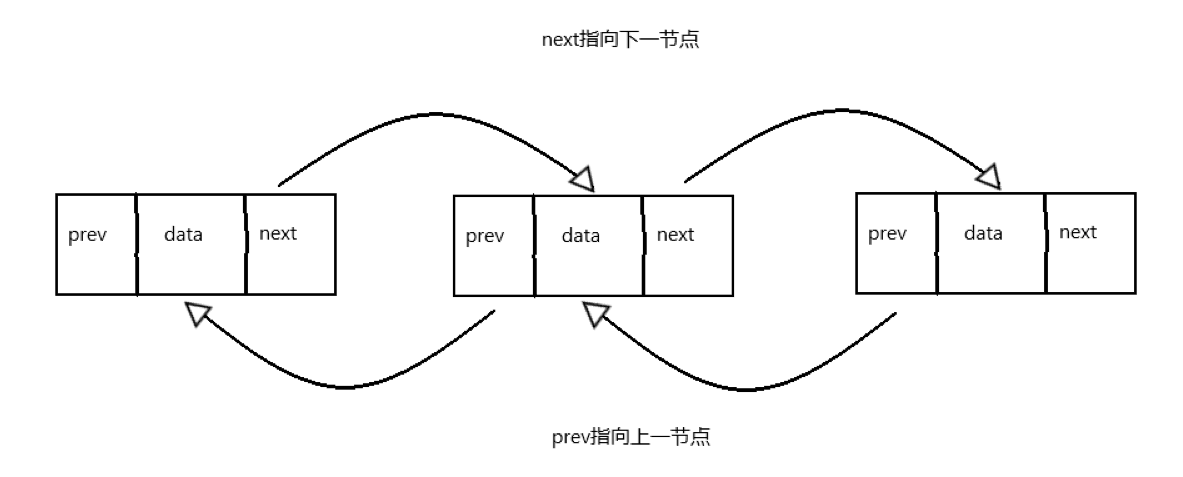
一、双向链表
双向链表与单链表基本相似,但是最大的区别在于双向链表在节点中除了指向下一节点的next指针外,还有指向前一节点的prev指针,这使得双向链表在可以在任意节点从头尾两个方向进行遍历,是“双向”的。
和单链表相比,双向链表在删除和查询等方面明显在操作上更具有灵活性,但是会消耗更多的内存,需要根据使用条件进行取舍。
java中的LinkedHashMap的本质即是一个双向链表。
二、双向链表的简单实现
修改原来的Node类,在里面添加一个新成员变量Node prev
/**
* @Author:huang
* @Date:2020-06-20 10:19
* @Description:节点类
*/
public class Node {
//节点序号
int num;
//数据
Object data;
//下一个节点
Node next;
//上一节点
Node prev;
public Node(int num, Object data) {
this.num = num;
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Node{" +
"num=" + num +
", data=" + data +
'}';
}
}
1.添加
添加与单向链表代码逻辑一样,但是新节点在添加时需要修改prev指针指向原来的尾节点。
举个例子,对于无排序插入,原本有节点A,现在要插入一个B:
- 找到A,然后让
A.next指向B - 让
B.prev指向A
而对于排序插入,就是原有节点A,C,要在中间插入B:
- 找到A,让
B.prev指向A - 让
B.next指向A.next,也就是让B的next指向C - 让
A.next.prev指向B,也就是让C的prev指向B - 让
A.next指向B
/**
* 添加节点到链表
* @param node 要插入的节点
*/
public void add(Node node) {
Node temp = head;
//遍历链表
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
//不是尾节点就继续遍历下一个节点
temp = temp.next;
}
//将尾节点指向即将插入的新节点
temp.next = node;
node.prev = temp;
}
/**
* 按顺序添加节点到链表
* @param node 要插入的节点
*/
public void addByOrder(Node node) {
Node temp = head;
//遍历链表
while (true) {
//如果链表到底了就直接插入
if (temp.next == null) {
temp.next = node;
node.prev = temp;
return;
}
else if (temp.next.num > node.num){
//如果后一节点比当新节点大,就插入当前节点
node.prev = temp;
node.next = temp.next;
temp.next.prev = node;
temp.next = node;
return;
}else if (temp.next.num == node.num){
//如果后一节点等于新节点,抛异常
throw new RuntimeException("插入节点与已有节点序号重复!");
}
//如果后一节点比当前节点小,就继续遍历
temp = temp.next;
}
}
2.删除
由于相对单链表,双向链表的节点可以自己找到上一节点,所以删除的时候可以直接找到要删除的节点进行操作。
举个例子,假设有节点A,B,C,现在要删除B:
- 找到B,让
B.prev.next=B.next,也就是让A的next指向C - 让
B.next.prev=B.prev,也就是让C的prev指向A
如果要删除的节点已经是尾节点了,那就跟单链表一样了。
/**
* 删除节点
* @param num 要删除的节点编号
*/
public void delete(int num) {
Node temp = head;
//判断链表是否为空
if (temp.next == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("链表为空!");
}
//遍历链表
while (true) {
//如果链表到底了
if (temp.next == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("编号为" + num + "的节点不存在!");
}
//如果找到了待删除节点的前一个节点
if (temp.num == num) {
//判断待删除节点是否为尾节点
if (temp.next == null){
temp.prev.next = null;
}else {
temp.prev.next = temp.next;
temp.next.prev = temp.prev;
}
return;
}
//继续遍历下一节点
temp = temp.next;
}
}
3.修改,查询(与单链表一致)
由于修改和查询与单链表基本一致,这里就不在赘述了,直接放代码:
/**
* 展示链表
*/
public void show() {
//判断链表是否为空
if (head.next == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("链表为空!");
}
Node temp = head.next;
//遍历链表
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
break;
}
System.out.println(temp.toString());
temp = temp.next;
}
}
/**
* 根据序号获取节点
* @param num 要获取的节点序号
* @return
*/
public Node get(int num){
//判断链表是否为空
if (head.next == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("链表为空!");
}
Node temp = head.next;
//遍历链表
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("编号为" + num + "的节点不存在!");
}
if (temp.num == num) {
return temp;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
}
/**
* 修改节点
* @param node 要更新的节点
*/
public void update(Node node) {
Node temp = head;
//判断链表是否为空
if (temp.next == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("链表为空!");
}
//获取要更新的节点序号
int nodeNum = node.num;
//遍历链表
while (true) {
//如果已经遍历完链表
if (temp == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("编号为" + temp.num + "的节点不存在!");
}
//如果找到了该节点
if (temp.num == nodeNum) {
temp.data = node.data;
return;
}
//继续遍历下一节点
temp = temp.next;
}
}