Three Equal
Memory limit: 256 MB
You are given an array AA of NN integers between 00 and 22. With cost 11 you can apply the following operation A_i = ((A_i + 1) \% 3)Ai=((Ai+1) % 3).
Find the minimum cost to make all elements equal.
Standard input
The first line contains one integer NN.
The second line contains NN integers representing the elements of the array AA.
Standard output
Output a single number representing the minimum cost to make all elements of AA equal.
Constraints and notes
- 1 leq N leq 10^31≤N≤103
- The elements of the array AA are integers between 00 and 22.
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
4 1 0 0 2 |
3 |
3 1 2 2 |
1 |
3 1 1 1 |
0 |
问你n个数到一个相同模数的最小值,那就直接枚举这三个模数好了,当时手残还打错一个字母
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; int b[4]; int main() { int n; cin>>n; for(int i=0,x;i<n;i++) { if(x%3==0)b[1]+=2,b[2]+=2; else if(x%3==1)b[0]+=2,b[3]+=1; else b[1]+=1,b[2]+=2; } cout<<min(min(b[0],b[1]),b[2]); return 0; }
Ricocheting Balls
Memory limit: 256 MB
There are NN falling balls situated at some height levels; more specifically the i^{ ext{th}}ith ball is H_iHi meters above the ground. The balls are supposed to be falling at 11 meter per second, but they're not; they're stuck in time, hovering.
You can repeat the following process as many times as you want (possibly 00 times): you will unfreeze the time for 11 second and then freeze it back up.
If a ball hits the ground, which is situated at the height level 00, it will ricohet and start ascending instead; therefore, the next time it is unfrozen, it will actually go upwards to the height level 11, then 22, 33, 44 and so on...
You want to find the moment of time that minimizes the sum of heights of all the balls. Print the value of the sum obtained at this moment of time.
Standard input
The first line contains an integer NN.
The next line contains NN integers, representing HH.
Standard output
Print an integer, the minimum sum of heights of all balls that can be obtained by the above-described process.
Constraints and notes
- 1 leq N leq 10^51≤N≤105
- 1 leq H_i leq 10^91≤Hi≤109
| Input | Output | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
4 1 4 5 2 |
6 |
Moment of time 00: [1, 4, 5, 2][1,4,5,2], summing to 1212. Moment of time 11: [0, 3, 4, 1][0,3,4,1], summing to 88. Moment of time 22: [1, 2, 3, 0][1,2,3,0], summing to 66. We can notice how the first ball starts ascending, after it hit the ground. Moment of time 33: [2, 1, 2, 1][2,1,2,1], summing to 66. |
9 1 7 1 1 1 5 3 6 3 |
17 |
小球每1s落下1m,问你这个距离地面距离的最小和,当然是选择中位数了
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N=1e5+5; int h[N]; int main() { int n; cin>>n; long long ans=0; for(int i=0; i<n; i++)cin>>h[i]; sort(h,h+n); for(int i=0; i<n; i++) ans+=abs(h[i]-h[(n-1)/2]); cout<<ans<<endl; return 0; }
Binary Isomorphism
Memory limit: 256 MB
You are given two binary trees. These two trees are called isomorphic if one of them can be obtained from other by a series of flips, i.e. by swapping the children of some nodes. Two leaves are isomorphic.
Both these trees will be given through their parents array. In a parents array,
- nodes are 11-based
- there is only one position rr where P_r = 0Pr=0. This means that rr is the root of the tree.
- for every node i eq ri≠r, its direct parent is P_iPi.
Standard input
The first line contains TT, the number of test cases.
For every test:
- the first line contains NN, representing the number of nodes in both of the trees
- the second line contains NN integers, representing the parents array of the first tree
- the third line contains NN integers, representing the parents array of the second tree
Standard output
For every test case, print a line containing 1 if the two trees are isomorphic, or 0 otherwise.
