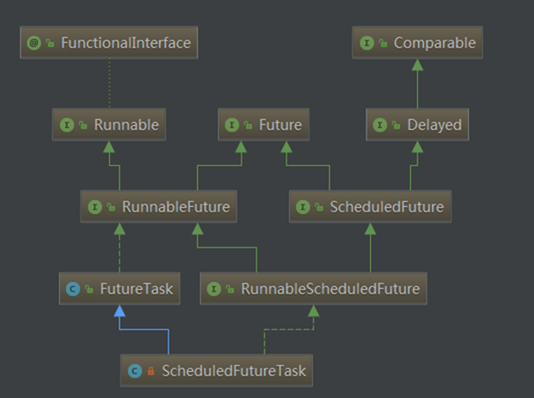
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor概述
ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor下文简称 STPE.
1 public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor 2 extends ThreadPoolExecutor 3 implements ScheduledExecutorService
STPE 可以看到继承线程池类,从名字也可以看出这个STPE是一个执行周期任务的线程池。STPE的几个特点 :
- 继承 ThreadPoolExecutor
- 内部使用DelayedQueue 即是任务达到某个时间要求才返回的任务队列
- 在运行之前,取消一个已提交的任务(task调用Cancel 方法),那么该任务不会执行,默认情况下,这样一个已经取消的任务不会自动从任务队列移除,直到延迟时间到了才移除,为了防止队列中保持已经取消的任务,使用 setRemoveOnCancelPolicy 设置true ,会在取消后立即移除队列。
下面看看几个周期方法 :
- schedule(); : 任务开始前延时A秒执行
- scheduleAtFixedRate(); (例如: 首个任务开始前延时A秒,时间为B秒的任务)
- scheduleWithFixedDelay(); (例如: 首个任务开始前延时A秒,执行任务后延时B秒再进行下一个任务)
内部结构 :
- DelayedWorkerQueue 内部类
- ScheduledFutureTask 内部类
- 几个控制变量
源码分析
重要的方法
先跟着流程走一遍,把工作思路先走一遍
1 public ScheduledFuture<?> schedule(Runnable command, 2 long delay, 3 TimeUnit unit) { 4 if (command == null || unit == null) 5 throw new NullPointerException(); 6 RunnableScheduledFuture<?> t = decorateTask(command, 7 new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command, null, 8 triggerTime(delay, unit))); 9 delayedExecute(t); 10 return t; 11 } 12 13 14 15 16 public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command, 17 long initialDelay, 18 long period, 19 TimeUnit unit) { 20 if (command == null || unit == null) 21 throw new NullPointerException(); 22 if (period <= 0) 23 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 24 //包装成 ScheduledFutureTask 25 ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft = 26 new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command, 27 null, 28 triggerTime(initialDelay, unit), 29 unit.toNanos(period)); 30 //装饰成 RunnableScheduledFuture 31 RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft); 32 sft.outerTask = t; 33 delayedExecute(t); 34 return t; 35 } 36 37 38 39 40 public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleWithFixedDelay(Runnable command, 41 long initialDelay, 42 long delay, 43 TimeUnit unit) { 44 if (command == null || unit == null) 45 throw new NullPointerException(); 46 if (delay <= 0) 47 throw new IllegalArgumentException(); 48 ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft = 49 new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command, 50 null, 51 triggerTime(initialDelay, unit), 52 unit.toNanos(-delay)); 53 RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft); 54 sft.outerTask = t; 55 delayedExecute(t); 56 return t; 57 }
可以看到三个方法最后都会调用 delayedExecute 方法。
1 private void delayedExecute(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) { 2 if (isShutdown()) 3 reject(task); 4 else { 5 //任务队列加入任务 6 super.getQueue().add(task); 7 // 此时任务有可能在执行了,判断是不是 Running 状态, 8 if (isShutdown() && 9 !canRunInCurrentRunState(task.isPeriodic()) && 10 remove(task)) 11 task.cancel(false); 12 else 13 ensurePrestart(); 14 } 15 } 16 17 18 /** 19 * Same as prestartCoreThread except arranges that at least one 20 * thread is started even if corePoolSize is 0. 21 * 22 * 此时任务已入列,即使是 corePoolSize 为 0 ,也要开线程执行 23 * 24 */ 25 void ensurePrestart() { 26 int wc = workerCountOf(ctl.get()); 27 if (wc < corePoolSize) 28 //以core线程数量为上限,增加线程执行 29 addWorker(null, true); 30 else if (wc == 0) 31 //不以core线程数量为上限,增加线程执行 32 addWorker(null, false); 33 }
可以看到,任务加入队列后就进行判断是否线程池shutdown , 最后 addWorker 方法,创建线程就OK了(addWorker 在ThreadPoolExecutor 我们上节已经分析过了,那么此时就等待线程从队列中获取任务就可以了)。
DelayedWorkQueue
下面贴出它的注释,这个队列从名字就可以看出是和 Delay 相关,同时是基于堆操作的,既然是堆,那么应该要知道二叉堆的上浮和下沉操作。
加入元素的操作。
1 static class DelayedWorkQueue extends AbstractQueue<Runnable> 2 implements BlockingQueue<Runnable>
