线程替代方案:
1、subprocess:
线程替代方案,完全跳过线程,使用进程
是派生进程的主要替代方案
Python2.4后引入
2、multiprocessiong
使用threading接口派生,使用子进程
允许为多核或者多cpu派生进程,接口跟threading非常相似
Python2.6后引入
3、concurrent.futures
新的异步执行模块
任务级别的操作
Python3.2后引入
多进程:
进程间通讯(InterProcessCommunication,IPC)
进程之间无任何共享状态
# 进程的创建
# 1、直接生产Process实例对象,案例如下
import multiprocessing from time import sleep, ctime def clock(interval): while True: print("The time is %s" % ctime()) sleep(interval) if __name__ == "__main__": p = multiprocessing.Process(target=clock, args=(5,)) p.start() while True: print("sleep...") sleep(1) ''' 输出打印如下: sleep... The time is Mon Oct 15 17:10:29 2018 sleep... sleep... sleep... sleep... sleep... The time is Mon Oct 15 17:10:34 2018 '''
# 2、派生子类,案例如下
import multiprocessing
from time import sleep, ctime
class ClockProcess(multiprocessing.Process):
'''
两个函数比较重要
1、init构造函数
2、run函数
'''
def __init__(self, interval):
super().__init__()
self.interval = interval
def run(self):
while True:
print("The time is %s" % ctime())
sleep(self.interval)
if __name__ == '__main__':
p = ClockProcess(5)
p.start()
while True:
print("sleep...")
sleep(1)
'''
输出打印如下:
sleep...
sleep...
The time is Mon Oct 15 17:24:53 2018
sleep...
sleep...
sleep...
sleep...
sleep...
The time is Mon Oct 15 17:24:58 2018
sleep...
sleep...
'''
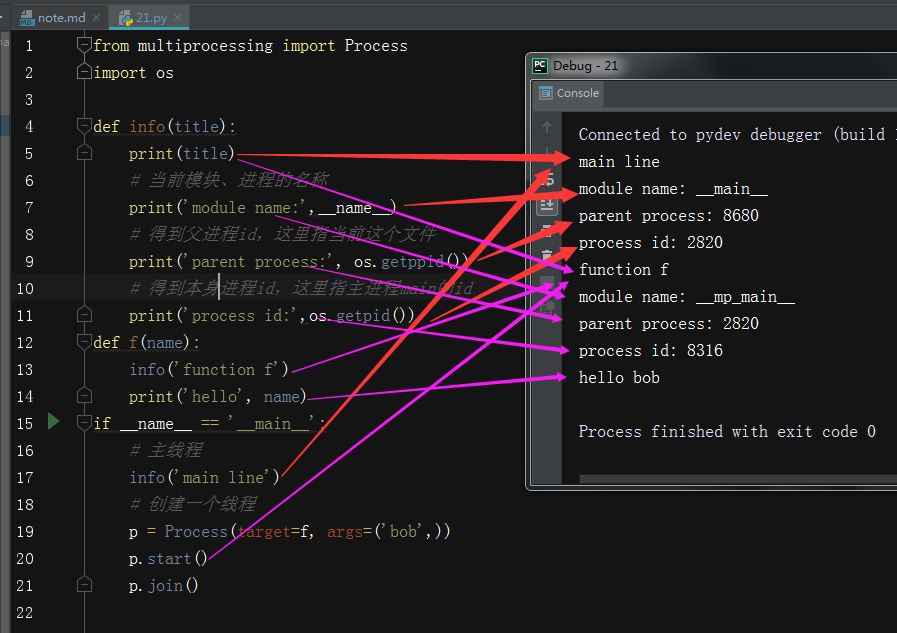
进程id,在os模块查看pid、ppid以及它们的关系,案例如下:21.py
''' 生产者消费者模型: JoinableQueue允许使用者通知生产者,任务已经被处理成功task_done(),通着进程使用共享的信号和条件变量来实现 '''
# 1、JoinableQueue的使用,案例如下:
import multiprocessing from time import ctime # 消费者 def consumer(input_q): print("Into consumer:", ctime()) while True: # 获取处理项 item = input_q.get() # 下面替换为有用的工作 print("pull", item, "out of q") # 下面表示发出信号通知任务完成 input_q.task_done() print("Out of consumer:", ctime()) # 生产者 def producer(sequence, output_q): # 表明生产开始 print("Into producer:", ctime()) # sequence存放商品或任务 for item in sequence: output_q.put(item) print("put", item, "into q") # 表明是生产结束 print("Out of producer:", ctime()) if __name__ == '__main__': q = multiprocessing.JoinableQueue() # 运行消费者进程 cons_p = multiprocessing.Process(target=consumer, args=(q,)) # 守护进程 cons_p.daemon = True cons_p.start() # 生产多个项,sequence代表想发给消费者的项序列 # 在实践中,这可能是生成器的输出或通过一些其他方式生产出来 sequence = [1, 2, 3, 4] producer(sequence, q) # 等待所有项被处理 q.join() ''' 打印输出如下: Into producer: Tue Oct 16 15:40:44 2018 put 1 into q put 2 into q put 3 into q put 4 into q Out of producer: Tue Oct 16 15:40:44 2018 Into consumer: Tue Oct 16 15:40:44 2018 pull 1 out of q pull 2 out of q pull 3 out of q pull 4 out of q '''
