为了便于理解,以下源码分析以 JDK 1.7 为主。
1. 存储结构
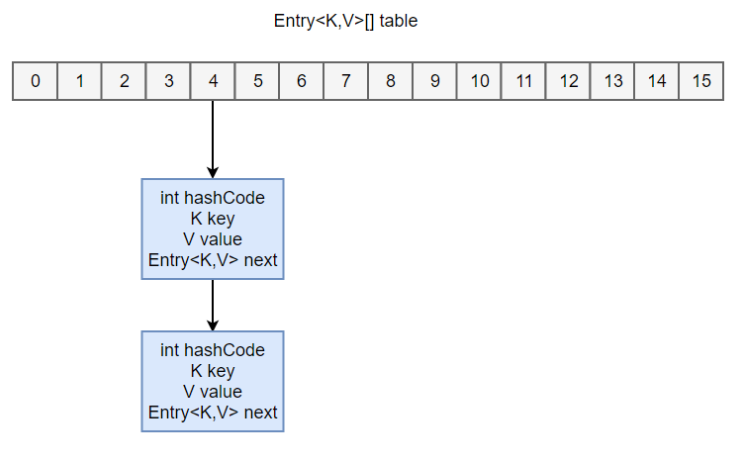
内部包含了一个 Entry 类型的数组 table。
transient Entry[] table;
Entry 存储着键值对。它包含了四个字段,从 next 字段我们可以看出 Entry 是一个链表。即数组中的每个位置被当成一个桶,一个桶存放一个链表。HashMap 使用拉链法来解决冲突,同一个链表中存放哈希值相同的 Entry。
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key; V value; Entry<K,V> next; int hash; Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) { value = v; next = n; key = k; hash = h; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return value; } public final V setValue(V newValue) { V oldValue = value; value = newValue; return oldValue; } public final boolean equals(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o; Object k1 = getKey(); Object k2 = e.getKey(); if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) { Object v1 = getValue(); Object v2 = e.getValue(); if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2))) return true; } return false; } public final int hashCode() { return Objects.hashCode(getKey()) ^ Objects.hashCode(getValue()); } public final String toString() { return getKey() + "=" + getValue(); } }
2. 拉链法的工作原理
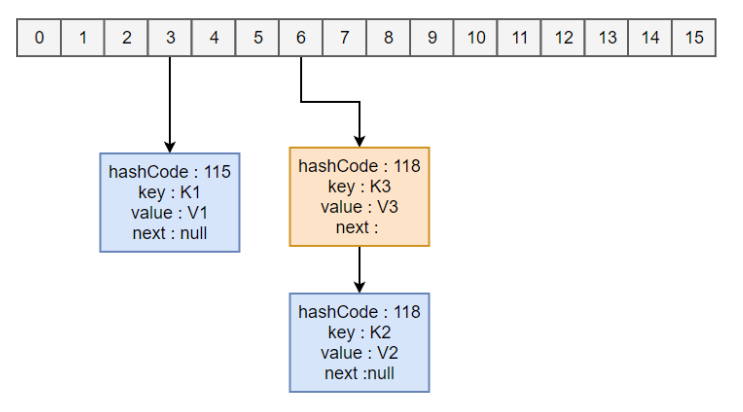
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("K1", "V1"); map.put("K2", "V2"); map.put("K3", "V3");
- 新建一个 HashMap,默认大小为 16;
- 插入 <K1,V1> 键值对,先计算 K1 的 hashCode 为 115,使用除留余数法得到所在的桶下标 115%16=3。
- 插入 <K2,V2> 键值对,先计算 K2 的 hashCode 为 118,使用除留余数法得到所在的桶下标 118%16=6。
- 插入 <K3,V3> 键值对,先计算 K3 的 hashCode 为 118,使用除留余数法得到所在的桶下标 118%16=6,插在 <K2,V2> 前面。
应该注意到链表的插入是以头插法方式进行的,例如上面的 <K3,V3> 不是插在 <K2,V2> 后面,而是插入在链表头部。
查找需要分成两步进行:
- 计算键值对所在的桶;
- 在链表上顺序查找,时间复杂度显然和链表的长度成正比。
3. put 操作
public V put(K key, V value) { if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) { inflateTable(threshold); } // 键为 null 单独处理 if (key == null) return putForNullKey(value); int hash = hash(key); // 确定桶下标 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); // 先找出是否已经存在键为 key 的键值对,如果存在的话就更新这个键值对的值为 value for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { Object k; if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; // 插入新键值对 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); return null; }
HashMap 允许插入键为 null 的键值对。但是因为无法调用 null 的 hashCode() 方法,也就无法确定该键值对的桶下标,只能通过强制指定一个桶下标来存放。HashMap 使用第 0 个桶存放键为 null 的键值对。
private V putForNullKey(V value) { for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { if (e.key == null) { V oldValue = e.value; e.value = value; e.recordAccess(this); return oldValue; } } modCount++; addEntry(0, null, value, 0); return null; }
