DRF view
View
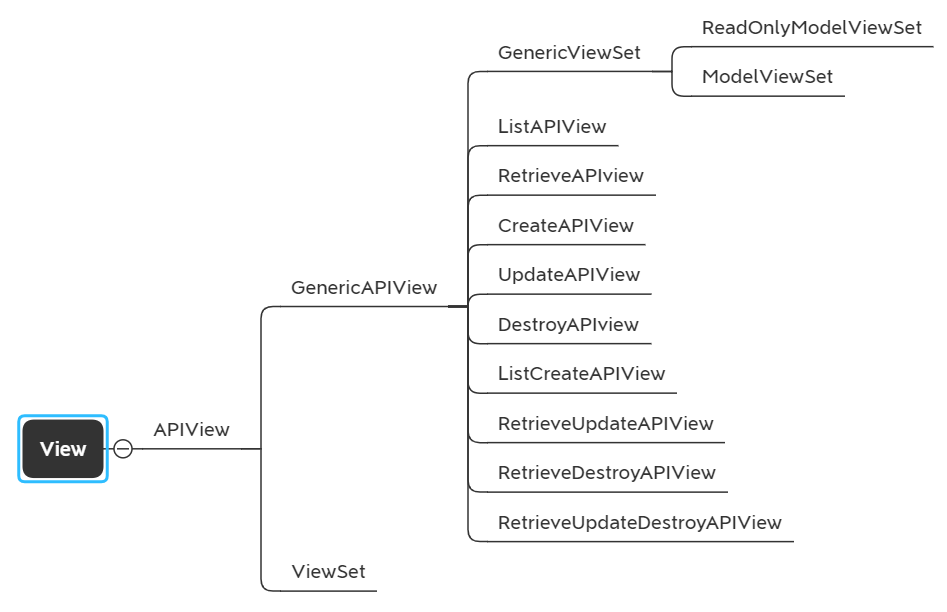
DRF中的view分成三个等级,最基本的APIView, 到GenericAPIView,再到GenericViewSet.
Django用“视图”这个概念封装处理用户请求并返回响应的逻辑。视图是一个可调用对象,它不仅可以是基于函数,也可以是基于类的。函数是通过判断request.method来区分不同的请求,而基于类的视图则对它进行了封装,只需要实现对应的方法即可,如get,post. 不管django还是restframework中的视图类都是基于这一点进行的封装。
APIView
APIView是drf中所有view的父类,本身继承于Django的View. 。最直接封装的是对request,response都进行了封装,response里面做了一些认证,权限,限流之类处理。而response返回的结果是经过系列化的json.
与django中的view类似的是,APIView中只需要实现对应的方法如 get, post等。
class ArticleView(APIView):
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# 取数据
pass
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# 增加数据
pass
def put(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# 全局更新
pass
def patch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# 局部更新
pass
def delete(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# 删除
pass
GenricAPIView
这里都是通用的APIView,所谓通用就是常用的增删改查,也就是restframework已经帮你封装好了。比如django的GenericView封装了ListView, DetailView,CreateView, UpdateView, DeleteView等通用视图类。drf中则封装得更多。
下面 分别看一下源码:
CreateAPIView
实现了post方法
class CreateAPIView(mixins.CreateModelMixin,
GenericAPIView):
"""
Concrete view for creating a model instance.
"""
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.create(request, *args, **kwargs)
ListAPIView
实现get方法
class ListAPIView(mixins.ListModelMixin,
GenericAPIView):
"""
Concrete view for listing a queryset.
"""
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.list(request, *args, **kwargs)
RetrieveAPIView
实现get方法,它与ListAPIView的不同是它获取单个对象,类似于django中的DetailView
class RetrieveAPIView(mixins.RetrieveModelMixin,
GenericAPIView):
"""
Concrete view for retrieving a model instance.
"""
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.retrieve(request, *args, **kwargs)
DestroyAPIView
实现delete方法
class DestroyAPIView(mixins.DestroyModelMixin,
GenericAPIView):
"""
Concrete view for deleting a model instance.
"""
def delete(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.destroy(request, *args, **kwargs)
UpdateAPIView
实现了put,patch两个方法,分别对应全局和局部更新。
class UpdateAPIView(mixins.UpdateModelMixin,
GenericAPIView):
"""
Concrete view for updating a model instance.
