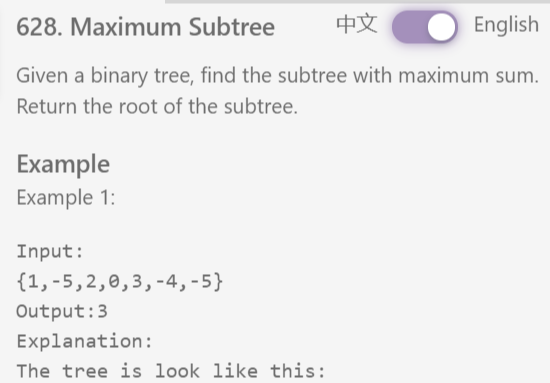
/** * Definition of TreeNode: * class TreeNode { * public: * int val; * TreeNode *left, *right; * TreeNode(int val) { * this->val = val; * this->left = this->right = NULL; * } * } */ class Solution { public: /** * @param root: the root of binary tree * @return: the maximum weight node */ int max_sum; TreeNode* max_node; TreeNode * findSubtree(TreeNode * root) { // write your code here if(root==NULL) return root; if(root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL) return root; max_sum = INT_MIN; max_node = NULL; dfs(root); return max_node; } int dfs(TreeNode* cur){ if(cur==NULL) return 0; int sum = dfs(cur->left)+dfs(cur->right)+cur->val; if(sum > max_sum){ max_sum = sum; max_node = cur; } return sum; } };



计算每个结点的高度并用一个map来存储对应的值,然后将高度从1开始到max_depth 逐层打印出来。
/** * Definition of TreeNode: * class TreeNode { * public: * int val; * TreeNode *left, *right; * TreeNode(int val) { * this->val = val; * this->left = this->right = NULL; * } * } */ class Solution { public: /* * @param root: the root of binary tree * @return: collect and remove all leaves */ int max_depth; unordered_map<int, vector<int>> depth; int dfs(TreeNode* cur){ if(cur == NULL) return 0; int d = max(dfs(cur->left), dfs(cur->right))+1; max_depth = max(max_depth, d); depth[d].push_back(cur->val); return d; } vector<vector<int>> findLeaves(TreeNode * root) { // write your code here vector<vector<int>> ans; max_depth = 0; dfs(root); for(int i=1; i<=max_depth; i++) ans.push_back(depth[i]); return ans; } };
二叉树翻转:

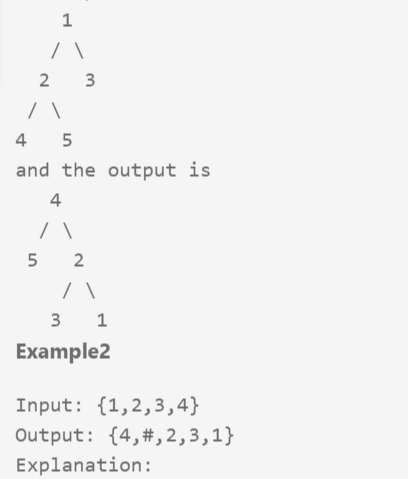
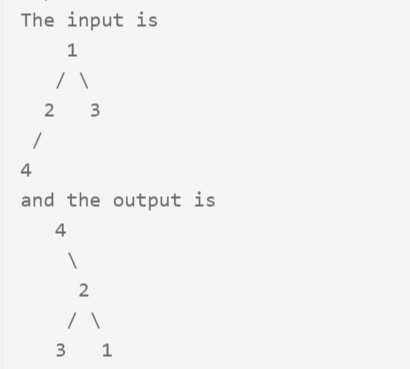

/** * Definition of TreeNode: * class TreeNode { * public: * int val; * TreeNode *left, *right; * TreeNode(int val) { * this->val = val; * this->left = this->right = NULL; * } * } */ class Solution { public: /** * @param root: the root of binary tree * @return: new root */ TreeNode* newRoot; TreeNode * upsideDownBinaryTree(TreeNode * root) { // write your code here if(root == NULL) return root; dfs(root); return newRoot; } void dfs(TreeNode* cur){ if(cur->left != NULL){ dfs(cur->left); cur->left->right = cur; cur->left->left = cur->right; cur->left = NULL; cur->right = NULL; } else newRoot = cur; } };