使用链表的头插法,也就是新的键值对插在链表的头部,而不是链表的尾部。
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { resize(2 * table.length); hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); } createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); } void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; // 头插法,链表头部指向新的键值对 table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); size++; } Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) { value = v; next = n; key = k; hash = h; }
4. 确定桶下标
很多操作都需要先确定一个键值对所在的桶下标。
int hash = hash(key); int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
4.1 计算 hash 值
final int hash(Object k) { int h = hashSeed; if (0 != h && k instanceof String) { return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k); } h ^= k.hashCode(); // This function ensures that hashCodes that differ only by // constant multiples at each bit position have a bounded // number of collisions (approximately 8 at default load factor). h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12); return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4); } public final int hashCode() { return Objects.hashCode(key) ^ Objects.hashCode(value); }
4.2 取模
令 x = 1<<4,即 x 为 2 的 4 次方,它具有以下性质:
x : 00010000
x-1 : 00001111
令一个数 y 与 x-1 做与运算,可以去除 y 位级表示的第 4 位以上数:
y : 10110010 x-1 : 00001111 y&(x-1) : 00000010
这个性质和 y 对 x 取模效果是一样的:
y : 10110010 x : 00010000 y%x : 00000010
我们知道,位运算的代价比求模运算小的多,因此在进行这种计算时用位运算的话能带来更高的性能。
确定桶下标的最后一步是将 key 的 hash 值对桶个数取模:hash%capacity,如果能保证 capacity 为 2 的 n 次方,那么就可以将这个操作转换为位运算。
static int indexFor(int h, int length) { return h & (length-1); }
5. 扩容-基本原理
设 HashMap 的 table 长度为 M,需要存储的键值对数量为 N,如果哈希函数满足均匀性的要求,那么每条链表的长度大约为 N/M,因此平均查找次数的复杂度为 O(N/M)。
为了让查找的成本降低,应该尽可能使得 N/M 尽可能小,因此需要保证 M 尽可能大,也就是说 table 要尽可能大。HashMap 采用动态扩容来根据当前的 N 值来调整 M 值,使得空间效率和时间效率都能得到保证。
和扩容相关的参数主要有:capacity、size、threshold 和 load_factor。
| 参数 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| capacity | table 的容量大小,默认为 16。需要注意的是 capacity 必须保证为 2 的 n 次方。 |
| size | table 的实际使用量。 |
| threshold | size 的临界值,size 必须小于 threshold,如果大于等于,就必须进行扩容操作。 |
| loadFactor | 装载因子,table 能够使用的比例,threshold = capacity * loadFactor。 |
static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; transient Entry[] table; transient int size; int threshold; final float loadFactor; transient int modCount;
从下面的添加元素代码中可以看出,当需要扩容时,令 capacity 为原来的两倍。
