前言:
只要是有表单存在,那么就有可能有对数据的校验需求。如:判断是否为整数、判断电子邮件格式等等。
WPF采用一种全新的方式 - Binding,来实现前台显示与后台数据进行交互,当然数据校验方式也不一样了。
本专题全面介绍一下WPF中4种Validate方法,帮助你了解如何在WPF中对binding的数据进行校验,并处理错误显示。
一、简介
正常情况下,只要是绑定过程中出现异常或者在converter中出现异常,都会造成绑定失败。
但是WPF不会出现任何异常,只会显示一片空白(当然有些Converter中的异常会造成程序崩溃)。
这是因为默认情况下,Binding.ValidatesOnException为false,所以WPF忽视了这些绑定错误。
但是如果我们把Binding.ValidatesOnException为true,那么WPF会对错误做出以下反应:
- 设置绑定元素的附加属性 Validation.HasError为true(如TextBox,如果Text被绑定,并出现错误)。
- 创建一个包含错误详细信息(如抛出的Exception对象)的ValidationError对象。
- 将上面产生的对象添加到绑定对象的Validation.Errors附加属性当中。
- 如果Binding.NotifyOnValidationError是true,那么绑定元素的附加属性中的Validation.Error附加事件将被触发。(这是一个冒泡事件)
我们的Binding对象,维护着一个ValidationRule的集合,当设置ValidatesOnException为true时,
默认会添加一个ExceptionValidationRule到这个集合当中。
PS:对于绑定的校验只在Binding.Mode 为TwoWay和OneWayToSource才有效,
即当需要从target控件将值传到source属性时,很容易理解,当你的值不需要被别人使用时,就很可能校验也没必要。
二、四种实现方法
1、在Setter方法中进行判断
直接在Setter方法中,对value进行校验,如果不符合规则,那么就抛出异常。然后修改XAML不忽视异常。
public class PersonValidateInSetter : ObservableObject { private string name; private int age; public string Name { get { return this.name; } set { if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(value)) { throw new ArgumentException("Name cannot be empty!"); } if (value.Length < 4) { throw new ArgumentException("Name must have more than 4 char!"); } this.name = value; this.OnPropertyChanged(() => this.Name); } } public int Age { get { return this.age; } set { if (value < 18) { throw new ArgumentException("You must be an adult!"); } this.age = value; this.OnPropertyChanged(() => this.Age); } } }
<Grid DataContext="{Binding PersonValidateInSetter}"> <Grid.RowDefinitions> <RowDefinition /> <RowDefinition /> </Grid.RowDefinitions> <Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" /> <ColumnDefinition /> </Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <TextBlock Text="Name:" /> <TextBox Grid.Column="1" Margin="1" Text="{Binding Name, ValidatesOnExceptions=True, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" /> <TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Text="Age:" /> <TextBox Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Margin="1" Text="{Binding Age, ValidatesOnExceptions=True, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" /> </Grid>
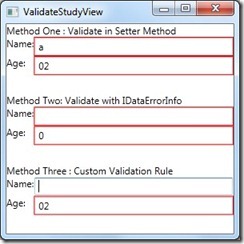
当输入的值,在setter方法中校验时出现错误,就会出现一个红色的错误框。
关键代码:ValidatesOnExceptions=True, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged。
PS:这种方式有一个BUG,首次加载时不会对默认数据进行检验。
2、继承IDataErrorInfo接口
使Model对象继承IDataErrorInfo接口,并实现一个索引进行校验。如果索引返回空表示没有错误,如果返回不为空,
表示有错误。另外一个Erro属性,但是在WPF中没有被用到。
public class PersonDerivedFromIDataErrorInfo : ObservableObject, IDataErrorInfo { private string name; private int age; public string Name { get { return this.name; } set { this.name = value; this.OnPropertyChanged(() => this.Name); } } public int Age { get { return this.age; } set { this.age = value; this.OnPropertyChanged(() => this.Age); } } // never called by WPF public string Error { get { return null; } } public string this[string propertyName] { get { switch (propertyName) { case "Name": if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(this.Name)) { return "Name cannot be empty!"; } if (this.Name.Length < 4) { return "Name must have more than 4 char!"; } break; case "Age": if (this.Age < 18) { return "You must be an adult!"; } break; } return null; } } }
<Grid DataContext="{Binding PersonDerivedFromIDataErrorInfo}"> <Grid.RowDefinitions> <RowDefinition /> <RowDefinition /> </Grid.RowDefinitions> <Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" /> <ColumnDefinition /> </Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <TextBlock Text="Name:" /> <TextBox Grid.Column="1" Margin="1" Text="{Binding Name, NotifyOnValidationError=True, ValidatesOnDataErrors=True, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" /> <TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Text="Age:" /> <TextBox Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Margin="1" Text="{Binding Age, NotifyOnValidationError=True, ValidatesOnDataErrors=True, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" />