"""
def put(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.update(request, *args, **kwargs)
def patch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.partial_update(request, *args, **kwargs)
下面则是一些组合的视图类
ListCreateAPIView
既实现了get方法,又实现了post方法,即可以获取所有对象,也可以添加对象。
class ListCreateAPIView(mixins.ListModelMixin,
mixins.CreateModelMixin,
GenericAPIView):
"""
Concrete view for listing a queryset or creating a model instance.
"""
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.list(request, *args, **kwargs)
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.create(request, *args, **kwargs)
RetrieveUpdateAPIView
实现了get, put, patch三个方法,这里的get是获取单个对象,put,patch则对应的更新
class RetrieveUpdateAPIView(mixins.RetrieveModelMixin,
mixins.UpdateModelMixin,
GenericAPIView):
"""
Concrete view for retrieving, updating a model instance.
"""
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.retrieve(request, *args, **kwargs)
def put(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.update(request, *args, **kwargs)
def patch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.partial_update(request, *args, **kwargs
RetrieveDestroyAPIView
实现了get,delete方法,能获取,删除单个对象。
class RetrieveDestroyAPIView(mixins.RetrieveModelMixin,
mixins.DestroyModelMixin,
GenericAPIView):
"""
Concrete view for retrieving or deleting a model instance.
"""
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.retrieve(request, *args, **kwargs)
def delete(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.destroy(request, *args, **kwargs)
RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView
这个是实现方法最多的视图类,get(获取单个对象),put,patch更新单个对象,delete则是删除单个对象,也就是这个类实现了对单个对象的查改删三种操作
class RetrieveUpdateDestroyAPIView(mixins.RetrieveModelMixin,
mixins.UpdateModelMixin,
mixins.DestroyModelMixin,
GenericAPIView):
"""
Concrete view for retrieving, updating or deleting a model instance.
"""
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.retrieve(request, *args, **kwargs)
def put(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.update(request, *args, **kwargs)
def patch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.partial_update(request, *args, **kwargs)
def delete(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return self.destroy(request, *args, **kwargs)
从上面这些通用视图类的继承关系我们可以看到,它们都是通过继承GenericAPIView,再加上其它的Mixin来实现的。事实上GenericAPIView中并没有实现增删改查中的任何一种操作,这些操作都是通过Mixin来完成的。
Mixins
知道了这些,当我们需要对通用视图类的行为作定制时,只需要对这些Mixin实现的方法进行重写即可。这一点后面再说,我们先看看restframework实现了哪些Mixin,是不是和上面的视图类能对应上呢?
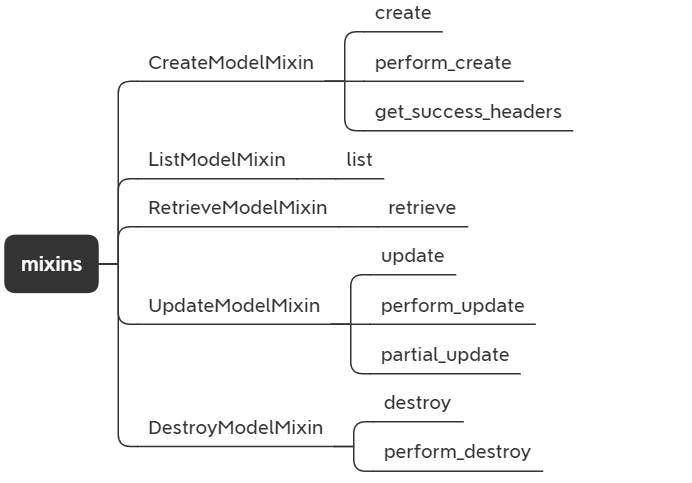
CreateModelMixin
CreateModelMixin中实现了三个方法,其中与增加对应的是前两个,create,perform_create.也就是说当我们继承CreateAPIView时,实际上是通过这两个方法来完成增加操作的。
class CreateModelMixin:
"""
Create a model instance.
