这一题很重要

#include <Eigen/Core> #include <Eigen/Dense> using namespace Eigen; #include <vector> #include <fstream> #include <iostream> #include <iomanip> #include "sophus/se3.h" using namespace std; typedef vector<Vector3d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Vector3d>> VecVector3d; typedef vector<Vector2d, Eigen::aligned_allocator<Vector3d>> VecVector2d; typedef Matrix<double, 6, 1> Vector6d; string p3d_file = "p3d.txt"; string p2d_file = "p2d.txt"; int main(int argc, char **argv) { VecVector2d p2d; VecVector3d p3d; Matrix3d K; double fx = 520.9, fy = 521.0, cx = 325.1, cy = 249.7; K << fx, 0, cx, 0, fy, cy, 0, 0, 1; // load points in to p3d and p2d // START YOUR CODE HERE ifstream f3d(p3d_file); ifstream f2d(p2d_file); double point_3d[3]; while(!f3d.eof()){ for(int i=0;i<3;i++)f3d>>point_3d[i]; p3d.push_back(Vector3d(point_3d[0],point_3d[1],point_3d[2])); } double point_2d[2]; while(!f2d.eof()){ for(int i=0;i<2;i++)f2d>>point_2d[i]; p2d.push_back(Vector2d(point_2d[0],point_2d[1])); } // END YOUR CODE HERE assert(p3d.size() == p2d.size()); int iterations = 100; double cost = 0, lastCost = 0; int nPoints = p3d.size(); cout << "points: " << nPoints << endl; Sophus::SE3 T_esti; // estimated pose for (int iter = 0; iter < iterations; iter++) { Matrix<double, 6, 6> H = Matrix<double, 6, 6>::Zero(); Vector6d b = Vector6d::Zero(); cost = 0; // compute cost for (int i = 0; i < nPoints; i++) { // compute cost for p3d[I] and p2d[I] // START YOUR CODE HERE Vector3d P_ = T_esti * Vector3d(p3d[i][0], p3d[i][1], p3d[i][2]); double x = P_[0]; double y = P_[1]; double z = P_[2]; double z2 = z * z; double x2 = x * x; double y2 = y * y; Vector3d u = K * P_; u = u / u[2]; Vector2d e(p2d[i][0] - u[0], p2d[i][1] - u[1]); cost += e.squaredNorm() / 2; // // END YOUR CODE HERE // // // compute jacobian Matrix<double, 