EC2 Instance Pricing Options
On-Demand
Pay by the hour or the second depending on the type of instnace you run. Great for flexbility. (Run proprotype application)
Spot
Purchase unused capacity at a discount of up to 90%. Prices fluctuate with supply and demand. Great for applications with flexible start and end times. (Run some algorithms for research purpose)
Reserved
Reserved capacity for one or three years. Up to 72% dicount on the hourly charge. Great if you have known, fixed requirements. (Run long-run applications)
Dedicated
A physical EC2 server dedicated for your use. Great if you have server-bound licenses to reuse or compilance requirements. (Run bank/secruty applciations)
Elastic Block Store - SDD Volumes
General Purpose SSD: gp2
Suitable for boot disks and general applications. Up to 16,000 IOPS per volume. Up to 99.9% durability.
Provisioned IOPS SSD: io1
Suitable for OLTP and latency-sensitive applications. 50 IOPS/GiB. Up to 64,000 IOPS per volume. High performacne and most expensive. Up to 99.9& durability.
Provisioned IOPS SSD: io2
Suitable for OLTP and latency sensitive applications. 500 IOPS/GiB. Up to 64,000 IOPS per volume. 99.999% durability. Latest generation Provisioned IOPS volume.
io1 and io2 are the same price. But io2 is more performance than io1.
Elastic Block Store - HDD Volumes
Throughput Optimized HDD: st1
Suitable for Big Data, data warehouses, ETL. Max throughput is 500 MB/s per volume. Cannot be a boot volume. Up to 99.9% durability.
Cold HDD: sc1
Max throughput of 250MB/s per volume. Less-frequently-accessed data. Cannot be a boot colume. Lowest cost. Up to 99.9% durability.
IOPS vs Throughput
| IOPS | Throughput |
|
Measures the number of read and write operations per second important metric for quick transcations, low latency apps, transctional workloads. The ability to action reads and writes very quickly Choose Provisioned IOPS SSD (io1 or io2) |
Measures the number of bits read or written per second (MB/s) Important metric forr large datasets, large I/O sizes, comple queries. (big data) The ability to deal with large datasets Choose Throughput Optiized HDD (st1) |
Create a EBS Volume
Encrypted snapshots
