许修改属性 40 const Person p2; 41 cout << p2.m_A << endl; 42 p2.show2(); 43 //常对象不可以调用普通成员函数 44 //常对象可以调用常函数 45 46 } 47 48 int main() 49 { 50 test01(); 51 52 system("pause"); 53 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 54 }
8、全局函数做友元函数
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Building 7 { 8 //让全局的好基友函数,变为我的好朋友,友元函数 9 friend void goodGay(Building* building); 10 11 public: 12 Building() 13 { 14 this->m_SittingRoom = "客厅"; 15 this->m_BedRoom = "卧室"; 16 } 17 18 //客厅 卧室 19 public: 20 string m_SittingRoom;//客厅 21 22 private: 23 string m_BedRoom;//卧室 24 }; 25 26 //全局函数 好基友 27 void goodGay(Building* building) 28 { 29 cout << "好基友正在访问" << building->m_SittingRoom << endl; 30 cout << "好基友正在访问" << building->m_BedRoom << endl; 31 } 32 33 //友元函数目的:访问类中的私有成员属性 34 void test01() 35 { 36 Building* building = new Building; 37 goodGay(building); 38 } 39 40 int main() 41 { 42 test01(); 43 44 system("pause"); 45 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 46 }
9、整个类做友元类
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 class Building;//先声明一下,防止报错 7 class goodGay 8 { 9 public: 10 goodGay(); 11 12 void visit(); 13 private: 14 Building* building; 15 16 }; 17 18 class Building 19 { 20 //让好基友类作为Building的好朋友 21 friend class goodGay; 22 23 public: 24 Building(); 25 public: 26 string m_SittingRoom;//客厅 27 private: 28 string m_BedRoom;//卧室 29 30 }; 31 32 goodGay::goodGay() 33 { 34 building = new Building; 35 } 36 37 void goodGay::visit() 38 { 39 cout << "好基友正在访问:" << this->building->m_SittingRoom << endl; 40 cout << "好基友正在访问:" << this->building->m_BedRoom << endl; 41 } 42 43 44 Building::Building() 45 { 46 this->m_SittingRoom = "客厅"; 47 this->m_BedRoom = "卧室"; 48 } 49 50 void test01() 51 { 52 goodGay gg; 53 gg.visit(); 54 } 55 56 int main() 57 { 58 test01(); 59 60 system("pause"); 61 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 62 }
10、类模板的分文件编写问题及解决
1).h、.cpp分别写声明和实现
2)但是由于类模板的成员函数运行阶段才去创建,导致包含.h头文件,不会创建函数的实现,无法解析外部命令
3)解决方案:包括.cpp文件,不推荐
4)不要进行分文件编写,类内进行声明和类外实现,最后把后缀名改为.hpp(约定俗成)
练习:
类模板的分文件编写.cpp
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 #include"Person.hpp" 6 7 //建议模板不要做分文件编写,写到一个类中即可,类内进行声明,类外实现,最后把后缀名改为.hpp(约定俗成) 8 9 void test01() 10 { 11 12 } 13 14 int main() 15 { 16 Person<string, int>p("猪八戒", 10); 17 p.showPerson(); 18 19 test01(); 20 21 system("pause"); 22 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 23 }
Person.hpp
1 #pragma once 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 template<class T1, class T2> 7 class Person 8 { 9 public: 10 Person(T1 name, T2 age); 11 12 void showPerson(); 13 14 T1 m_Name; 15 T2 m_Age; 16 }; 17 18 template<class T1, class T2> 19 Person<T1, T2>::Person(T1, T2 age) 20 { 21 this->m_Name = name; 22 this->m_Age = age; 23 } 24 25 template<class T1, class T2> 26 void Person<T1, T2>::showPerson() 27 { 28 cout << "姓名:" << this->m_Name << " 年龄:" << this->m_Age << endl; 29 }
