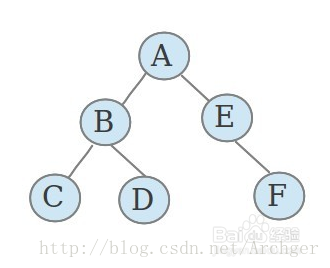
二叉树的遍历分为三类:前序遍历、中序遍历和后序遍历。
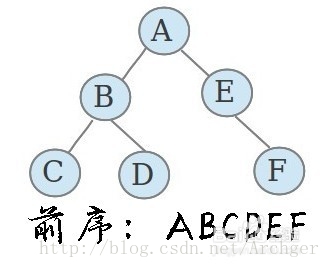
(1)前序遍历
先访问根节点,再遍历左子树,最后遍历右子树;并且在遍历左右子树时,仍需先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树。
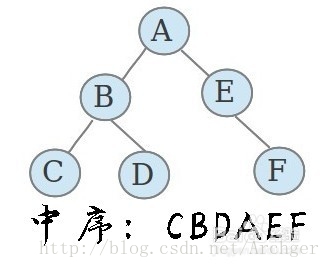
(2)中序遍历
先遍历左子树、然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树;并且在遍历左右子树的时候。仍然是先遍历左子树,然后访问根节点,最后遍历右子树。
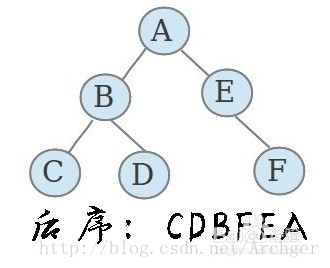
(3)后序遍历
先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根节点;同样,在遍历左右子树的时候同样要先遍历左子树,然后遍历右子树,最后访问根节点。
(4)层序遍历
用BFS每一层的向下遍历。
代码实现
二叉树的构建、查找、删除
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int val;
node *lch, *rch;
};
//插入数值
node *insert(node *p, int x)
{
if (p == NULL)
{
node *q = new node;
q->val = x;
q->lch = q->rch = NULL;
return q;
}
else
{
if (x < p->val) p->lch = insert(p->lch, x);
else p->rch = insert(p->rch, x);
return p;
}
}
//查找数值
bool find(node *p, int x)
{
if (p == NULL) return false;
else if (x == p->val) return true;
else if (x < p->val) return find(p->lch, x);
else return find(p->rch, x);
}
//删除数值
node *remove(node *p, int x)
{
if (p == NULL) return NULL;
else if (x < p->val) p->lch = remove(p->lch, x);
else if (x > p->val) p->rch = remove(p->rch, x);
else if (p->lch == NULL)
{
node *q = p->rch;
delete p;
return q;
}
else if (p->lch->rch == NULL)
{
node *q = p->lch;
q->rch = p->rch;
delete p;
return q;
}
else
{
node *q;
for (q = p->rch; q->rch->rch != NULL; q = q->rch);
node *r = q->rch;
q->rch = r->lch;
r->lch = p->lch;
r->rch = p->rch;
delete p;
return r;
}
return p; //没有找到p点
}
int main()
{
node *head = NULL;
int n;
cout << "1: insert 2: find 3: remove
";
while (cin >> n)
{
int x;
if (n == 1)
{
cin >> x;
head = insert(head, x);
}
else if (n == 2)
{
cin >> x;
if (find(head, x))
{
cout << "Find it!
";
}
else
{
cout << "Not find!