If you can create an EBS volume from an excrypted snapshot, then you will get an encrypted volume.
Unencrypted snapshots
If the snapshot is unencrypted then any volume you create from it is also going to be unencrypted.
Elastic Load Balancer
3 options to choose from:
Application Load Balancer
HTTP and HTTPS. Intelligent load balancing. Routes requests to a specific web server based on the type of request.
Normally you also need to create a Secruty Group (For HTTP:80), becasue default SG doesn't support HTTP inbound / outbound.
Network Load Balancer
TCP and high performance
Classic Load Balancer (LEGACY)
HTTP/HTTPS and TCP.
X-Forwarded-For Header
Identify the originating IP address a client connecting throught a load balancer. Reason is because through a ELB, the IP address to server is the same as Load balancer. But we really want to know the real IP address of user instead of Load balancer. Therefore we can use `X_Forwarded-For`.

504 Error
Gateway timeout. The application is not responding within the timeout period. Troubleshoot the web application or database server.
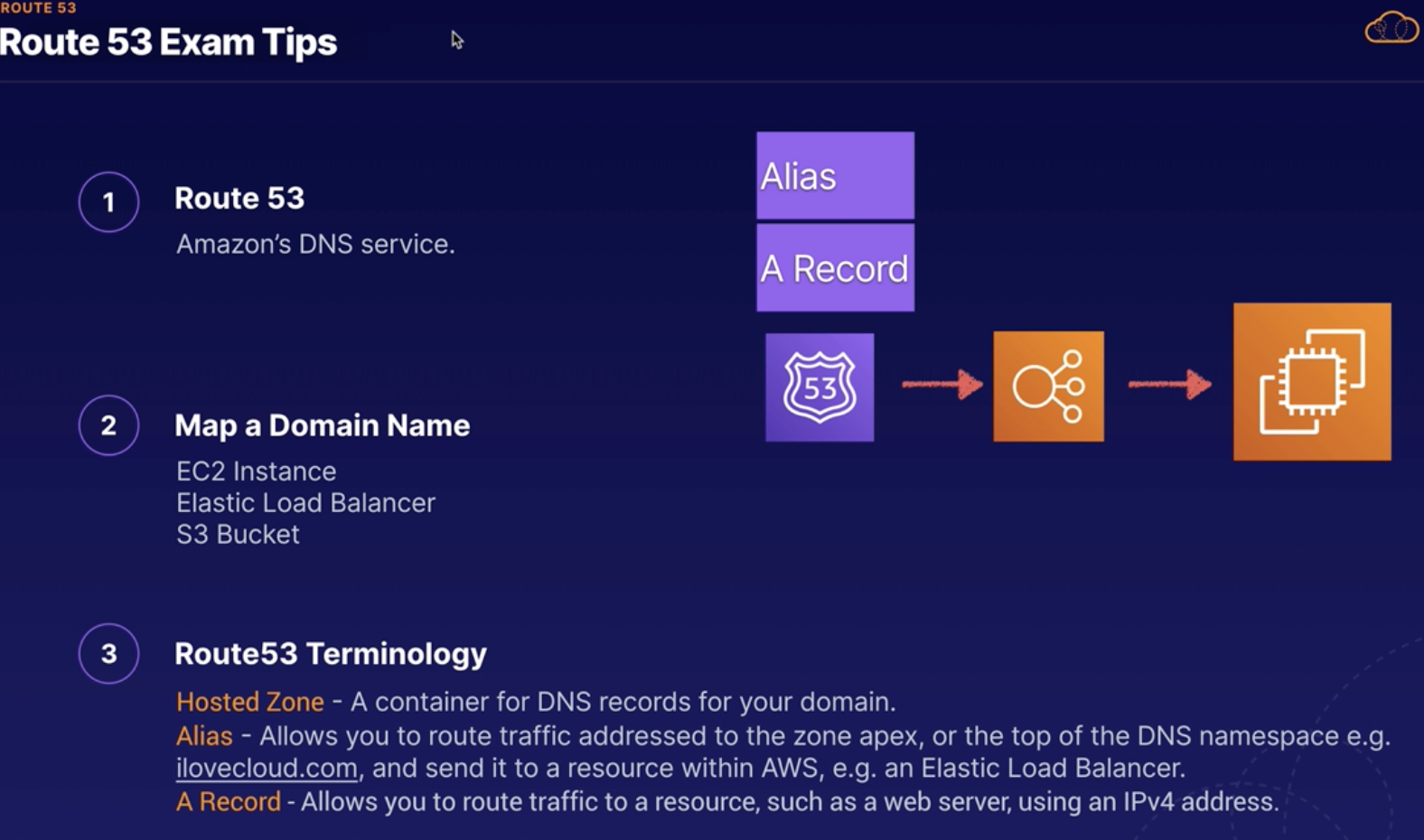
Route53
RDS
- SQLServer, PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, Aurora;
- RDS is for OLTP Workloads: Greate for processing lots of samll transactions like customer orders, banking transcations, payments, and booking system.
- Not Suitable for OLAP.
OLTP vs OLAP
OLTP: Online Transcation Processing
Processes data from transactions in real-time, customer orders, banking transcations, payments, and booking systems.
OLTP is all about data processing, and completing large numbers of small transcations in realtime.
OLAP: Online Analytics Processing
Processes complex queries to analyze historical data, eg analyzing net profit figures from the past 3 years, and sales forecasting.
OLAP is all about data analysis using large amounts of data, and complex queries that take a long time to complete.
Exmples:
- Net Profit analysis: cars sales in 3 different regions.
- Large amounts of Data
- Analysis NOT transcations
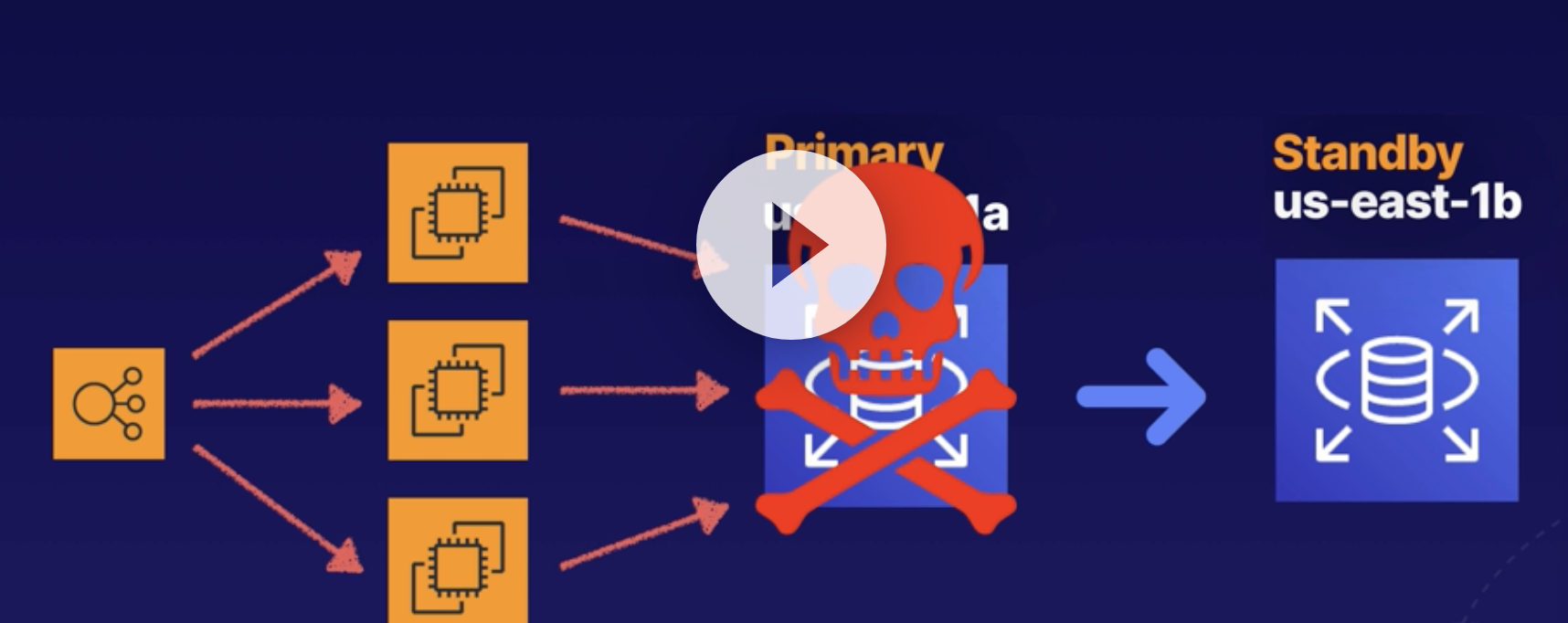
What is Multi-AZ
It is an exact copy of yourproduction database in another Availability Zone.