11、成员函数做友元函数
1 #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 2 #include<iostream> 3 #include<string> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 //只让visit作为Building的好朋友,visit2不可以访问私有属性 7 class Building; 8 class goodGay 9 { 10 public: 11 goodGay(); 12 13 void visit(); 14 void visit2(); 15 private: 16 Building* building; 17 18 }; 19 20 class Building 21 { 22 //让成员函数visit作为友元函数 23 friend void goodGay::visit(); 24 25 public: 26 Building(); 27 public: 28 string m_SittingRoom;//客厅 29 private: 30 string m_BedRoom;//卧室 31 32 }; 33 34 goodGay::goodGay() 35 { 36 building = new Building; 37 } 38 39 void goodGay::visit() 40 { 41 cout << "好基友正在访问:" << this->building->m_SittingRoom << endl; 42 cout << "好基友正在访问:" << this->building->m_BedRoom << endl; 43 } 44 45 void goodGay::visit2() 46 { 47 cout << "好基友正在访问:" << this->building->m_SittingRoom << endl; 48 //cout << "好基友正在访问:" << this->building->m_BedRoom << endl; 49 } 50 51 Building::Building() 52 { 53 this->m_SittingRoom = "客厅"; 54 this->m_BedRoom = "卧室"; 55 } 56 57 void test01() 58 { 59 goodGay gg; 60 gg.visit(); 61 gg.visit2(); 62 } 63 64 int main() 65 { 66 test01(); 67 68 system("pause"); 69 return EXIT_SUCCESS; 70 }
二、总结
1 静态成员变量和静态成员函数
1.1 静态成员变量
1.1.1 编译阶段分配内存
1.1.2 所有对象共享数据
1.1.3 通过对象访问、通过类名访问
1.1.4 有权限控制
1.1.5 类内声明 类外初始化
1.2 静态成员函数
1.2.1 可以访问静态成员变量,不可以方法普通成员变量
1.2.2 普通成员函数 都可以访问
1.2.3 静态成员函数也有权限
1.2.4 可以通过对象访问,也可以通过类名进行访问
2 单例模式案例 – 主席
2.1 目的 为了让类中只有一个实例,实例不需要自己释放
2.2 将 默认构造 和 拷贝构造 私有化
2.3 内部维护一个 对象指针
2.4 私有化唯一指针
2.5 对外提供 getInstance方法来访问这个指针
2.6 保证类中只能实例化唯一一个对象
3 单例模式案例 – 打印机案例
3.1 类似主席案例
3.2 提供打印功能
3.3 提供统计打印次数功能
4 C++对象模型初探
4.1 成员变量和成员函数是分开存储的
4.2 空类的大小 1
4.3 只有非静态成员属性才属于对象身上
5 this指针使用
5.1 指针永远指向当前对象
5.2 解决命名冲突
5.3 *this 指向对象本体
5.4 非静态的成员函数才有this指针
6 空指针访问成员函数
6.1 如果成员函数没有用到this,那么空指针可以直接访问
6.2 如果成员函数用的this指针,就要注意,可以加if判断,如果this为NULL就return
7 常函数 常对象
7.1 常函数 void func() const {} 常函数
7.2 常函数 修饰是this指针 const Type * const this
7.3 常函数 不能修改this指针执行的值
7.4 常对象 在对象前 加入 const修饰 const Person p1
7.5 常对象 不可以调用普通的成员函数
7.6 常对象 可以调用常函数
7.7 用mutable修饰的关键字是在常函数可以修改的
8 友元
8.1 全局函数做友元函数
8.1.1 全局函数写到 类中做声明 并且最前面写关键字 friend
8.2 让整个类 做友元类
8.2.1 friend class 类名
8.2.2 友元类 是单向,不可传递的
8.3 让成员函数做友元函数
8.3.1 friend void goodGay::visit();
8.4 类模板的分文件编写问题及解决
8.4.1 .h、.cpp分别写声明和实现
8.4.2 但是由于类模板的成员函数运行阶段才去创建,导致包含.h头文件,不会创建函数的实现,无法解析外部命令
8.4.3 解决方案:包括.cpp文件,不推荐
8.4.4 不要进行分文件编写,类内进行声明和类外实现,最后把后缀名改为.hpp(约定俗成)
在学习c++基础总结了笔记,并分享出来。有问题请及时联系博主:Alliswell_WP,转载请注明出处。