Constraints and notes
- 1 leq T leq 201≤T≤20
- 1 leq N leq 10^51≤N≤105. The sum of all values of NN in a test is leq 10^5≤105
| Input | Output | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
3 4 3 0 2 3 3 4 0 3 5 5 1 0 3 4 5 1 4 2 0 5 0 1 2 1 4 0 1 4 1 2 |
0 1 1 |
13243142 1523442351 1234512543 |
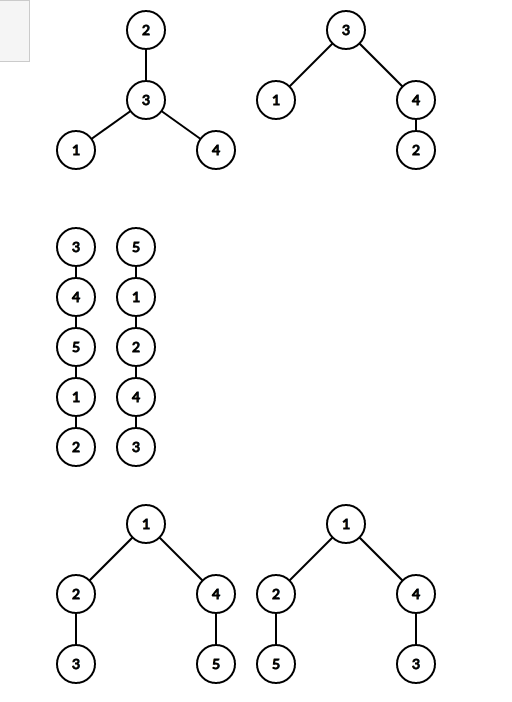
给你两个二叉树,看其是否同构
需要dfs看其每个节点孩子数是否相同
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int N=1e5+5; vector<int>v[N]; vector<int>v2[N]; int dfs(int x,int y) { if(v[x].size()!=v2[y].size())return 0; if(v[x].size()==0)return 1; if(v[x].size()==1)return dfs(v[x][0],v2[y][0]); else { if(dfs(v[x][0],v2[y][0])&&dfs(v[x][1],v2[y][1])||dfs(v[x][0],v2[y][1])&&dfs(v[x][1],v2[y][0])) return 1; return 0; } } int main() { int T; scanf("%d",&T); while(T--) { int n,rt1,rt2; scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) v[i].clear(),v2[i].clear(); for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { int x; scanf("%d",&x); if(x==0) rt1=i; else v[x].push_back(i); } for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { int x; scanf("%d",&x); if(x==0) rt2=i; else v2[x].push_back(i); } printf("%d ",dfs(rt1,rt2)); } return 0; }
还可以去括号匹配的思想
#include <bits/stdc++.h> #define mod 1000000007 #define p 666013 using namespace std; int put[300010]; vector <int> adia[200010]; pair <int, int> dfs(int nod) { vector <pair <int, int>> fii; for (auto i : adia[nod]) { fii.push_back(dfs(i)); } sort(fii.begin(), fii.end()); int lact(1); int ans = '('; for (auto i : fii) { ans += 1ll * i.first * put[lact] % mod; lact += i.second; } ans += 1ll * ')' * lact; lact++; return { ans, lact }; } void solve() { int n; cin >> n; vector <pair <int, int>> v; for (int q(0); q < 2; q++) { for (int i(1); i <= n; i++) adia[i] = vector <int> (); int root; for (int i(1); i <= n; i++) { int tata; cin >> tata; if (tata == 0) root = i; else adia[tata].push_back(i); } auto x = dfs(root); v.push_back(x); } cout << (v[0] == v[1]) << ' '; } int main() { put[0] = 1; for (int i(1); i < 300010; i++) put[i] = 1ll * 666013 * put[i - 1] % mod; int t; cin >> t; while (t--) solve(); return 0; }
Russian Dolls Ways
Memory limit: 256 MB
You have NN Russian dolls, for the i^{th}ith doll you know its size A_iAi.