Normally the 'Standby' is NOT public accessiable.
But If Primary RDS failed, then AWS will automaticlly redirect to Standby instances
Mutli-ZA is for disaster recovery, not for improving performacne, so you cannot connect to the Standby when the Primayr DB is active.
So What is used for improve performance?
Read Replica
A Read Replica is a READ-ONLY copy of your primary database.
Greate for read-heavy workloads and takes the load off from your primary database.
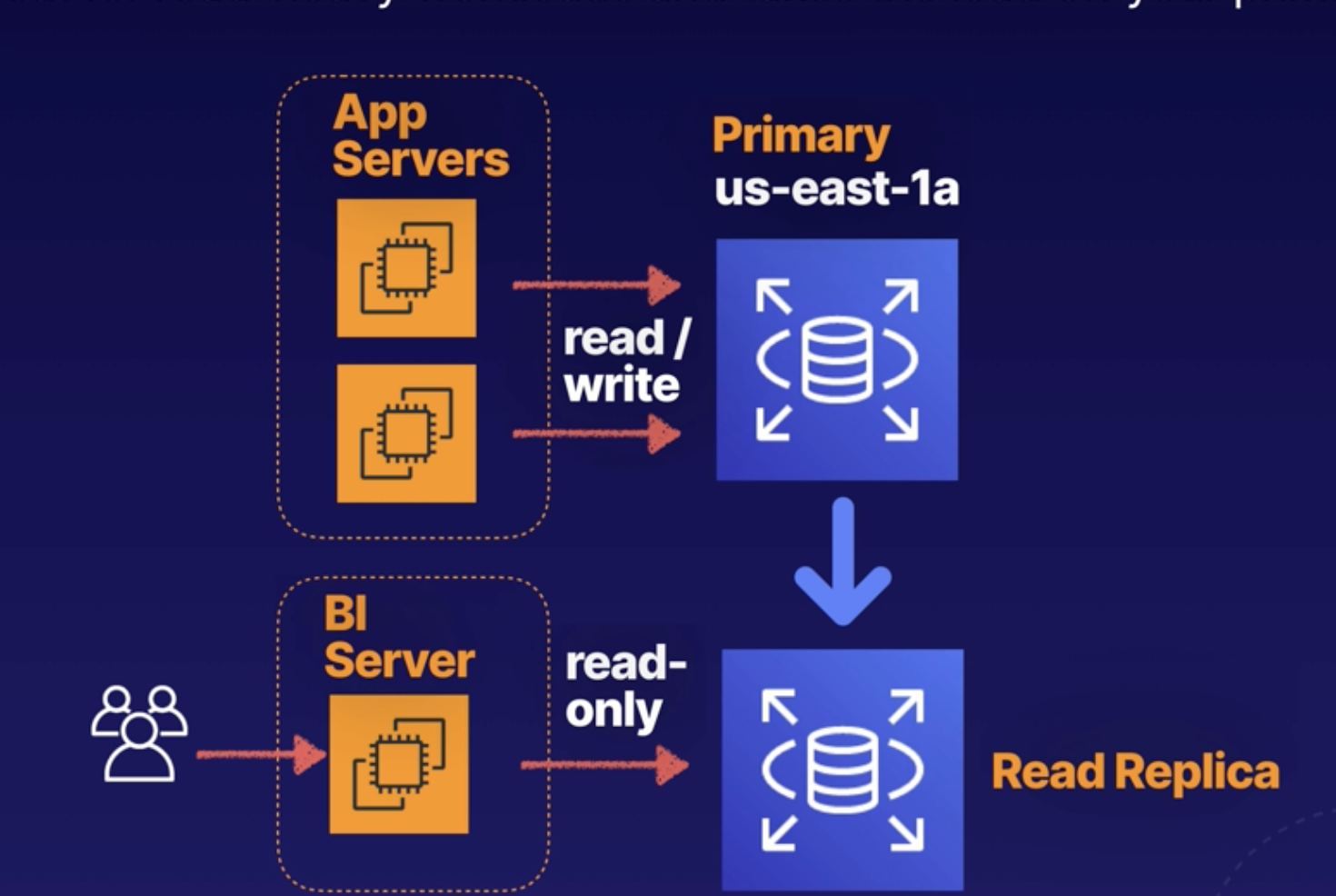
A Read Replica can locate in the same AZ or a different AZ or even cross region.
- Scaling Read Performance: Primarily used for scaling, not for DR
- Requires Automatic Backup: Automatic backups mut be enabled in order to deploy a read replica.
- Multple Read Replicas are supported (MYSQL, ORACLE.... ), up to 5 replicas.
RDS backup and Snapshots
The restored version of the database will always be a new RDS instance with a new DNS endpoint.