# 2、JoinableQueue队列里哨兵的使用,案例如下:
import multiprocessing
from time import ctime
# 消费者
def consumer(input_q):
print("Into consumer:", ctime())
while True:
item = input_q.get()
if item is None:
break
print("pull", item, "out of q")
print("Out of consumer:", ctime())
# 生产者
def producer(sequence, output_q):
# 表明生产开始
print("Into producer:", ctime())
# sequence存放商品或任务
for item in sequence:
output_q.put(item)
print("put", item, "into q")
# 表明是生产结束
print("Out of producer:", ctime())
if __name__ == '__main__':
q = multiprocessing.Queue()
# 运行消费者进程
cons_p = multiprocessing.Process(target=consumer, args=(q,))
cons_p.start()
# 生产多个项,sequence代表想发给消费者的项序列
# 在实践中,这可能是生成器的输出或通过一些其他方式生产出来
sequence = [1, 2, 3, 4]
producer(sequence, q)
q.put(None)
cons_p.join()
'''
输出打印如下:
Into producer: Tue Oct 16 16:35:08 2018
put 1 into q
put 2 into q
put 3 into q
put 4 into q
Out of producer: Tue Oct 16 16:35:08 2018
Into consumer: Tue Oct 16 16:35:08 2018
pull 1 out of q
pull 2 out of q
pull 3 out of q
pull 4 out of q
Out of consumer: Tue Oct 16 16:35:08 2018
'''
# 3、多线程共享变量简单应用
# 讲解:遇到多进程调用时,假若第一个进程把队列里的哨兵取出来了,其他进程发现取不到哨兵了,就会一直耗着,以下是JoinableQueue队列里哨兵的改进,有几个进程用哨兵,队列里就放几个哨兵,案例如下:
import multiprocessing
from time import ctime
# 消费者
def consumer(input_q):
print("Into consumer:", ctime())
while True:
item = input_q.get()
if item is None:
break
print("pull", item, "out of q")
print("Out of consumer:", ctime())
# 生产者
def producer(sequence, output_q):
# 表明生产开始
print("Into producer:", ctime())
# sequence存放商品或任务
for item in sequence:
output_q.put(item)
print("put", item, "into q")
# 表明是生产结束
print("Out of producer:", ctime())
if __name__ == '__main__':
q = multiprocessing.Queue()
# 运行消费者进程
cons_p1 = multiprocessing.Process(target=consumer, args=(q,))
cons_p1.start()
cons_p2 = multiprocessing.Process(target=consumer, args=(q,))
cons_p2.start()
# 生产多个项,sequence代表想发给消费者的项序列
# 在实践中,这可能是生成器的输出或通过一些其他方式生产出来
sequence = [1, 2, 3, 4]
producer(sequence, q)
q.put(None)
q.put(None)
cons_p1.join()
cons_p2.join()
'''
输出打印如下:
Into producer: Tue Oct 16 16:44:31 2018
put 1 into q
put 2 into q
put 3 into q
put 4 into q
Out of producer: Tue Oct 16 16:44:31 2018
Into consumer: Tue Oct 16 16:44:31 2018
pull 1 out of q
pull 2 out of q
pull 3 out of q
pull 4 out of q
Out of consumer: Tue Oct 16 16:44:31 2018
Into consumer: Tue Oct 16 16:44:32 2018
Out of consumer: Tue Oct 16 16:44:32 2018
'''