A doll of size jj can be put inside a doll of size ii if j < ij<i. In addition, a doll of size ii can nest only onesmaller doll jj. But that doll jj, can nest another smaller doll, in a recursive manner.
For example, if you have three dolls of sizes 33, 1010 and 77, you can put the first doll inside the third, and then the third inside the second.
Your goal is to count the number of nestings that minimizes the number of dolls at the end.
Consider the array PP of size NN where P_iPi is index of the doll in which the doll ii is nested into. If doll iiis not nested into any other doll, P_i = 0Pi=0. Two ways are considered distinct if there is a 1 leq i leq N1≤i≤Nsuch that P1_i eq P2_iP1i≠P2i.
Standard input
The first line contains a single integer NN.
The second line contains NN integers representing the elements of AA, the sizes of the dolls.
Standard output
Output a single number representing the number of ways to nest the dolls in order to achieve the minimum number of dolls at the end, modulo 10^9+7109+7.
Constraints and notes
- 1 leq N leq 10^51≤N≤105
- 1 leq A_i leq 10^91≤Ai≤109
| Input | Output | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
3 1 2 3 |
1 |
The minimum number of dolls at the end is 11 |
4 1 2 2 3 |
4 |
The minimum number of dolls at the end is 22. The PP array from the input is [2, 4, 0, 0][2,4,0,0] [2, 0, 4, 0][2,0,4,0] [3, 4, 0, 0][3,4,0,0] [3, 0, 4, 0][3,0,4,0] |
6 1 1 2 2 3 3 |
4 |
The minimum number of dolls at the end is 22. The PP array from the input is [3, 4, 5, 6, 0, 0][3,4,5,6,0,0] [4, 3, 5, 6, 0, 0][4,3,5,6,0,0] [3, 4, 6, 5, 0, 0][3,4,6,5,0,0] [4, 3, 6, 5, 0, 0][4,3,6,5,0,0] |
俄罗斯套娃,就是让你求一下这个长度为n的序列最多能分成几个序列,其实就是重复个数最多的那个个数k
然后就是每个值都要选一个大小为k的盒子
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int MD=1e9+7; long long ans=1; unordered_map<int,int> M; vector<int>V; int main() { ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0); int n; cin>>n; for(int i=0,x;i<n;i++)cin>>x,M[x]++; for(auto X:M)V.push_back(X.second); sort(V.begin(),V.end()); int k=*V.rbegin(); V.pop_back(); for(auto X:V) for(int i=0;i<X;i++)ans=ans*(k-i)%MD; cout<<ans; }
Strange Substring
Memory limit: 256 MB
You are given two strings AA and BB, consisting only of lowercase letters from the English alphabet. Count the number of distinct strings SS, which are substrings of AA, but not substrings of BB.
Standard input
The first line contains AA.
The second line contains BB.
Standard output
Print the answer on the first line.
Constraints and notes
- 1 leq |A|, |B| leq 10^51≤∣A∣,∣B∣≤105
| Input | Output |
|---|---|
abcab bcab |
3 |
aaa aa |
1 |
acabad abcacd |
12 |
题意很好理解,就是让你找是A的子串,但是不是B的子串的个数
benq的SA+LCP
#include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; struct suffix_array { suffix_array(const char* S) : N(strlen(S)) { vector<int> V; for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) V.push_back(S[i]); init(V); } suffix_array(const vector<int>& VV) : N(VV.size()) { vector<int> V(VV); init(V); } int N; vector<int> SA; vector<int> RA; void compress(vector<int>& V, vector<int>& C) { copy(V.begin(), V.end(), C.begin()); sort(C.begin(), C.end()); auto cend = unique(C.begin(), C.end()); for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) { V[i] = lower_bound(C.begin(), cend, V[i]) - C.begin() + 