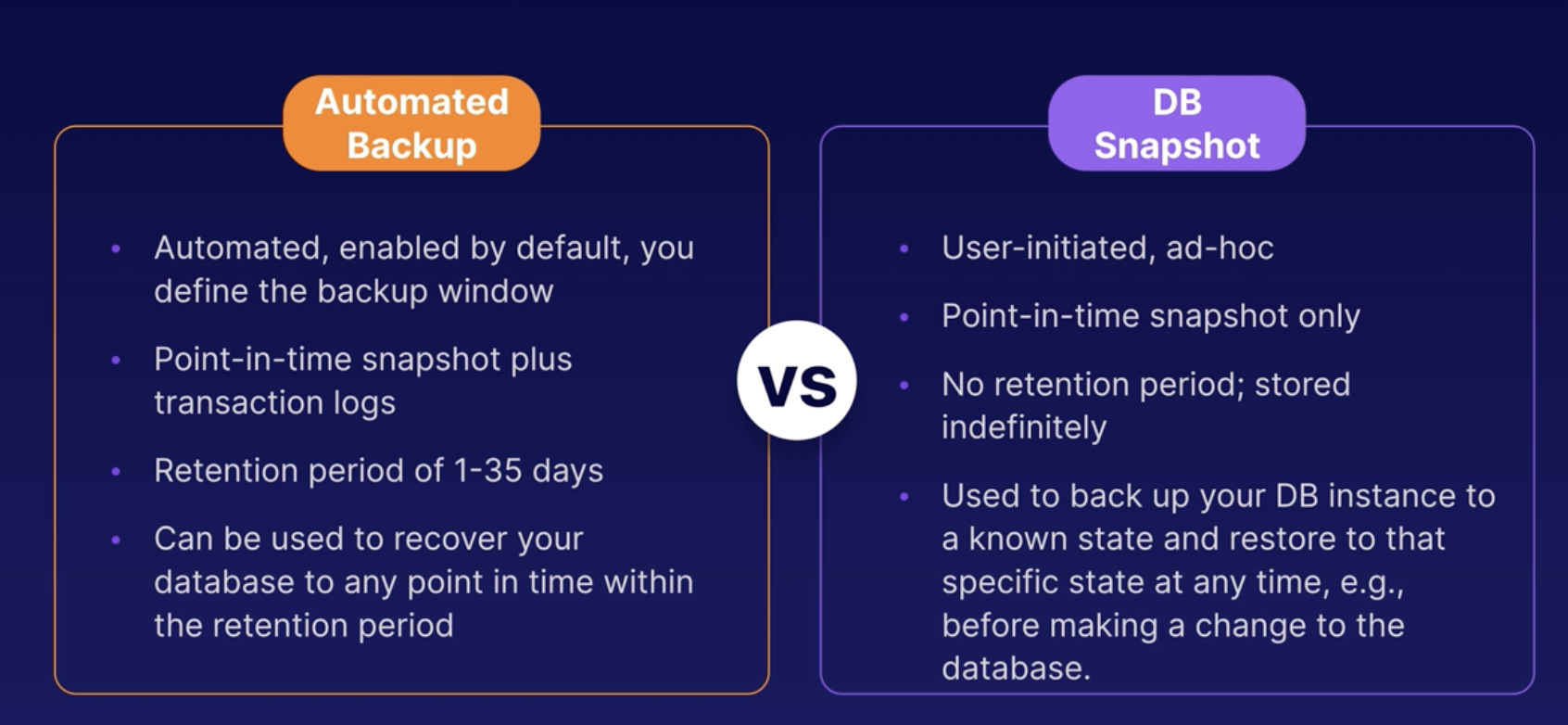
Two ways to backup RDS
Database snapshot
Overview
Manual, ad-hoc, and user-initiated. It provides a snapshot of the storage volume attached to the DB instance.
Automated backup
Overview
- Enabled by default.
- It creates daily backups or snapshots that run during a backup window that you define.
- Transaction logs are used to replay trasaction.
- Stored in S3
- You get free storage space equal to the size of your database
Point-In-Time Recovery
Recover your database to any point in time within a "retention period" of 1-35 days.
Full Daily Backup
RDS takes a full daily backup, or snapshot, and also stores transaction logs throught the day.
The Recovery Process
When you do a recovery, AWS will first choose the most recent daily backup and then apply transaction logs relevant to that day, up to recovery point.