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { Entry<K,V> e = table[bucketIndex]; table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e); if (size++ >= threshold) resize(2 * table.length); }
扩容使用 resize() 实现,需要注意的是,扩容操作同样需要把 oldTable 的所有键值对重新插入 newTable 中,因此这一步是很费时的。
void resize(int newCapacity) { Entry[] oldTable = table; int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; return; } Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; transfer(newTable); table = newTable; threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor); } void transfer(Entry[] newTable) { Entry[] src = table; int newCapacity = newTable.length; for (int j = 0; j < src.length; j++) { Entry<K,V> e = src[j]; if (e != null) { src[j] = null; do { Entry<K,V> next = e.next; int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); e.next = newTable[i]; newTable[i] = e; e = next; } while (e != null); } } }
6. 扩容-重新计算桶下标
在进行扩容时,需要把键值对重新放到对应的桶上。HashMap 使用了一个特殊的机制,可以降低重新计算桶下标的操作。
假设原数组长度 capacity 为 16,扩容之后 new capacity 为 32:
capacity : 00010000
new capacity : 00100000
对于一个 Key,
- 它的哈希值如果在第 6 位上为 0,那么取模得到的结果和之前一样;
- 如果为 1,那么得到的结果为原来的结果 +16。
7. 计算数组容量
HashMap 构造函数允许用户传入的容量不是 2 的 n 次方,因为它可以自动地将传入的容量转换为 2 的 n 次方。
先考虑如何求一个数的掩码,对于 10010000,它的掩码为 11111111,可以使用以下方法得到:
mask |= mask >> 1 11011000 mask |= mask >> 2 11111110 mask |= mask >> 4 11111111
mask+1 是大于原始数字的最小的 2 的 n 次方。
num 10010000
mask+1 100000000
以下是 HashMap 中计算数组容量的代码:
static final int tableSizeFor(int cap) { int n = cap - 1; n |= n >>> 1; n |= n >>> 2; n |= n >>> 4; n |= n >>> 8; n |= n >>> 16; return (n < 0) ? 1 : (n >= MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) ? MAXIMUM_CAPACITY : n + 1; }
8. 链表转红黑树
从 JDK 1.8 开始,一个桶存储的链表长度大于 8 时会将链表转换为红黑树。
9. 与 HashTable 的比较
- HashTable 使用 synchronized 来进行同步。
- HashMap 可以插入键为 null 的 Entry。
- HashMap 的迭代器是 fail-fast 迭代器。
- HashMap 不能保证随着时间的推移 Map 中的元素次序是不变的。
从0开始学架构
数据库大神、前阿里资深技术专家丁奇帮你梳理学习 MySQL 的主线知识,就开发过程中经常遇到的具体问题和你分析讨论,并帮你理解问题的本质。你将收获 MySQL 核心技术详解与原理说明和36 个 MySQL 常见痛点问题解析。
原价99元,扫我海报购买,到手只要 46 元。

深入拆解Java虚拟机
作为 Java 程序员,如果你不去深入理解 Java 虚拟机,基本就与进阶加薪无缘了。这个专栏覆盖 JVM 的所有知识点,Oracle Labs高级研究员带你全方位拆解 JVM,系统学习Java性能分析、调优,掌握进阶必备技能。
原价68元,扫我海报购买,到手只要 37 元。

数据结构与算法之美
订阅量Top1,超过4W人学习的算法课堂,专栏最大的特色有三:生动的手绘图片,清晰的案例演示,真实的大厂项目,前Google工程师王争带你趣味学习算法,一门真正为工程师打造的算法私教课。
原价99元,扫我海报购买,到手只要 46 元。

微服务架构实战160讲
《微服务架构实践160讲》视频课程,杨波老师通过原理讲解和实战操作的方式,帮你深入理解主流微服务技术栈组建和架构,踏上从程序员到架构师的进阶之路。
原价299元,扫我海报购买,到手只要 99 元。

从0开始学架构
每个程序员都有成为架构师的梦想,李运华是一位资深技术专家,14年的技术老兵,有超过10年的架构经验和独门的架构设计方法论,经受了2.8万学员锤炼,用户留言超过20万字,照着做,你也能成为架构师。
原价99元,扫我海报购买,到手只要 46 元。