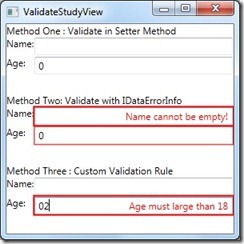
PS:这种方式,没有了第一种方法的BUG,但是相对很麻烦,既需要继承接口,又需要添加一个索引,如果遗留代码,那么这种方式就不太好。
3、自定义校验规则
一个数据对象或许不能包含一个应用要求的所有不同验证规则,但是通过自定义验证规则就可以解决这个问题。
在需要的地方,添加我们创建的规则,并进行检测。
通过继承ValidationRule抽象类,并实现Validate方法,并添加到绑定元素的Binding.ValidationRules中。
public class MinAgeValidation : ValidationRule { public int MinAge { get; set; } public override ValidationResult Validate(object value, CultureInfo cultureInfo) { ValidationResult result = null; if (value != null) { int age; if (int.TryParse(value.ToString(), out age)) { if (age < this.MinAge) { result = new ValidationResult(false, "Age must large than " + this.MinAge.ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)); } } else { result = new ValidationResult(false, "Age must be a number!"); } } else { result = new ValidationResult(false, "Age must not be null!"); } return new ValidationResult(true, null); } }
<Grid> <Grid.RowDefinitions> <RowDefinition /> <RowDefinition /> </Grid.RowDefinitions> <Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" /> <ColumnDefinition /> </Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <TextBlock Text="Name:" /> <TextBox Grid.Column="1" Margin="1" Text="{Binding Name}"> </TextBox> <TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Text="Age:" /> <TextBox Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Margin="1"> <TextBox.Text> <Binding Path="Age" UpdateSourceTrigger="PropertyChanged" ValidatesOnDataErrors="True"> <Binding.ValidationRules> <validations:MinAgeValidation MinAge="18" /> </Binding.ValidationRules> </Binding> </TextBox.Text> </TextBox> </Grid>
这种方式,也会有第一种方法的BUG,暂时还不知道如何解决,但是这个能够灵活的实现校验,并且能传参数。
效果图:
4、使用数据注解(特性方式)
在System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotaions命名空间中定义了很多特性,
它们可以被放置在属性前面,显示验证的具体需要。放置了这些特性之后,
属性中的Setter方法就可以使用Validator静态类了,来用于验证数据。
public class PersonUseDataAnnotation : ObservableObject { private int age; private string name; [Range(18, 120, ErrorMessage = "Age must be a positive integer")] public int Age { get { return this.age; } set { this.ValidateProperty(value, "Age"); this.SetProperty(ref this.age, value, () => this.Age); } } [Required(ErrorMessage = "A name is required")] [StringLength(100, MinimumLength = 3, ErrorMessage = "Name must have at least 3 characters")] public string Name { get { return this.name; } set { this.ValidateProperty(value, "Name"); this.SetProperty(ref this.name, value, () => this.Name); } } protected void ValidateProperty<T>(T value, string propertyName) { Validator.ValidateProperty(value,
new ValidationContext(this, null, null) { MemberName = propertyName });
}
}
<Grid> <Grid.RowDefinitions> <RowDefinition /> <RowDefinition /> </Grid.RowDefinitions> <Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" /> <ColumnDefinition /> </Grid.ColumnDefinitions> <TextBlock Text="Name:" /> <TextBox Grid.Column="1" Margin="1" Text="{Binding Name, ValidatesOnExceptions=True, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" /> <TextBlock Grid.Row="1" Text="Age:" /> <TextBox Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Margin="1" Text="{Binding Age, ValidatesOnExceptions=True, UpdateSourceTrigger=PropertyChanged}" /> </Grid>
使用特性的方式,能够很自由的使用自定义的规则,而且在.Net4.5中新增了很多特性,可以很方便的对数据进行校验。
例如:EmailAddress, Phone, and Url等。
三、自定义错误显示模板
在上面的例子中,我们可以看到当出现验证不正确时,绑定控件会被一圈红色错误线包裹住。
这种方式一般不能够正确的展示出,错误的原因等信息,所以有可能需要自己的错误显示方式。
前面,我们已经讲过了。当在检测过程中,出现错误时,WPF会把错误信息封装为一个ValidationError对象,
并添加到Validation.Errors中,所以我们可以取出错误详细信息,并显示出来。
1、为控件创建ErrorTemplate
下面就是一个简单的例子,每次都把错误信息以红色展示在空间上面。这里的AdornedElementPlaceholder相当于
控件的占位符,表示控件的真实位置。这个例子是在书上直接拿过来的,只能做基本展示用。
<ControlTemplate x:Key="ErrorTemplate"> <Border BorderBrush="Red" BorderThickness="2"> <Grid> <AdornedElementPlaceholder x:Name="_el" /> <TextBlock Margin="0,0,6,0" HorizontalAlignment="Right" VerticalAlignment="Center" Foreground="Red" Text="{Binding [0].ErrorContent}" /> </Grid> </Border> </ControlTemplate>
<TextBox x:Name="AgeTextBox" Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1" Margin="1" Validation.ErrorTemplate="{StaticResource ErrorTemplate}" >
使用方式非常简单,将上面的模板作为逻辑资源加入项目中,然后像上面一样引用即可。
效果图:
对知识梳理总结,希望对大家有帮助!