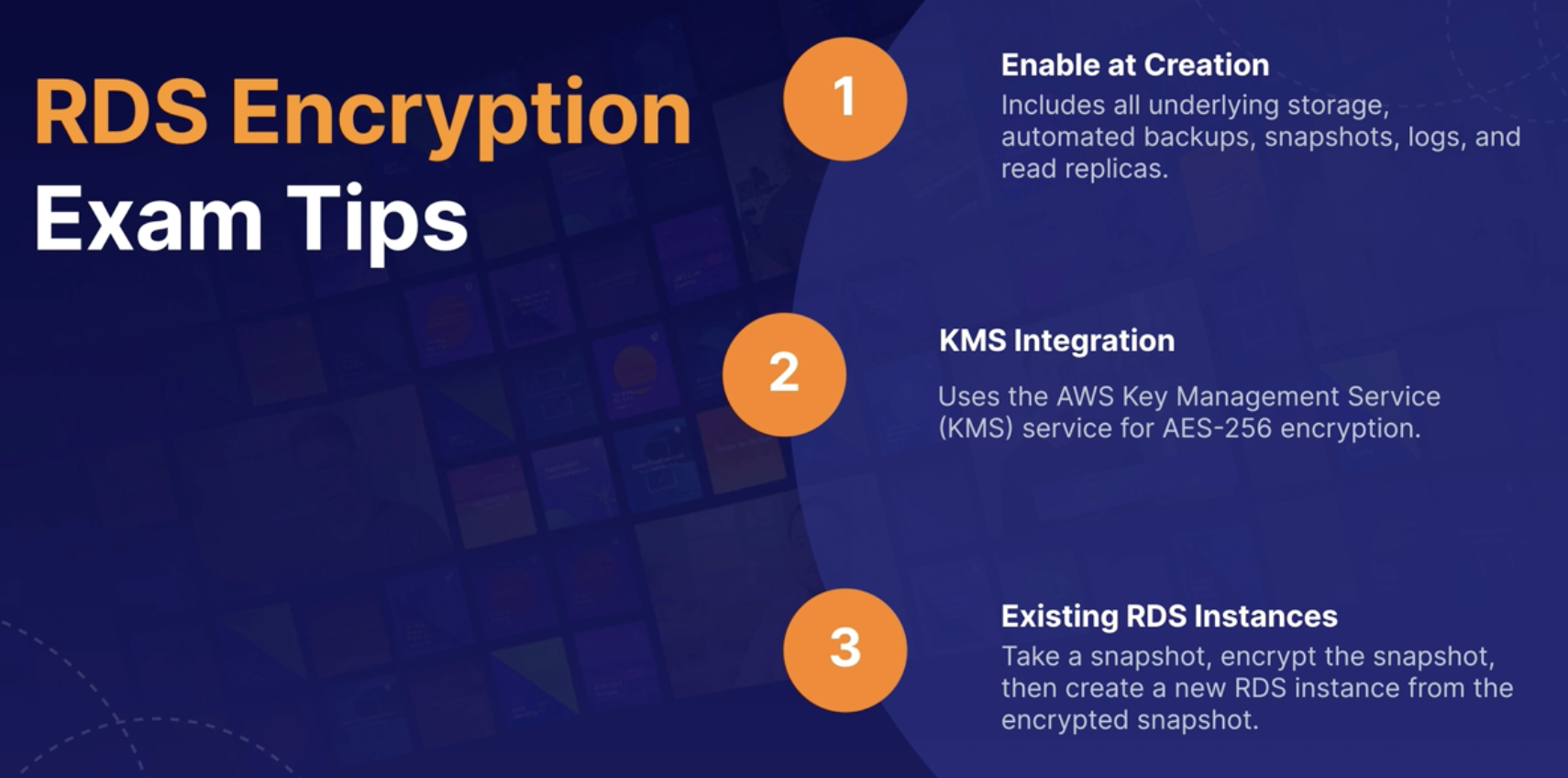
Encrypting
You cannot encryption on an unenrypted RDS DB instance later on. Only encrypte RDS during creation time.
If you already have an Unenrypted DB, you wnat to encrypte it?
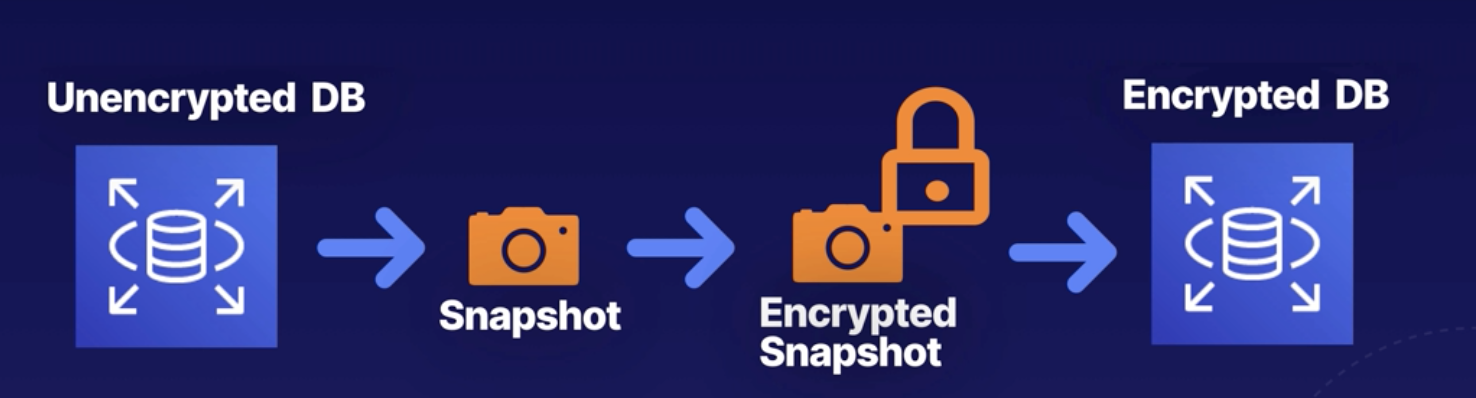
Take snapshot, then encrypted snapshot then do a DB restored.
