1 导入实验需要的包
import torch
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"] = "TRUE"
2 人工构造数据集
生成正/负样本各 50 个,特征数为 2,进行二分类(0、1).
n_data = torch.ones(50, 2) x1 = torch.normal(2 * n_data, 1) y1 = torch.zeros(50) x2 = torch.normal(-2 * n_data, 1) y2 = torch.ones(50) x = torch.cat((x1, x2), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) y = torch.cat((y1, y2), 0).type(torch.FloatTensor) datax = x.numpy()
3 绘制数据散点图
fig,ax = plt.subplots() #第 一 类样本 ax.scatter(x.numpy()[:50, 0], x.numpy()[:50, 1], s=35, c='b', marker='o', label='class 0') #第 二 类样本 ax.scatter(x.numpy()[50:, 0], x.numpy()[50:, 1], s=35, c='r', marker='x', label='class 1') ax.legend() plt.show()

4 初始化模型参数
设置 $theta=[w_0,w_1,w_2]$ 初始化为 1 ,学习率 $alpha=0.004$,迭代次数 $iters =20000$ ,其中 $w_0$ 代表偏置 $b$
theta = np.zeros((3,1)) alpha = 0.004 iters = 20000 Train_Loss_list = []
5 定义模型
#设置sigmoid函数,通过传进去的值算出概率,通过概率来做出判断 def sigmoid(inX): #inX指的是wT*x,这里的w和x都是向量 return 1.0 / (1 + np.exp(-inX))
6 定义损失函数
损失函数使用交叉熵损失
# 实现逻辑回归的代价函数,两个部分,-y(log(hx)和-(1-y)log(1-hx) def cost_Func(theta, X, y): A = sigmoid(X@theta) first = y*np.log(A) second = (1-y)*np.log(1-A) return -np.sum(first+second)/len(X)
7 定义优化算法
采用随机梯度下降法,更新参数
def gradientDescent (X,y,theta,iters,alpha): global Train_Loss_list m = len(X) for i in range(iters+1): A=sigmoid(X@theta) theta = theta-(alpha/m)*X.T@(A-y) cost =cost_Func(theta,X,y) Train_Loss_list.append(cost) if i % 1000==0: print("第"+str(i)+" 次的损失为 "+str(cost)) print(len(Train_Loss_list)) return theta
8 训练模型
获得训练 20000次 中的损失变化,以及最终的权重和偏置。
x = x.numpy() #增加一列全为 1 ,方便与偏置项相乘。 ones = np.ones(100) x = np.c_[ones,x] y = y.numpy().reshape(100,1) theta = np.zeros((3,1)) #print("theta.shape=",theta.shape) theta_final = gradientDescent(x,y,theta,iters,alpha) #得到最终的 权重和偏置。 print("theta_final=[",theta_final[0][0],theta_final[1][0],theta_final[2][0]," ]")
9 绘制训练损失图
x11= range(0,20001) y11= Train_Loss_list plt.xlabel('Train loss vs. epoches') plt.ylabel('Train loss') plt.plot(x11, y11,'.',c='b',label="Train_Loss") plt.legend() plt.show()
10 预测函数定义
def predict(X,theta): prob = sigmoid(X@theta) return [1 if x>=0.5 else 0 for x in prob]
使用预测函数获取原始数据集的准确率
y_ = np.array(predict(x,theta_final)) y_pre = y_.reshape(len(y_),1 ) acc = np.mean(y_pre == y) print(acc)
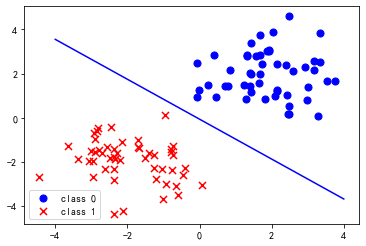
11 结果可视化
使用一条直线将两类数据区分开来。
coef1 = -theta_final[0,0] / theta_final[2,0] coef2 = -theta_final[1,0] / theta_final[2,0] x1 = np.linspace(-4,4,100) f = coef1+coef2*x1 fig,ax = plt.subplots() ax.plot(x1,f,c='blue') ax.scatter(datax[:50, 0],datax[:50, 1], s=50, c='b', marker='o', label='class 0') ax.scatter(datax[50:, 0], datax[50:, 1], s=50, c='r', marker='x', label='class 1') ax.legend() plt.show()