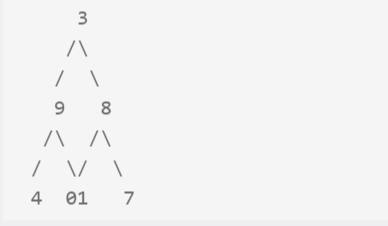


/** * Definition of TreeNode: * class TreeNode { * public: * int val; * TreeNode *left, *right; * TreeNode(int val) { * this->val = val; * this->left = this->right = NULL; * } * } */ class Solution { public: /** * @param root: the root of tree * @return: the vertical order traversal */ int mincol, maxcol; unordered_map<int, vector<int>> mp; void bfs(TreeNode* cur){ queue<TreeNode*> q1; queue<int> q2; //记录列数 q1.push(cur); q2.push(0); while(!q1.empty()){ TreeNode* node = q1.front(); q1.pop(); int col = q2.front(); q2.pop(); mp[col].push_back(node->val); mincol = min(mincol, col); maxcol = max(maxcol, col); if(node->left){ q1.push(node->left); q2.push(col-1); } if(node->right){ q1.push(node->right); q2.push(col+1); } } } vector<vector<int>> verticalOrder(TreeNode * root) { // write your code here vector<vector<int>> ans; if(root == NULL) return ans; mincol = 0, maxcol = 0; bfs(root); for(int i=mincol; i<=maxcol; i++){ ans.push_back(mp[i]); } return ans; } };
/** * Definition of TreeNode: * class TreeNode { * public: * int val; * TreeNode *left, *right; * TreeNode(int val) { * this->val = val; * this->left = this->right = NULL; * } * } */ class Solution { public: /** * @param root: the root of tree * @return: the vertical order traversal */ vector<vector<int>> verticalOrder(TreeNode * root) { // write your code here vector<vector<int>> ans; unordered_map<int, vector<int>> col; queue<int> q1; //列数进队列 queue<TreeNode*> q2; //结点进队列 int col_min = 0, col_max = 0; //记录列数的最小值和最大值 if(root == NULL) return ans; q1.push(0); q2.push(root); //BFS while(!q1.empty()){ int c = q1.front(); TreeNode* node = q2.front(); q1.pop(); q2.pop(); //将对应层数的node值放进map中 col[c].push_back(node->val); col_min = min(col_min, c); col_max = max(col_max, c); if(node->left){ q1.push(c-1); q2.push(node->left); } if(node->right){ q1.push(c+1); q2.push(node->right); } } for(int i=col_min; i<=col_max; i++){ ans.push_back(col[i]); } return ans; } };




/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: /* * @param root: The root of the BST. * @param p: You need find the successor node of p. * @return: Successor of p. */ TreeNode * inorderSuccessor(TreeNode * root, TreeNode * p) { // write your code here if(root==NULL || p==NULL) return NULL; TreeNode* ans = NULL, *cur = root; //case 1,2 //case1 root<p : ans 在右子树中 //case2 root>p : ans 可能为root或root的左子树中 while(cur!=p){ if(p->val < cur->val){ ans = cur; cur = cur->left; } if(p->val > cur->val) cur = cur->right; } //case 3 root==p : if p有右子树, then ans is 右子树中最小的结点 if(p->right != NULL){ cur = p->right; while(cur->left != NULL) cur = cur->left; ans = cur; } return ans; } };