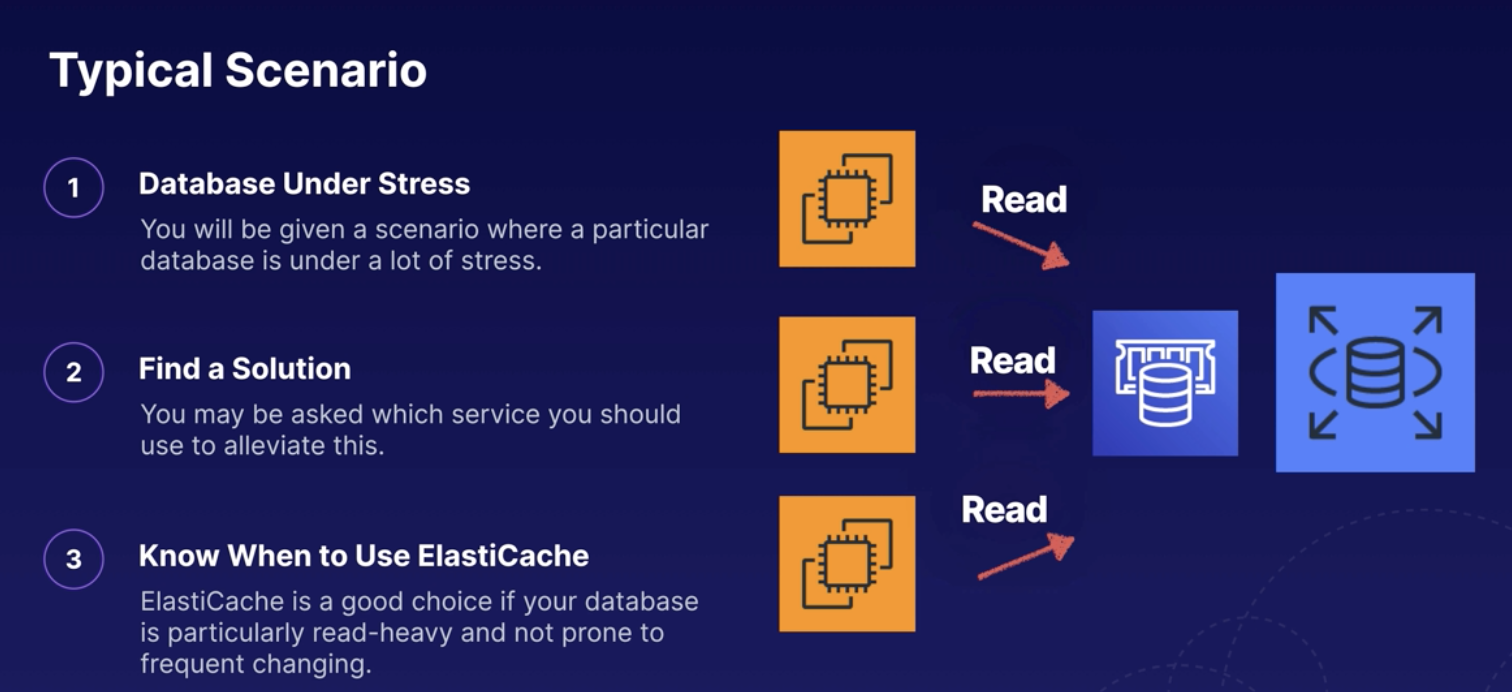
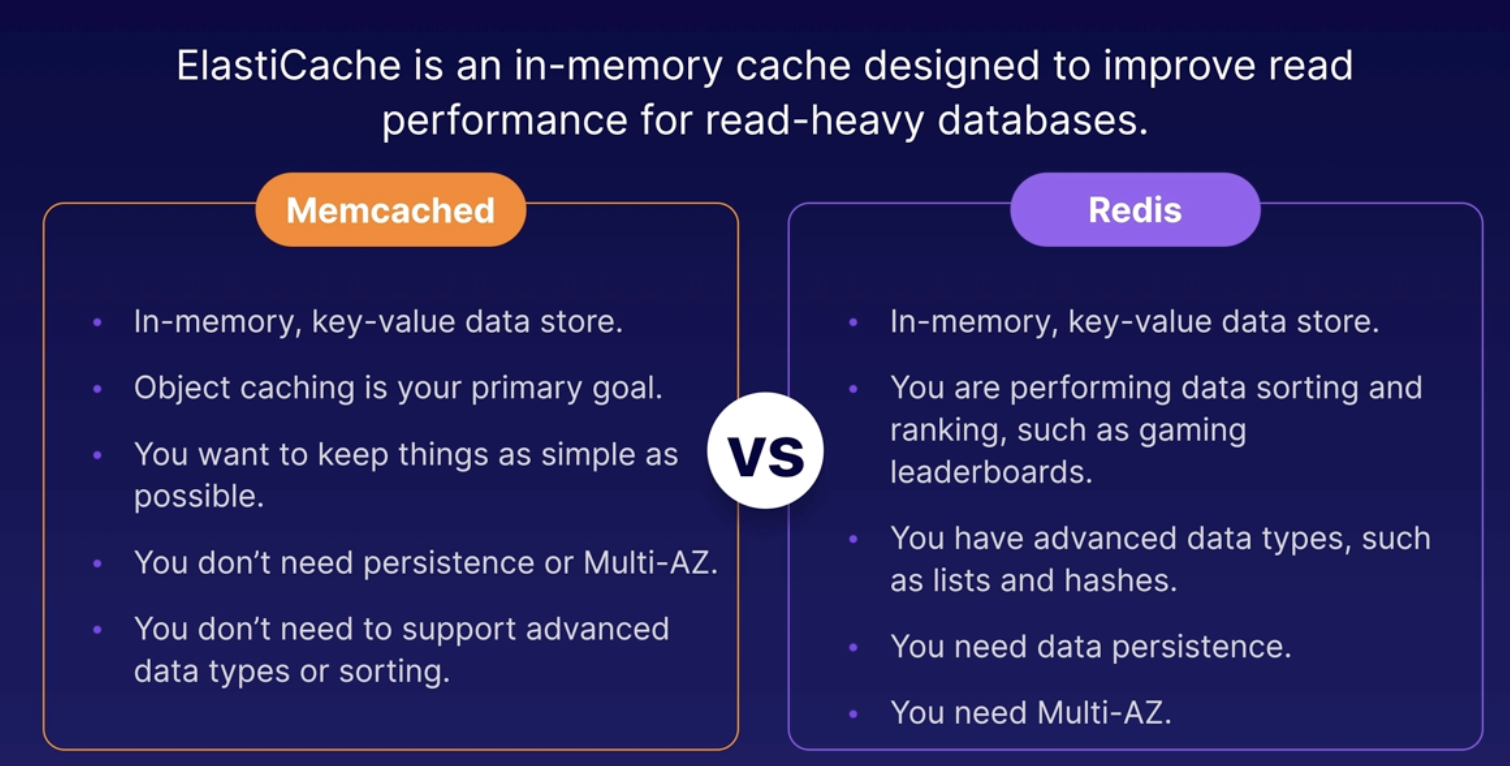
Elasticache
- In-Memory Cache for fast data access
- Key Value pair
- Imporves Database performance
- Greate for Read-Heavy Database Workloads
- Storing session data for distributed application

Parameter Store






Ref: Regional and zonal Reserved Instances (scope)
When you purchase a Reserved Instance, you determine the scope of the Reserved Instance. The scope is either regional or zonal.
Regional: When you purchase a Reserved Instance for a Region, it's referred to as a regional Reserved Instance.
Zonal: When you purchase a Reserved Instance for a specific Availability Zone, it's referred to as a zonal Reserved Instance.