"""
def create(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
serializer = self.get_serializer(data=request.data)
serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True)
self.perform_create(serializer)
headers = self.get_success_headers(serializer.data)
return Response(serializer.data, status=status.HTTP_201_CREATED, headers=headers)
def perform_create(self, serializer):
serializer.save()
def get_success_headers(self, data):
try:
return {'Location': str(data[api_settings.URL_FIELD_NAME])}
except (TypeError, KeyError):
return {}
ListModelMixin
只实现了一个list方法,即ListAPIView通过它来返回对象列表。
class ListModelMixin:
"""
List a queryset.
"""
def list(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
queryset = self.filter_queryset(self.get_queryset())
page = self.paginate_queryset(queryset)
if page is not None:
serializer = self.get_serializer(page, many=True)
return self.get_paginated_response(serializer.data)
serializer = self.get_serializer(queryset, many=True)
return Response(serializer.data)
RetrieveModelMixin
实现了retrieve方法,获取单个对象。
class RetrieveModelMixin:
"""
Retrieve a model instance.
"""
def retrieve(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
instance = self.get_object()
serializer = self.get_serializer(instance)
return Response(serializer.data)
UpdateModelMixin
实现了update,perform_update,partial_update方法,update,partial_update分别对应的全局与局部更新,在这里如果我们需要对保存的数据作一定的定制可以重写perform_update方法。
class UpdateModelMixin:
"""
Update a model instance.
"""
def update(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
partial = kwargs.pop('partial', False)
instance = self.get_object()
serializer = self.get_serializer(instance, data=request.data, partial=partial)
serializer.is_valid(raise_exception=True)
self.perform_update(serializer)
if getattr(instance, '_prefetched_objects_cache', None):
# If 'prefetch_related' has been applied to a queryset, we need to
# forcibly invalidate the prefetch cache on the instance.
instance._prefetched_objects_cache = {}
return Response(serializer.data)
def perform_update(self, serializer):
serializer.save()
def partial_update(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
kwargs['partial'] = True
return self.update(request, *args, **kwargs)
DestroyModelMixin
最后一个Mixin是DestoryModelMixin,实现了destory,perform_destory方法,即删除。
class DestroyModelMixin:
"""
Destroy a model instance.
"""
def destroy(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
instance = self.get_object()
self.perform_destroy(instance)
return Response(status=status.HTTP_204_NO_CONTENT)
def perform_destroy(self, instance):
instance.delete()
ListAPIView应用举例:
很显然,Mixin的个数并没有上面的View那么多,这是因为View可能对Mixin进行组合来达到实现不同功能的目的。那我们在写自己的视图类时是不是也可以随意组合通用视图类呢?如果仔细看一下上面那些通用视图类中实现的方法,就会发现也有些是不能组合到一起的,比如ListAPIView,RetrieveAPIView,它们都实现了get方法,使用时就会出问题。
前面说到“当我们需要对通用视图类的行为作定制时,只需要对这些Mixin实现的方法进行重写即可”指的就是这些Mixin中的方法,比如在使用ListAPIView时我们要获取 额外的信息,就可以重写list方法:
这里拿最近写的一个订单视图类举例,我重写list方法,将订单信息进行了数据结构的重组,返回一个嵌套的字典
class Order(ListAPIView):
authentication_classes = [UserAuthentication, ]
serializer_class = ser_order.OrderModelSerializer
queryset = models.Order.objects.all().order_by('-id')
# filter_backends = [ser_order.OrderFilterBackends, ]
def list(self, *args, **kwargs):
response = super(Order, self).list(*args, **kwargs)
if response.status_code != status.HTTP_200_OK:
return response
order_dict = OrderedDict()
# 将订单的状态码,状态描述文字组成字典
for item in models.Order.status_choices:
order_dict[item[0]] = {'text': item[1], 'child': []}
# 将每个状态对应的订单信息放到child列表中,即根据状态码进行了分类
for row in response.data:
order_dict[row['status']]['child'].append(row)
response.data = order_dict
return response
ViewSet
ViewSet其实是对前面内容的更高层的封装,但我们可以看到在ViewSet类中并没有实现任何特殊的内容,它只是继承了两个类ViewSetMixin, APIView.
