Spring
代理模式
代理模式分为两大类:静态代理 & 动态代理
1、静态代理
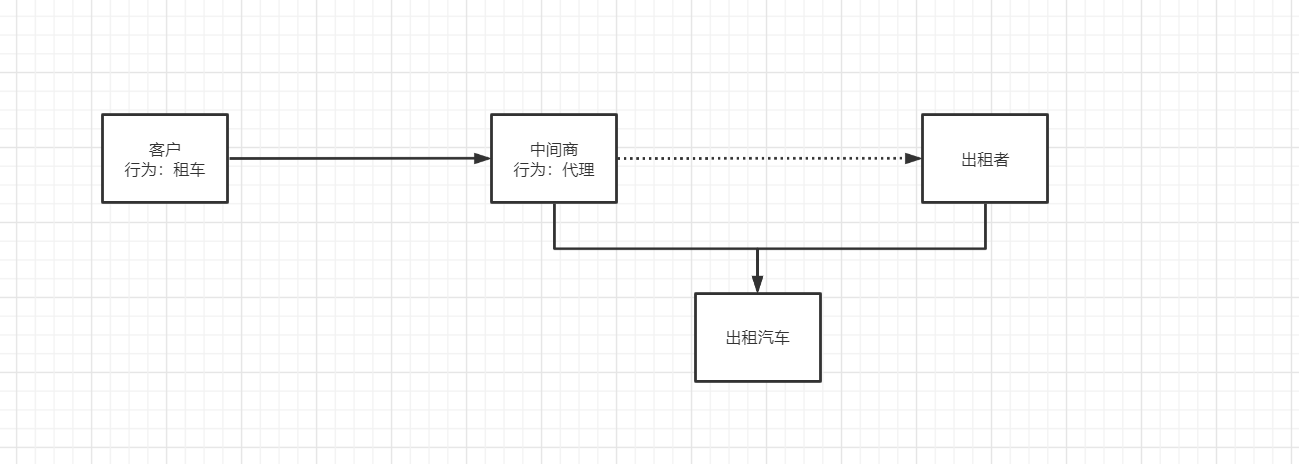
我们以租车为例
角色分析:
- 抽象角色
- 真实角色
- 代理角色
- 客户
代码实现:
1.接口
package com.charles.dao; // 租车 public interface RentCarMapper { public void rent(); }
2.真实角色
public class HostRent implements RentCarMapper { @Override public void rent() { System.out.println("车主出租"); } }
3.代理角色
public class RentCarProxy { private HostRent hostRent; public RentCarProxy(){} public RentCarProxy(HostRent hostRent){ this.hostRent = hostRent; } public void rent(){ hostRent.rent(); visitCar(); sign(); receive(); } public void visitCar(){ System.out.println("中间商带客户看车"); } public void sign(){ System.out.println("签署借租合同"); } public void receive(){ System.out.println("中间商赚差价"); } }
4.客户
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { HostRent hostRent = new HostRent(); RentCarProxy rentCarProxy = new RentCarProxy(hostRent); System.out.println("客户租车"); rentCarProxy.rent(); } }
运行结果

这样的好处是:方便管理,分工明确
缺点是:开发效率低
这种思想正是AOP思想,而开发效率低的缺点,我们用动态代理来解决。
2、动态代理
动态代理顾名思义就是动态的代理类,我们这里使用的是基于接口的代理----JDK 动态代理
用到两个类:Proxy & InvocationHandler
代码展示:
代理类
public class RentCarProxy implements InvocationHandler { private HostRent hostRent; public void setHostRent(HostRent hostRent) { this.hostRent = hostRent; } public Object getProxy() { return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(), hostRent.getClass().getInterfaces(), this); } @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { visitCar(); sign(); receive(); Object invoke = method.invoke(hostRent, args); return invoke; } public void visitCar(){ System.out.println("中间商带客户看车"); } public void sign(){ System.out.println("签署借租合同"); } public void receive(){ System.out.println("中间商赚差价"); } }
客户
public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { HostRent hostRent = new HostRent(); RentCarProxy rentCarProxy = new RentCarProxy(); // 通过调用程序处理角色来调用接口 rentCarProxy.setHostRent(hostRent); // 动态生成的代理 RentCarMapper proxy = (RentCarMapper) rentCarProxy.getProxy(); proxy.rent(); } }
这样弥补了静态代理的短缺