关于Mybatis的学习主要参考了狂神的视频
-
一级缓存
(1).使用范围:从sqlSession会话开始到结束
(2).使用:默认打开,无法关闭
(3).测试使用(需要打开日志观察数据库的连接情况):
public static void Maintest(){ SqlSession sqlSession = Connection.getSqlSession(); UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("UId","3180421016"); List<UserBean> userBeans = userMapper.queryByIf(map); map.put("UName","关晨亮"); //userMapper.updateById(map); System.out.println(userMapper.queryByIf(map).get(0).equals(userBeans.get(0))); sqlSession.close(); } //result:true,将结果集打印,可以看出两次结果集打印之间是没有再做数据库连接的(4).缓存失效的4种情况:
-
sqlSession不同
public static void Maintest(){ SqlSession sqlSession1 = Connection.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = Connection.getSqlSession(); UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class); UserMapper userMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class); HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("UId","3180421016"); List<UserBean> userBeans = userMapper1.queryByIf(map); System.out.println(userBeans); sqlSession1.close(); System.out.println(userBeans.get(0).equals(userMapper2.queryByIf(map).get(0))); sqlSession2.close(); } -
sqlSession相同,两次查询操作之间存在增删改操作
public static void Maintest(){ SqlSession sqlSession = Connection.getSqlSession(); UserMapper userMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class); HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("UId","3180421016"); List<UserBean> userBeans = userMapper.queryByIf(map); map.put("UName","关晨亮"); userMapper.updateById(map); System.out.println(userMapper.queryByIf(map).get(0).equals(userBeans.get(0))); sqlSession.close(); } //result:false,将结果集打印,可以看出两次结果集打印之间是有再次做过数据库连接的 -
sqlSession相同,查询条件不同(此时缓存中没有相关数据)
public static void Maintest(){ SqlSession sqlSession1 = Connection.getSqlSession(); UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class); HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("UId","3180421016"); List<UserBean> userBeans = userMapper1.queryByIf(map); System.out.println(userBeans); map.put("UId","2"); userBeans = userMapper1.queryByIf(map); System.out.println(userBeans); sqlSession1.close(); } //打开日志可以看到,发生了两次对于数据库的连接请求 -
通过session.clearCache()主动刷新缓存
public static void Maintest(){ SqlSession sqlSession1 = Connection.getSqlSession(); UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class); HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("UId","3180421016"); List<UserBean> userBeans = userMapper1.queryByIf(map); System.out.println(userBeans); sqlSession1.clearCache(); userBeans = userMapper1.queryByIf(map); System.out.println(userBeans); sqlSession1.close(); }
-
-
二级缓存
(1).简介
- 作用范围:整个namespace,也就是一个mapper
- 实现:不同的mapper查出的数据会放在对应的缓存(map)中
(2).使用:
- 在主配置文件中显式地开启二级缓存
<settings> <!-- <setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/>--> <setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> </settings>- 在Mapper.xml中配置(为什么要开启readOnly会在后面解释)
<cache readOnly="true"/>或
<cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>- 测试
public static void Maintest(){ SqlSession sqlSession1 = Connection.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = Connection.getSqlSession(); UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class); UserMapper userMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class); HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("UId","3180421016"); List<UserBean> userBeans = userMapper1.queryByIf(map); sqlSession1.close(); System.out.println(userBeans.get(0).equals(userMapper2.queryByIf(map).get(0))); sqlSession2.close(); } /result:true(3).注意
- 需要实体序列化
客户端访问了某个能开启会话功能的资源, web服务器就会创建一个与该客户端对应的HttpSession对象,每个HttpSession对象都要站用一定的内存空间。如果在某一时间段内访问站点的用户很多,web服务器内存中就会积累大量的HttpSession对象,消耗大量的服务器内存,即使用户已经离开或者关闭了浏览器,web服务器仍要保留与之对应的HttpSession对象,在他们超时之前,一直占用web服务器内存资源。
web服务器通常将那些暂时不活动但未超时的HttpSession对象转移到文件系统或数据库中保存,服务器要使用他们时再将他们从文件系统或数据库中装载入内存,这种技术称为Session的持久化。
将HttpSession对象保存到文件系统或数据库中,需要采用序列化的方式将HttpSession对象中的每个属性对象保存到文件系统或数据库中;将HttpSession对象从文件系统或数据库中装载如内存时,需要采用反序列化的方式,恢复HttpSession对象中的每个属性对象。所以存储在HttpSession对象中的每个属性对象必须实现Serializable接口
public class UserBean implements Serializable { private String UId; private String UName; private int USet; private int UAuth; private String UPassword; private int UState; }- 必须打开只读,否则两次比较的结果不同
只读的缓存会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。 因此这些对象不能被修改。这就提供了可观的性能提升。而可读写的缓存会(通过序列化)返回缓存对象的拷贝。 速度上会慢一些,但是更安全,因此默认值是 false。
<cache readOnly="true"/>-
缓存优先放在以及会话中,当会话关闭后,缓存才会被转移到二级会话
public static void Maintest(){ SqlSession sqlSession1 = Connection.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = Connection.getSqlSession(); UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class); UserMapper userMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class); HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("UId","3180421016"); List<UserBean> userBeans = userMapper1.queryByIf(map); System.out.println(userBeans); System.out.println(userBeans.get(0).equals(userMapper2.queryByIf(map).get(0))); sqlSession1.close(); sqlSession2.close(); } //false,因为还没有关闭就开始比较了public static void Maintest(){ SqlSession sqlSession1 = Connection.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession2 = Connection.getSqlSession(); UserMapper userMapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(UserMapper.class); UserMapper userMapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(UserMapper.class); HashMap map = new HashMap(); map.put("UId","3180421016"); List<UserBean> userBeans = userMapper1.queryByIf(map); System.out.println(userBeans); sqlSession1.close(); System.out.println(userBeans.get(0).equals(userMapper2.queryByIf(map).get(0))); sqlSession2.close(); } //true,因为是会话关闭之后再比较的 -
对于查询(select),我们可以使用useCache来选择是否取消缓存;对于增删改,可以使用flushCache来选择是否取消更新缓存
-
缓存原理,这边用狂神的图来加深理解
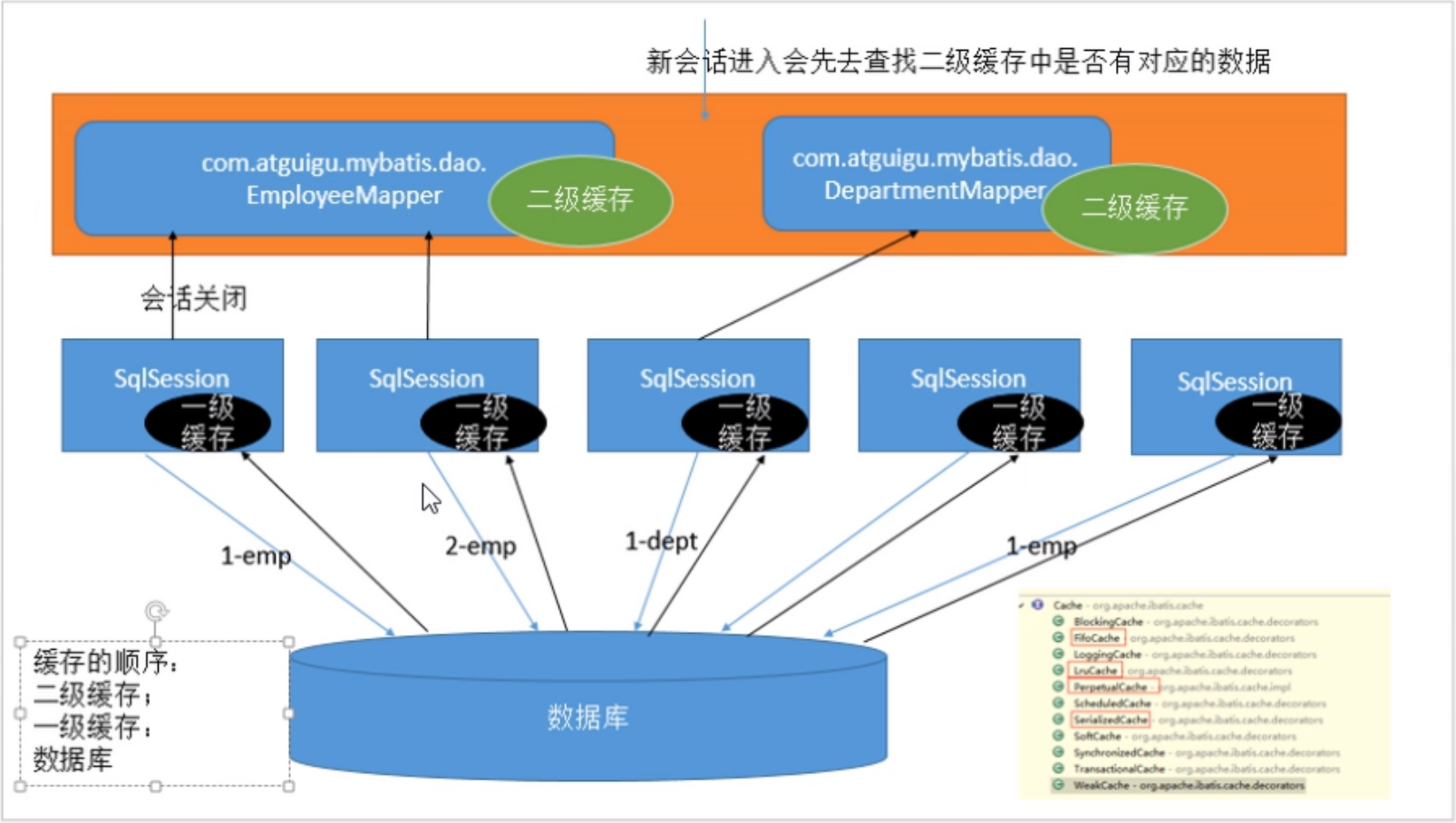
-
使用ehcache外部缓存
(1).导包
(2).写配置文件.xml
(3).在主配置文件中使用:设定cache标签的type属性
注:现在多用redis数据库