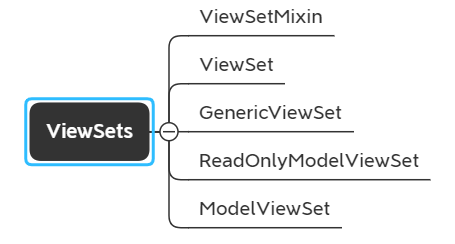
ViewSetMixin
ViewSetMixin是viewset的基础,由于代码太多我们就只看看它的最重要的方法:as_view()它将请求方法与对应的Mixin中的方法关联起来,比如‘get' -->'list', 'post'-->'create', 'put'-->'update'
class ViewSetMixin:
"""
This is the magic.
Overrides `.as_view()` so that it takes an `actions` keyword that performs
the binding of HTTP methods to actions on the Resource.
For example, to create a concrete view binding the 'GET' and 'POST' methods
to the 'list' and 'create' actions...
view = MyViewSet.as_view({'get': 'list', 'post': 'create'})
"""
@classonlymethod
def as_view(cls, actions=None, **initkwargs):
"""
Because of the way class based views create a closure around the
instantiated view, we need to totally reimplement `.as_view`,
and slightly modify the view function that is created and returned.
"""
# The name and description initkwargs may be explicitly overridden for
# certain route configurations. eg, names of extra actions.
cls.name = None
cls.description = None
# The suffix initkwarg is reserved for displaying the viewset type.
# This initkwarg should have no effect if the name is provided.
# eg. 'List' or 'Instance'.
cls.suffix = None
# The detail initkwarg is reserved for introspecting the viewset type.
cls.detail = None
# Setting a basename allows a view to reverse its action urls. This
# value is provided by the router through the initkwargs.
cls.basename = None
# actions must not be empty
if not actions:
raise TypeError("The `actions` argument must be provided when "
"calling `.as_view()` on a ViewSet. For example "
"`.as_view({'get': 'list'})`")
# sanitize keyword arguments
for key in initkwargs:
if key in cls.http_method_names:
raise TypeError("You tried to pass in the %s method name as a "
"keyword argument to %s(). Don't do that."
% (key, cls.__name__))
if not hasattr(cls, key):
raise TypeError("%s() received an invalid keyword %r" % (
cls.__name__, key))
# name and suffix are mutually exclusive
if 'name' in initkwargs and 'suffix' in initkwargs:
raise TypeError("%s() received both `name` and `suffix`, which are "
"mutually exclusive arguments." % (cls.__name__))
def view(request, *args, **kwargs):
self = cls(**initkwargs)
# We also store the mapping of request methods to actions,
# so that we can later set the action attribute.
# eg. `self.action = 'list'` on an incoming GET request.
self.action_map = actions
# Bind methods to actions
# This is the bit that's different to a standard view
for method, action in actions.items():
handler = getattr(self, action)
setattr(self, method, handler)
if hasattr(self, 'get') and not hasattr(self, 'head'):
self.head = self.get
self.request = request
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
# And continue as usual
return self.dispatch(request, *args, **kwargs)
# take name and docstring from class
update_wrapper(view, cls, updated=())
# and possible attributes set by decorators
# like csrf_exempt from dispatch
update_wrapper(view, cls.dispatch, assigned=())
# We need to set these on the view function, so that breadcrumb
# generation can pick out these bits of information from a
# resolved URL.
view.cls = cls
view.initkwargs = initkwargs
view.actions = actions
return csrf_exempt(view)
def initialize_request(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Set the `.action` attribute on the view, depending on the request method.
"""
request = super().initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
method = request.method.lower()
if method == 'options':
# This is a special case as we always provide handling for the
# options method in the base `View` class.
# Unlike the other explicitly defined actions, 'metadata' is implicit.
self.action = 'metadata'
else:
self.action = self.action_map.get(method)
return request
def reverse_action(self, url_name, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Reverse the action for the given `url_name`.
"""
url_name = '%s-%s' % (self.basename, url_name)
kwargs.setdefault('request', self.request)
return reverse(url_name, *args, **kwargs)
@classmethod
def get_extra_actions(cls):
"""
Get the methods that are marked as an extra ViewSet `@action`.
"""
return [method for _, method in getmembers(cls, _is_extra_action)]
def get_extra_action_url_map(self):
"""
Build a map of {names: urls} for the extra actions.