1 public void put(Runnable e) { 2 offer(e); 3 } 4 5 //插入一个元素 6 public boolean offer(Runnable x) { 7 if (x == null) 8 throw new NullPointerException(); 9 RunnableScheduledFuture<?> e = (RunnableScheduledFuture<?>)x; 10 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 11 lock.lock(); 12 try { 13 int i = size; 14 if (i >= queue.length) 15 //扩容 16 grow(); 17 size = i + 1; 18 19 //当前队列中没元素 20 if (i == 0) { 21 queue[0] = e; 22 setIndex(e, 0); 23 } else { 24 //已有元素可,二叉堆上浮操作(上浮意味着都尾部添加再上浮上去) 25 siftUp(i, e); 26 } 27 //无元素队列加入时的情况 ,即是说有元素时是不会唤醒的 28 if (queue[0] == e) { 29 leader = null; 30 //唤醒第一个 31 available.signal(); 32 } 33 } finally { 34 lock.unlock(); 35 } 36 return true; 37 } 38 39 40 /** 41 * Sifts element added at bottom up to its heap-ordered spot. 42 * Call only when holding lock. 43 * 44 * 必须加锁 45 * 46 */ 47 private void siftUp(int k, RunnableScheduledFuture<?> key) { 48 while (k > 0) { 49 int parent = (k - 1) >>> 1; 50 RunnableScheduledFuture<?> e = queue[parent]; 51 if (key.compareTo(e) >= 0) 52 break; 53 // 父类元素大于下面的子类元素 ,交换 54 queue[k] = e; 55 setIndex(e, k); 56 k = parent; 57 } 58 queue[k] = key; 59 setIndex(key, k); 60 }
上面的 offer 方法是加锁操作。
下面是take 方法,为什么要看take 方法呢?这是因为在ThreadPoolExecute 执行任务,线程获取队列中的方法,调用的是队列的take 方法或是 poll 方法。
1 public RunnableScheduledFuture<?> take() throws InterruptedException { 2 //加锁,所以只有一个线程可以进来 3 final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock; 4 lock.lockInterruptibly(); 5 try { 6 for (;;) { 7 RunnableScheduledFuture<?> first = queue[0]; 8 if (first == null) 9 //没有了就阻塞, await方法会释放所有的锁,其他的也会进来的 10 //唤醒之后,继续for循环 11 available.await(); 12 else { 13 //拿到任务,要是到了延迟的时间就返回任务 14 long delay = first.getDelay(NANOSECONDS); 15 if (delay <= 0) 16 return finishPoll(first); 17 18 //拿到任务,但是还没到时间执行任务 19 first = null; // don't retain ref while waiting 20 //下面的代码就是先来的拿到 leader ,然后执行 awaitNanos();其它的就 await 21 if (leader != null) 22 available.await(); 23 else { 24 Thread thisThread = Thread.currentThread(); 25 leader = thisThread; 26 try { 27 available.awaitNanos(delay); 28 } finally { 29 if (leader == thisThread) 30 leader = null; 31 } 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 } finally { 36 //唤醒后面的 37 if (leader == null && queue[0] != null) 38 available.signal(); 39 lock.unlock(); 40 } 41 }
这个地方使用到了ConditionObject 的 await 唤醒的操作在 有元素加入到队列中,调用 signal 方法,释放锁后就会唤醒下一个元素。同时我们可以看到,leader 的作用在这里起到了 “leader---只能有一个获取得到”的作用。
ScheduledFutureTask
1 private class ScheduledFutureTask<V> 2 extends FutureTask<V> implements RunnableScheduledFuture<V>
ScheduledFutureTask 继承Runnable并又线程执行,我们直接看run方法。
1 2 /** 3 * Overrides FutureTask version so as to reset/requeue if periodic. 4 */ 5 public void run() { 6 boolean periodic = isPeriodic(); 7 if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(periodic)) 8 cancel(false); 9 //是不是时间周期任务 10 else if (!periodic) 11 ScheduledFutureTask.super.run(); 12 //周期任务 13 else if (ScheduledFutureTask.super.runAndReset()) { 14 //设置下次执行的时间周期 15 setNextRunTime(); 16 //重新执行这个任务 17 reExecutePeriodic(outerTask); 18 } 19 } 20 21 22 23 /** 24 * Executes the computation without setting its result, and then 25 * resets this future to initial state, failing to do so if the 26 * computation encounters an exception or is cancelled. This is 27 * designed for use with tasks that intrinsically execute more 28 * than once. 29 * 30 * @return {@code true} if successfully run and reset 31 */ 32 //父类的 runAndReset 33 protected boolean runAndReset() { 34 //对变量 runner 进行CAS 操作 , 35 if (state != NEW || 36 !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, 37 null, Thread.currentThread())) 38 return false; 39 boolean ran = false; 40 int s = state; 41 try { 42 Callable<V> c = callable; 43 if (c != null && s == NEW) { 44 try { 45 //上面的call 方法调用的 run 方法 46 c.call(); // don't set result 47 ran = true; 48 } catch (Throwable ex) { 49 setException(ex); 50 } 51 } 52 } finally { 53 // runner must be non-null until state is settled to 54 // prevent concurrent calls to run() 55 runner = null; 56 // state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent 57 // leaked interrupts 58 s = state; 59 if (s >= INTERRUPTING) 60 handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s); 61 } 62 return ran && s == NEW; 63 } 64 65 66 //父类的 run 方法 67 public void run() { 68 if (state != NEW || 69 !UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset, 70 null, Thread.currentThread())) 71 return; 72 try { 73 Callable<V> c = callable; 74 if (c != null && state == NEW) { 