The main thing is "..busniess crictial application...", so you want "Capacity reservation"
Regional Reserved Instances Zonal Reserved Instances Ability to reserve capacity A regional Reserved Instance does not reserve capacity. A zonal Reserved Instance reserves capacity in the specified Availability Zone.
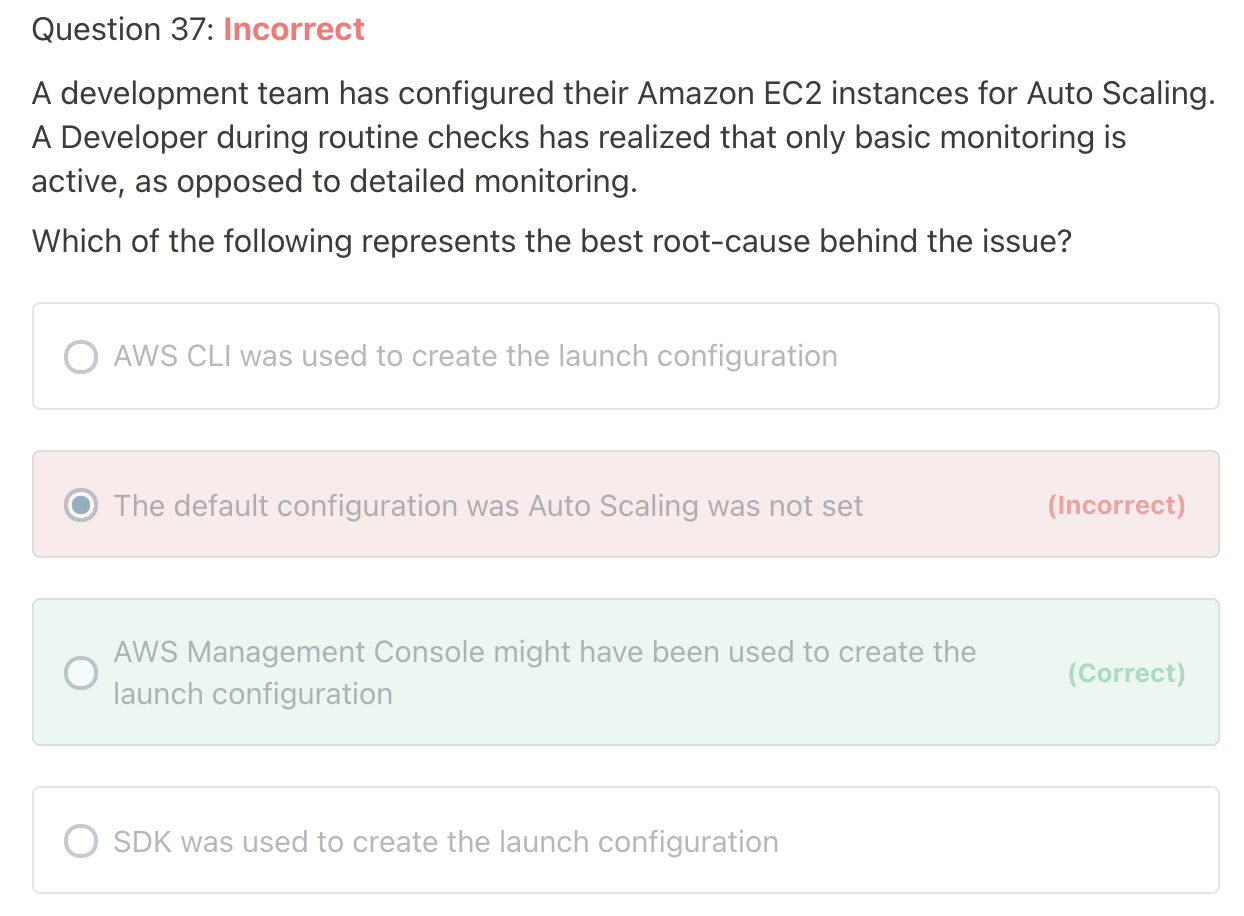
Ref: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/autoscaling/ec2/userguide/enable-as-instance-metrics.html
By default, basic monitoring is enabled when you use the AWS Management Console to create a launch template or launch configuration.