This method will noop if `detail` was not provided as a view initkwarg.
"""
action_urls = OrderedDict()
# exit early if `detail` has not been provided
if self.detail is None:
return action_urls
# filter for the relevant extra actions
actions = [
action for action in self.get_extra_actions()
if action.detail == self.detail
]
for action in actions:
try:
url_name = '%s-%s' % (self.basename, action.url_name)
url = reverse(url_name, self.args, self.kwargs, request=self.request)
view = self.__class__(**action.kwargs)
action_urls[view.get_view_name()] = url
except NoReverseMatch:
pass # URL requires additional arguments, ignore
return action_url
ViewSet
class ViewSet(ViewSetMixin, views.APIView):
"""
The base ViewSet class does not provide any actions by default.
"""
pass
GenericViewSet
GenericViewSet不提供任何方法,但由于它继承了GenericAPIView,所以也具体了如get_object,get_queryset,get_serializer等方法。另外它还继承 了ViewSetMixin,所以也具体了对应的方法如view方法等。
class GenericViewSet(ViewSetMixin, generics.GenericAPIView):
"""
The GenericViewSet class does not provide any actions by default,
but does include the base set of generic view behavior, such as
the `get_object` and `get_queryset` methods.
"""
pass
ReadOnlyModelViewSet
ReadOnlyModelViewSet 主要达到read only的作用,即它不提供增删改的功能,而只获取对象,因为它只实现了list, retrieve功能。
class ReadOnlyModelViewSet(mixins.RetrieveModelMixin,
mixins.ListModelMixin,
GenericViewSet):
"""
A viewset that provides default `list()` and `retrieve()` actions.
"""
pass
ModelViewSet
ModelViewSet继承GenericViewSet,及一个Mixin. 但GenericViewSet又继承了ViewSetMixin,GenericAPIView,这样看ModelViewSet继承了所有的Mixin和通用视图类的父类。
class GenericViewSet(ViewSetMixin, generics.GenericAPIView):
"""
The GenericViewSet class does not provide any actions by default,
but does include the base set of generic view behavior, such as
the `get_object` and `get_queryset` methods.
"""
pass
class ModelViewSet(mixins.CreateModelMixin,
mixins.RetrieveModelMixin,
mixins.UpdateModelMixin,
mixins.DestroyModelMixin,
mixins.ListModelMixin,
GenericViewSet):
"""
A viewset that provides default `create()`, `retrieve()`, `update()`,
`partial_update()`, `destroy()` and `list()` actions.
"""
pass
那么ViewSet到底高级在哪呢?
ViewSet应用举例:
class UserListViewSet(GenericViewSet, ListModelMixin):
"""
API endpoint that allows users to be viewed or edited.
"""
queryset = User.objects.all().order_by('-date_joined')
serializer_class = UserSerializer
如果我们使用上面的视图类:那么在as_view中我们就该指定get 与list的关系:
UserListViewSet.as_view({'get': 'list'})
但通常有更简单的用法:先看代码:
from rest_framework import viewsets
from rest_framework import serializers
class UserSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.User
fields = ('url', 'username', 'email', 'groups')
class GroupSerializer(serializers.HyperlinkedModelSerializer):
class Meta:
model = models.Group
fields = ('url', 'name')
class UserViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
"""
API endpoint that allows users to be viewed or edited.
"""
queryset = User.objects.all().order_by('-date_joined')
serializer_class = UserSerializer
class GroupViewSet(viewsets.ModelViewSet):
"""
API endpoint that allows groups to be viewed or edited.
"""
queryset = Group.objects.all()
serializer_class = GroupSerializer
views.py
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from rest_framework import routers
from auth import views
router = routers.DefaultRouter()
router.register(r'users', views.UserViewSet)
router.register(r'groups', views.GroupViewSet)
# Wire up our API using automatic URL routing.
# Additionally, we include login URLs for the browsable API.
urlpatterns = [
url(r'^', include(router.urls)),
]
VIewSet常常配合router使用,router可以自动将常用的 get绑定list,post绑定create这些操作完成,而不需要你在as_view中指定对应的关系了,连这个都省去了。