75 V result; 76 boolean ran; 77 try { 78 //这是调用了 call 方法 79 result = c.call(); 80 ran = true; 81 } catch (Throwable ex) { 82 result = null; 83 ran = false; 84 setException(ex); 85 } 86 if (ran) 87 set(result); 88 } 89 } finally { 90 // runner must be non-null until state is settled to 91 // prevent concurrent calls to run() 92 runner = null; 93 // state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent 94 // leaked interrupts 95 int s = state; 96 if (s >= INTERRUPTING) 97 handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s); 98 } 99 } 100 101 /** 102 * Sets the next time to run for a periodic task. 103 */ 104 private void setNextRunTime() { 105 long p = period; 106 if (p > 0) 107 time += p; 108 else 109 time = triggerTime(-p); 110 } 111 112 113 114 /** 115 * Requeues a periodic task unless current run state precludes it. 116 * Same idea as delayedExecute except drops task rather than rejecting. 117 * 118 * @param task the task 119 */ 120 void reExecutePeriodic(RunnableScheduledFuture<?> task) { 121 if (canRunInCurrentRunState(true)) { 122 //又再一次加入队列 123 super.getQueue().add(task); 124 if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(true) && remove(task)) 125 task.cancel(false); 126 else 127 //再次开始执行 128 ensurePrestart(); 129 } 130 }
我们看到了最终都会执行任务父类里,一个变量的 call方法,我们现在看看这个 call 方法。
1 /** 2 * Creates a periodic action with given nano time and period. 3 */ 4 ScheduledFutureTask(Runnable r, V result, long ns, long period) { 5 super(r, result); 6 this.time = ns; 7 this.period = period; 8 this.sequenceNumber = sequencer.getAndIncrement(); 9 } 10 11 period : 正数(时间周期),负数(固定延迟后执行任务),0(不是可重复的任务) 12 13 //父类构造函数 14 //上面的super(r, result); 15 public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) { 16 this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result); 17 this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable 18 } 19 20 21 //上面的Executors.callable 22 public static <T> Callable<T> callable(Runnable task, T result) { 23 if (task == null) 24 throw new NullPointerException(); 25 return new RunnableAdapter<T>(task, result); 26 } 27 28 29 30 static final class RunnableAdapter<T> implements Callable<T> { 31 final Runnable task; 32 final T result; 33 RunnableAdapter(Runnable task, T result) { 34 this.task = task; 35 this.result = result; 36 } 37 public T call() { 38 //实际调用的是 run方法 39 task.run(); 40 return result; 41 } 42 }
可以看到 call 方法里其实执行的是 任务的 run 方法,然后返回个 result .
另外还有几个控制变量,他们在 delayedExecute 和 重写父类的方法 onShutdown 有关,主要的作用是取消任务后是否立即从队列中删除。
1 /** 2 * False if should cancel/suppress periodic tasks on shutdown. 3 */ 4 private volatile boolean continueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdown; 5 6 /** 7 * False if should cancel non-periodic tasks on shutdown. 8 */ 9 private volatile boolean executeExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdown = true; 10 11 /** 12 * True if ScheduledFutureTask.cancel should remove from queue 13 */ 14 private volatile boolean removeOnCancel = false;
1 /** 2 * Cancels and clears the queue of all tasks that should not be run 3 * due to shutdown policy. Invoked within super.shutdown. 4 */ 5 @Override void onShutdown() { 6 BlockingQueue<Runnable> q = super.getQueue(); 7 boolean keepDelayed = 8 getExecuteExistingDelayedTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(); 9 boolean keepPeriodic = 10 getContinueExistingPeriodicTasksAfterShutdownPolicy(); 11 if (!keepDelayed && !keepPeriodic) { 12 for (Object e : q.toArray()) 13 if (e instanceof RunnableScheduledFuture<?>) 14 ((RunnableScheduledFuture<?>) e).cancel(false); 15 q.clear(); 16 } 17 else { 18 // Traverse snapshot to avoid iterator exceptions 19 for (Object e : q.toArray()) { 20 if (e instanceof RunnableScheduledFuture) { 21 RunnableScheduledFuture<?> t = 22 (RunnableScheduledFuture<?>)e; 23 if ((t.isPeriodic() ? !keepPeriodic : !keepDelayed) || 24 t.isCancelled()) { // also remove if already cancelled 25 if (q.remove(t)) 26 t.cancel(false); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 tryTerminate(); 32 }
参考资料 :
无