";
}
}
else
{
cin >> x;
head = remove(head, x);
}
}
}非递归遍历
先序遍历
void PreOrder2(node *p)
{
stack<node*> stack;
while (p || stack.size())
{
if (p)
{
stack.push(p);
cout << p->val<<" ";
p = p->lch;
}
else
{
p = stack.top();
stack.pop();
p = p->rch;
}
}
}中序遍历
void InOrder2(node *p)
{
stack<node*> stack;
while (p || stack.size())
{
if (p)
{
stack.push(p);
p = p->lch;
}
else
{
p = stack.top();
stack.pop();
cout << p->val << " ";
p = p->rch;
}
}
}后序遍历
void PostOrder2(node *p)
{
stack<node*> stack;
while (p || stack.size())
{
while (p)
{
p->left = 1;
p = p->lch;
stack.push(p);
}
while ((stack.top()->left) && (stack.top()->right) && stack.size())
{
p = stack.top();
stack.pop();
cout << p->val << " ";
}
if (stack.size())
{
p->right = 1;
p = p->rch;
}
}
}递归遍历
void view(node *p)
{
if (p)
{
cout << p->val << " ";
}
}先序遍历
void PreOrder(node *p)
{
if (p)
{
view(p);
PreOrder(p->lch);
PreOrder(p->rch);
}
}中序遍历
void InOrder(node *p)
{
if (p)
{
InOrder(p->lch);
view(p);
InOrder(p->rch);
}
}后序遍历
void PostOrder(node *p)
{
if (p)
{
PostOrder(p->lch);
PostOrder(p->rch);
view(p);
}
}层序遍历
void LevelOrder(node *p)
{
queue<node*> queue;
queue.push(p);
while (queue.size())
{
p = queue.front();
queue.pop();
cout << p->val << " ";
if (p->lch) queue.push(p->lch);
if (p->rch) queue.push(p->rch);
}
}整体代码测试
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int val;
node *lch, *rch;
bool left, right;
};
//插入数值
node *insert(node *p, int x)
{
if (p == NULL)
{
node *q = new node;
q->val = x;
q->lch = q->rch = NULL;
return q;
}
else
{
if (x < p->val) p->lch = insert(p->lch, x);
else p->rch = insert(p->rch, x);
return p;
}
}
//查找数值
bool find(node *p, int x)
{
if (p == NULL) return false;
else if (x == p->val) return true;
else if (x < p->val) return find(p->lch, x);
else return find(p->rch, x);
}
//删除数值
node *remove(node *p, int x)
{
if (p == NULL) return NULL;
else if (x < p->val) p->lch = remove(p->lch, x);
else if (x > p->val) p->rch = remove(p->rch, x);
else if (p->lch == NULL)
{
node *q = p->rch;
delete p;
return q;
}
else if (p->lch->rch == NULL)
{
node *q = p->lch;
q->rch = p->rch;
delete p;
return q;
}
else
{
node *q;
for (q = p->rch; q->rch->rch != NULL; q = q->rch);
node *r = q->rch;
q->rch = r->lch;
r->lch = p->lch;
r->rch = p->rch;
delete p;
return r;
}
return p; //没有找到p点
}
void view(node *p)
{
if (p)
{
cout << p->val << " ";
}
}
void PreOrder(node *p)
{
if (p)
{
view(p);
PreOrder(p->lch);
PreOrder(p->rch);
}
}
void InOrder(node *p)
{
if (p)
{
InOrder(p->lch);
view(p);
InOrder(p->rch);
}
}
void PostOrder(node *p)
{
if (p)
{
PostOrder(p->lch);
PostOrder(p->rch);
view(p);
}
}
void PreOrder2(node *p)
{
stack<node*> stack;
while (p || stack.size())
{
if (p)
{
stack.push(p);
cout << p->val<<" ";
p = p->lch;
}
else
{
p = stack.top();
stack.pop();
p = p->rch;
}
}
}
void InOrder2(node *p)
{
stack<node*> stack;
while (p || stack.size())
{
if (p)
{
stack.push(p);
p = p->lch;
}
else
{
p = stack.top();
stack.pop();
cout << p->val << " ";
p = p->rch;
}
}
}
void PostOrder2(node *p)
{
stack<node*> stack;
while (p || stack.size())
{
while (p)
{
p->left = 1;
p = p->lch;
stack.push(p);
}
while ((stack.top()->left) && (stack.top()->right) && stack.size())
{
p = stack.top();
stack.pop();
cout << p->val << " ";
}
if (stack.size())
{
p->right = 1;
p = p->rch;
}
}
}
void LevelOrder(node *p)
{
queue<node*> queue;
queue.push(p);
while (queue.size())
{
p = queue.front();
queue.pop();
cout << p->val << " ";
if (p->lch) queue.push(p->lch);
if (p->rch) queue.push(p->rch);
}
}
int main()
{
node *head = NULL;
int n;
cout << "1: insert 2: find 3: remove
";
cout << "4: PreOrder 5: InOrder 6: PostOrder
";
cout << "7: PreOrder2 8: InOrder2 9: PostOrder2
";
cout << "10: LevelOrder
";
while (cin >> n)
{
int x;
if (n == 1)
{
cin >> x;
head = insert(head, x);
}
else if (n == 2)
{
cin >> x;
if (find(head, x))
{
cout << "Find it!
";
}
else
{
cout << "Not find!
";
}
}
else if (n == 3)
{
cin >> x;
head = remove(head, x);
}
else if (n == 4)
{
PreOrder(head);
cout << endl;
}
else if (n == 5)
{
InOrder(head);
cout << endl;
}
else if (n == 6)
{
PostOrder(head);
cout << endl;
}
else if (n == 7)
{
PreOrder2(head);
cout << endl;
}
else if (n == 8)
{
InOrder2(head);
cout << endl;
}
else if (n == 9)
{
PostOrder(head);
cout << endl;
}
else if (n == 10)
{
LevelOrder(head);
cout << endl;
}
}
}其他详解
CSDN中关于二叉树遍历的其他详解