By default, basic monitoring is enabled when you create a launch template using the AWS CLI and SDK.

A Spot Instance is an unused EC2 instance that is available for less than the On-Demand price. Your Spot Instance runs whenever capacity is available and the maximum price per hour for your request exceeds the Spot price. Any instance present with unused capacity will be allocated.
You can specify that Amazon EC2 should do one of the following when it interrupts a Spot Instance:
Stop the Spot Instance
Hibernate the Spot Instance
Terminate the Spot Instance
The default is to terminate Spot Instances when they are interrupted.

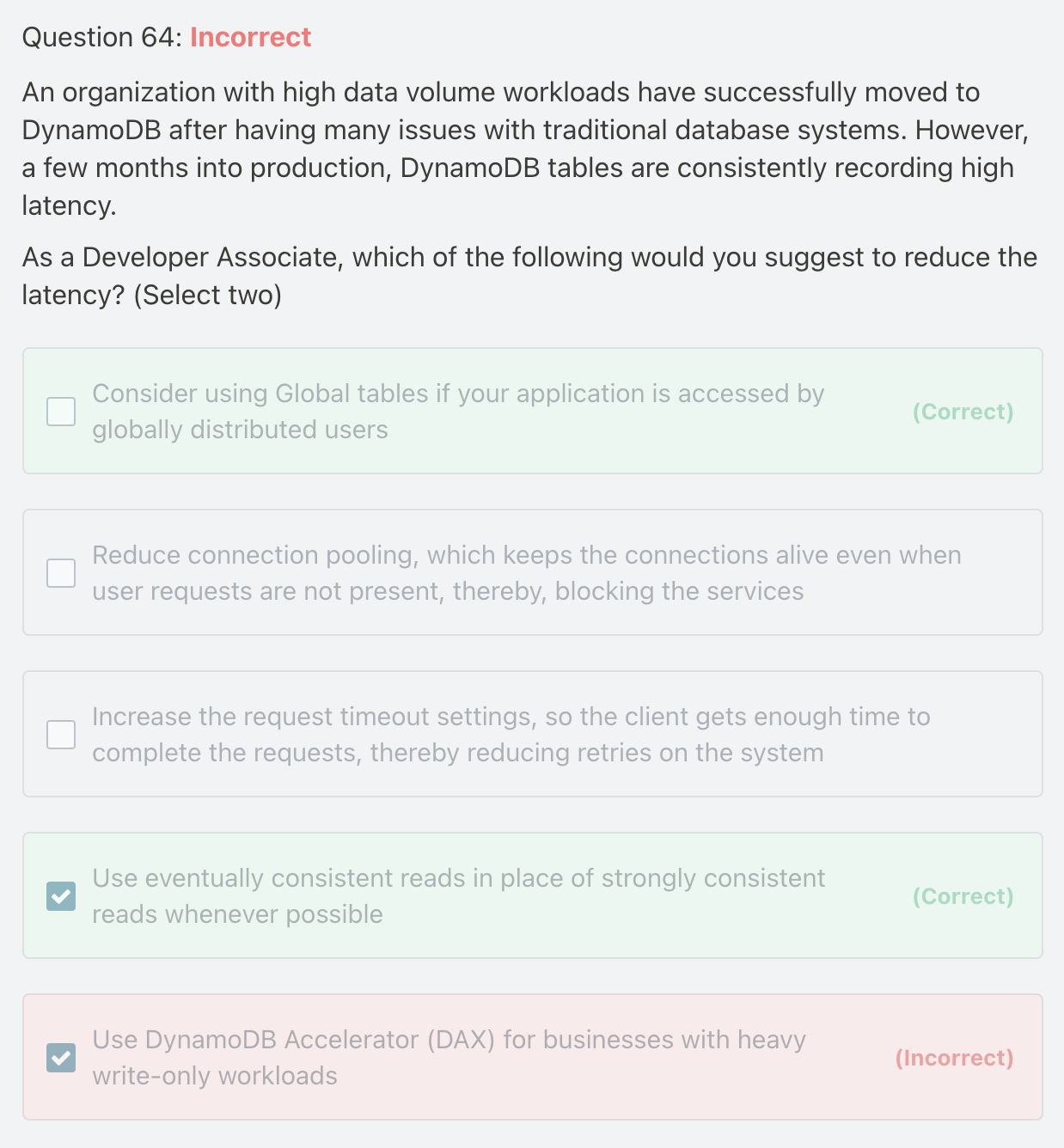
DAX for read-only
If you have globally dispersed users, consider using global tables. With global tables, you can specify the AWS Regions where you want the table to be available. This can significantly reduce latency for your users. So, reducing the distance between the client and the DynamoDB endpoint is an important performance fix to be considered.