1; } V.push_back(0); C.push_back(0); } void compute_sa(vector<int>& V, vector<int>& C) { vector<int> T(N + 1); for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++) SA.push_back(i); for(int ski = 0; V[SA[N]] < N; ski = ski ? ski << 1 : 1) { fill(C.begin(), C.end(), 0); for(int i = 0; i < ski; i++) T[i] = N - i; for(int i = 0, p = ski; i <= N; i++) if(SA[i] >= ski) T[p++] = SA[i] - ski; for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++) C[V[i]]++; for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++) C[i] += C[i - 1]; for(int i = N; i >= 0; i--) SA[--C[V[T[i]]]] = T[i]; T[SA[0]] = 0; for(int j = 1; j <= N; j++) { int a = SA[j]; int b = SA[j - 1]; T[a] = T[b] + (a + ski >= N || b + ski >= N || V[a] != V[b] || V[a + ski] != V[b + ski]); } V.swap(T); } } void compute_lcp(const vector<int>& OV) { LCP = vector<int>(N); int len = 0; for(int i = 0; i < N; i++, len = max(0, len - 1)) { int si = RA[i]; int j = SA[si - 1]; for(; i + len < N && j + len < N && OV[i + len] == OV[j + len]; len++); LCP[si - 1] = len; } } void init(vector<int>& V) { vector<int> OV(V); vector<int> C(N); compress(V, C); compute_sa(V, C); RA.resize(N + 1); for(int i = 0; i <= N; i++) RA[SA[i]] = i; compute_lcp(OV); } vector<int> LCP; }; int main() { ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); string S; vector<pair<int, int> > A; int N = 2; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { string T; cin >> T; S += T; S += "?"; for (int j = 0; j < T.size(); j++) { A.push_back(make_pair(i, T.size() - j)); } A.push_back(make_pair(-1, -1)); } A.push_back(make_pair(-1, -1)); vector<long long> result(N); suffix_array sa(S.c_str()); sa.LCP.push_back(0); for (int i = 1; i <= sa.N; ) { int j = sa.SA[i]; int ind = A[j].first; if (ind == -1) { ++i; continue; } int sz = 1; while (i + sz <= sa.N && A[sa.SA[i + sz]].first == ind) { ++sz; } int ln = sa.LCP[i - 1]; for (int j = i; j < i + sz; j++) { result[ind] += max(A[sa.SA[j]].second - max(ln, sa.LCP[j]), 0); ln = min(ln, sa.LCP[j]); } i += sz; } cout << result[0]; return 0; }
一种我倾向于的写法
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #define N 2000000 using namespace std; struct node{ int son[27]; int len,fail; bool sig; }tri[N]; char S[N]; int len,L,lst; int in[N],d[N]; void add(int last,int c,bool sig){ static int v,u,up,up1; v=++L; u=last; tri[v].len=tri[u].len+1; for (;u&&!tri[u].son[c];u=tri[u].fail)tri[u].son[c]=v; if (!u)tri[v].fail=1; else{ up=tri[u].son[c]; if (tri[up].len==tri[u].len+1)tri[v].fail=up; else{ up1=++L; tri[up1]=tri[up]; tri[up1].len=tri[u].len+1; tri[up].fail=tri[v].fail=up1; for (;u&&tri[u].son[c]==up;u=tri[u].fail)tri[u].son[c]=up1; } } tri[v].sig=sig; lst=v; } int main(){ scanf(" %s",S+1); len=strlen(S+1); lst=1,L=1; for (int i=1;i<=len;i++)add(lst,S[i]-'a',0); scanf(" %s",S+1); len=strlen(S+1); add(lst,26,1); for (int i=1;i<=len;i++)add(lst,S[i]-'a',1); for (int i=1;i<=L;i++)in[tri[i].fail]++; int l=0,r=0; for (int i=1;i<=L;i++) if (!in[i])d[++r]=i; while (l!=r){ ++l; tri[tri[d[l]].fail].sig|=tri[d[l]].sig; if (!(--in[tri[d[l]].fail])) d[++r]=tri[d[l]].fail; } long long ans=0; for (int i=1;i<=L;i++) if (!tri[i].sig) ans+=tri[i].len-tri[tri[i].fail].len; printf("%lld ",ans); return 0; }