返回一颗二叉树中,值相同的结点的路径。
参考连接:http://zxi.mytechroad.com/blog/tree/leetcode-687-longest-univalue-path/
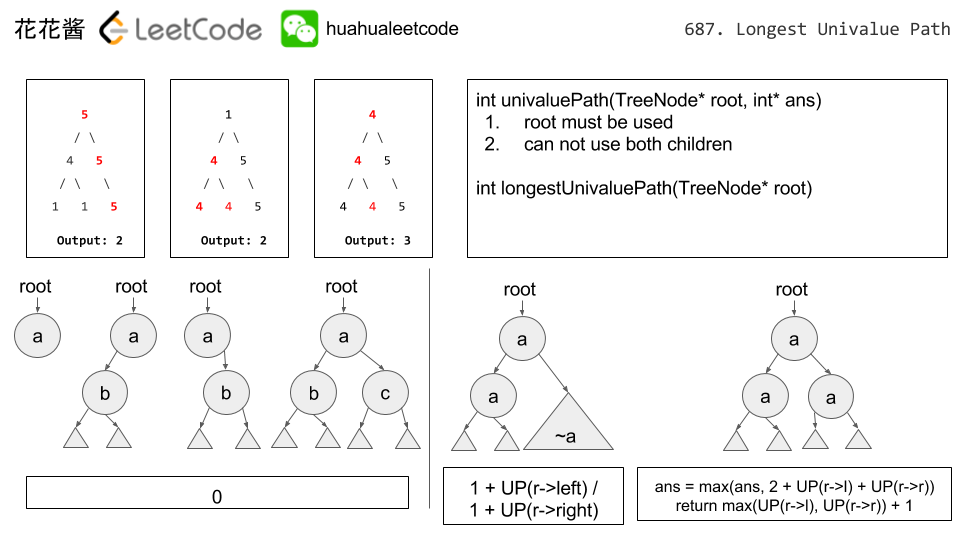
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: int longestUnivaluePath(TreeNode* root) { if(root == NULL) return 0; int ans = 0; univaluePath(root, ans); return ans; } int univaluePath(TreeNode* root, int& ans){ if(root == NULL) return 0; int l = univaluePath(root->left, ans); int r = univaluePath(root->right, ans); int pl = 0; int pr = 0; if(root->left && root->val == root->left->val) pl = l+1; if(root->right && root->val == root->right->val) pr= r+1; ans = max(ans, pl+pr); return max(pl, pr); } };
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { if(root == NULL) return false; if(root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) return root->val == sum; int new_sum = sum - root->val; return hasPathSum(root->left, new_sum) || hasPathSum(root->right, new_sum); } };

/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { vector<vector<int>> ans; vector<int> curr; pathSum(root, sum, curr, ans); return ans; } void pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum, vector<int>& curr, vector<vector<int>>& ans){ if(root == NULL) return; if(root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL){ if(root->val == sum){ //ans.push_back(curr); //ans.back().push_back(root->val); curr.push_back(root->val); ans.push_back(curr); curr.pop_back(); } // root->val != sum return; } curr.push_back(root->val); int new_sum = sum - root->val; pathSum(root->left, new_sum, curr, ans); pathSum(root->right, new_sum, curr, ans); curr.pop_back(); } };
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ class Solution { public: vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { vector<vector<int>> ans; vector<int> cur; path(root, sum, cur, ans); return ans; } void path(TreeNode* root, int sum, vector<int>& cur, vector<vector<int>>& ans){ if(root == NULL) return; sum -= root->val; if(root->left==NULL && root->right==NULL){ if(sum == 0){ cur.push_back(root->val); ans.push_back(cur); cur.pop_back(); } return; } cur.push_back(root->val); path(root->left, sum, cur, ans); path(root->right, sum, cur, ans); cur.pop_back(); } };
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * struct TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode *left; * TreeNode *right; * TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {} * }; */ //不需要是root node & leaf node 结尾 class Solution { public: int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) { if(root == NULL) return 0; //root + left + right return dfs(root, sum) + pathSum(root->left, sum) + pathSum(root->right, sum); } int dfs(TreeNode* root, int sum){ if(root == NULL) return 0; int new_sum = sum - root->val; // sum -= root->val; return (new_sum==0? 1 : 0)+ dfs(root->left, new_sum) + dfs(root->right, new_sum); } };