题目:
问题描述 :
Have you ever played quoit in a playground? Quoit is a game in which flat rings are pitched at some toys, with all the toys encircled awarded.
In the field of Cyberground, the position of each toy is fixed, and the ring is carefully designed so it can only encircle one toy at a time. On the other hand, to make the game look more attractive, the ring is designed to have the largest radius. Given a configuration of the field, you are supposed to find the radius of such a ring.
In the field of Cyberground, the position of each toy is fixed, and the ring is carefully designed so it can only encircle one toy at a time. On the other hand, to make the game look more attractive, the ring is designed to have the largest radius. Given a configuration of the field, you are supposed to find the radius of such a ring.
Assume that all the toys are points on a plane. A point is encircled by the ring if the distance between the point and the center of the ring is strictly less than the radius of the ring. If two toys are placed at the same point, the radius of the ring is considered to be 0.
输入:
The input consists of several test cases. For each case, the first line contains an integer N (2 <= N <= 100,000), the total number of toys in the field. Then N lines follow, each contains a pair of (x, y) which are the coordinates of a toy. The input is terminated by N = 0.
输出:
For each test case, print in one line the radius of the ring required by the Cyberground manager, accurate up to 2 decimal places.
样例输入:
2 0 0 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 3 -1.5 0 0 0 0 1.5 0
样例输出:
0.71 0.00 0.75
题解:

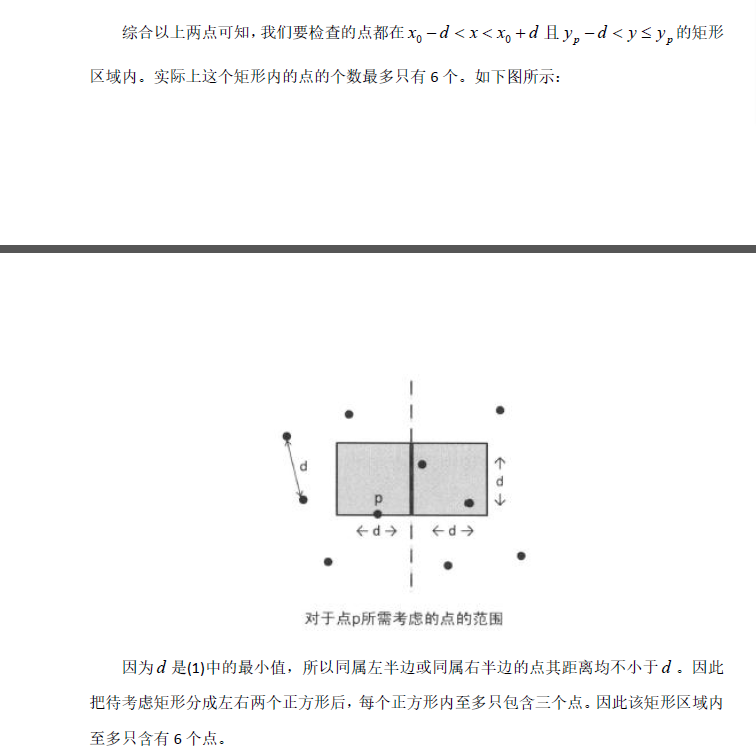
心得:
平面分治经典模板题···核心思想就是按xy坐标排序后分成左右两边分治··复杂度nlogn;
代码:
#include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<cmath> #include<ctime> #include<cctype> #include<cstring> #include<string> #include<algorithm> using namespace std; const int N=1e+5; struct point { double x; double y; }p[N],px[N]; bool compx(point a,point b) { return a.x<b.x; } bool compy(point a,point b) { return a.y<b.y; } inline double dis(point a,point b) { return sqrt((a.x-b.x)*(a.x-b.x)+(a.y-b.y)*(a.y-b.y)); } int n; double work(int l,int r) { double ans; if(l+1==r) return dis(p[l],p[r]); if(l+2==r) return min(dis(p[l],p[l+1]),min(dis(p[l],p[r]),dis(p[l+1],p[r]))); int mid=(l+r)/2; ans=min(work(l,mid),work(mid+1,r)); int cnt=0; for(int i=l;i<=r;i++) { if(p[i].x>=p[mid].x-ans&&p[i].x<=p[mid].x+ans) px[++cnt]=p[i]; } sort(px+1,px+cnt+1,compy); for(int i=1;i<=cnt;i++) for(int j=i+1;j<=cnt;j++) { if(px[j].y-px[i].y>=ans) break; ans=min(ans,dis(px[i],px[j])); } return ans; } int main() { freopen("a.in","r",stdin); while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF) { if(n==0) break; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) scanf("%lf%lf",&p[i].x,&p[i].y); sort(p+1,p+n+1,compx); printf("%.2lf ",work(1,n)/2); } return 0; }