2, 6> J; // // START YOUR CODE HERE J(0,0)=fx/z; J(0,1)=0; J(0,2)=-fx*x/z2; J(0,3)=-fx*x*y/z2; J(0,4)=fx+fx*x2/z2; J(0,5)=-fx*y/z; J(1,0)=0; J(1,1)=fy/z; J(1,2)=-fy*y/z2; J(1,3)=-fy-fy*y2/z2; J(1,4)=fy*x*y/z2; J(1,5)=fy*x/z; J=-J;//注意这里1 // END YOUR CODE HERE H += J.transpose() * J; b += -J.transpose() * e; } // solve dx Vector6d dx; // START YOUR CODE HERE dx=H.ldlt().solve(b); // END YOUR CODE HERE if (isnan(dx[0])) { //cout << "result is nan!" << endl; break; } if (iter > 0 && cost >= lastCost) { // cost increase, update is not good //cout << "break!!!!"<<"cost: " << cost << ", last cost: " << lastCost << endl; break; } // update your estimation // START YOUR CODE HERE T_esti = Sophus::SE3::exp(dx)*T_esti; // END YOUR CODE HERE lastCost = cost; //cout << "iteration " << iter << " cost=" << cout.precision(12) << cost << endl; } clock_t end=clock(); cout << "estimated pose: " << T_esti.matrix() << endl<<"Time use: "<<(end-start)*1000/CLOCKS_PER_SEC<<"ms"<<endl; return 0; }
注意点:
1. 首先读取文件还是使用ifstream方式使用>>操作符输入到数组里
2. 各矩阵规模:H 6*6 b 6*1 e 3*1
3. 优化问题的策略:
根据之前李代数一讲的推导,在扰动模型中有以下两式:
SO3
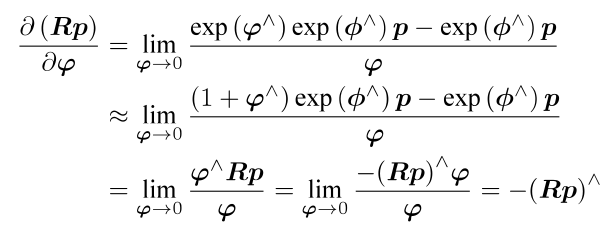
SE3
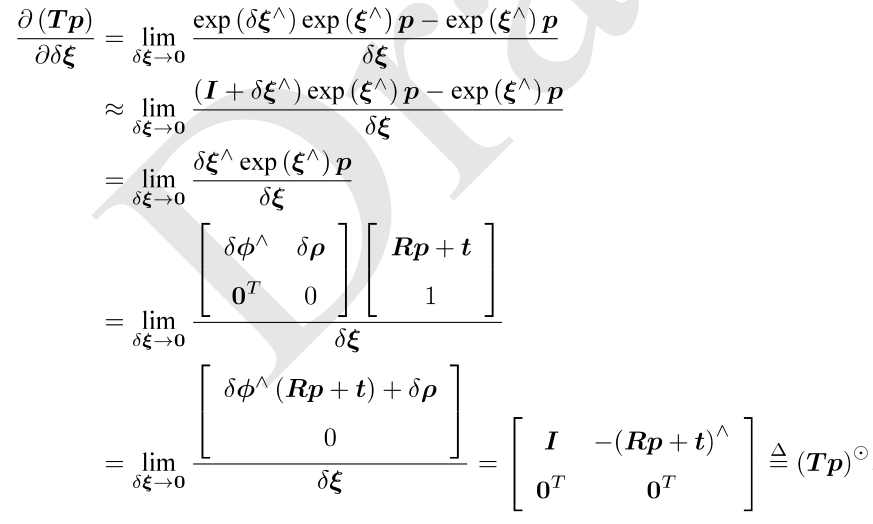
在本题中的PnP问题使用BA法求解时,待求解量为T,或者说T对应的李代数,每次需要求解的是该李代数相对于误差项定义的导数
(常规SLAM中是用基础少点的方法如P3P,EPnP等方法解出粗略位姿以方便进行优化,再使用BA整体优化以便快速收敛)
该优化问题定义为: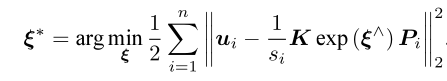
后续推导:
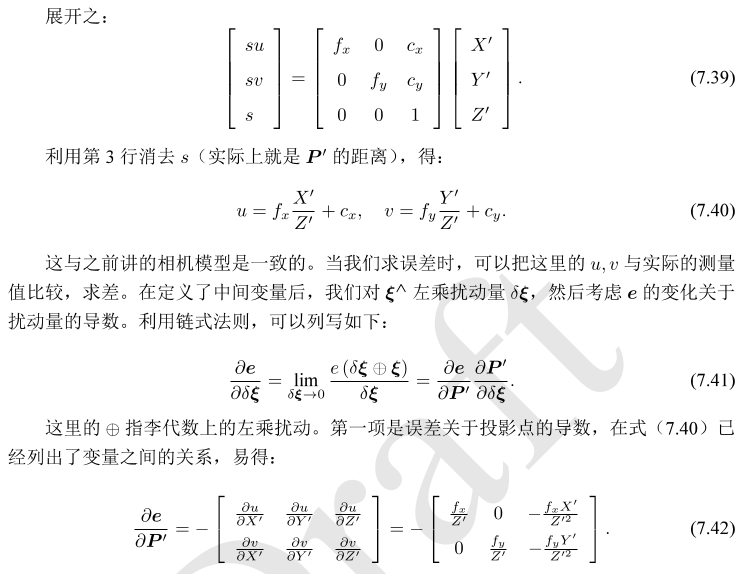

代码中使用的即为7.45式,注意的是矩阵外的负号是由于误差项形式表示为观测值减预测值
另外,非线性优化求解的几类方法,都是对δx求导数,所以此处的扰动模型对δξ求导正好吻合,并且扰动模型比起求导模型形式更简单。
注意由于扰动偏导的形式为
在解出扰动量后,对T进行更新是使用的李代数左乘 T_esti = Sophus::SE3::exp(dx)*T_esti;
后面的优化模型以该题方法为基础,不过大部分不用手动求解高斯牛顿,皆为调用g2o或者ceres来构造优化项,需要提升性能时需要手动求导数,所以对上方原理需要有较熟练的掌握,也需要对基础的几何模型能够做到手写。
opencv关于空间问题的文档把几何模型阐述得很清楚,可以作为以后的参考。
https://docs.opencv.org/3.0-beta/modules/calib3d/doc/camera_calibration_and_3d_reconstruction.html