在启动MongoDB后,程序会对相应的参数,上次遗留的锁文件,日志文件等等进行相应的处理,同时也会开启一些支撑其他部分运行的服务线程,为了精读MongoDB的代码,领会其全局设计理念,所以我对这些不是特别核心的部分,也通过博文给自己来做一个总结,方便自己以后查阅。
程序在mian函数里进行了对输入参数的所有处理,程序使用Boost库实现了跨平台的命令行参数的兼容性,这部分的代码非常庞大,也非常的乱,所以也没有必要太过记载,在main函数的底部进行了initAndListen(cmdLine.port, appsrvPath);调用,这个函数就是我们的重点部分。
在void _initAndListen(int listenPort, const char *appserverLoc = NULL)内函数首先进行了一些运行环境的相关检验,如:判断当前系统是不是32bit系统:bool is32bit = sizeof(int*) == 4;接着输出一些版本信息(这部分代码就不贴了)后面进行了acquirePathLock()方法的调用。
string name = ( boost::filesystem::path( dbpath ) / "mongod.lock" ).native_file_string();
bool oldFile = false;
//oldFile为true的概念是存在mongod.lock并且它的filesize大于0,。 正常结束的进程会将mongodb.lock大小设置为0(包括CTRL+C)
if ( boost::filesystem::exists( name ) && boost::filesystem::file_size( name ) > 0 ) {
oldFile = true;
}
// we check this here because we want to see if we can get the lock
// if we can't, then its probably just another mongod running
lockFile = open( name.c_str(), O_RDWR | O_CREAT , S_IRWXU | S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO );
if( lockFile <= 0 ) {
uasserted( 10309 , str::stream() << "Unable to create / open lock file for lockfilepath: " << name << ' ' << errnoWithDescription());
}
if (flock( lockFile, LOCK_EX | LOCK_NB ) != 0) { //man 2 flock 查看参数
close ( lockFile );//若另一个mongod程序锁住了该文件,则flock LOCK_EX会失败(即返回结果!=0),抛出下面的异常,此处保证了一个dbpath不能被两个mongod程序同时打开
lockFile = 0;
uassert( 10310 , "Unable to acquire lock for lockfilepath: " + name, 0 );
}
if ( oldFile ) {
//若上次异常结束
string errmsg;
if (cmdLine.dur) {
//若开启了-dur属性
if (!dur::haveJournalFiles()) {
vector<string> dbnames;
getDatabaseNames( dbnames );//获取同一目录下的所有xx.ns的xx,存入dbnames
if ( dbnames.size() == 0 ) {//在没有任何xx.ns的情况下,不需要修复,所以也就不需要处理了,直接让程序继续运行
// this means that mongod crashed
// between initial startup and when journaling was initialized
// it is safe to continue
}
else {
errmsg = str::stream()
<< "************** \n"
<< "old lock file: " << name << ". probably means unclean shutdown,\n"
<< "but there are no journal files to recover.\n"
<< "this is likely human error or filesystem corruption.\n"
<< "found " << dbnames.size() << " dbs.\n"
<< "see: http://dochub.mongodb.org/core/repair for more information\n"
<< "*************";
}
}
}
else {
//若没有开启了-dur属性又存在.lock文件,则给出错误信息到errmsg
errmsg = str::stream()
<< "************** \n"
<< "old lock file: " << name << ". probably means unclean shutdown\n"
<< "recommend removing file and running --repair\n"
<< "see: http://dochub.mongodb.org/core/repair for more information\n"
<< "*************";
}
//若有上面errmsg有任何错误信息,则停止程序
if (!errmsg.empty()) {
cout << errmsg << endl;
close ( lockFile );
lockFile = 0;
uassert( 12596 , "old lock file" , 0 );
}
}
// Not related to lock file, but this is where we handle unclean shutdown
if( !cmdLine.dur && dur::haveJournalFiles() ) {//如果竟不是-dur模式启动,但又有Journal日志文件,则异常退出,因为无法处理未持久化的数据
cout << "**************" << endl;
cout << "Error: journal files are present in journal directory, yet starting without --dur enabled." << endl;
cout << "It is recommended that you start with journaling enabled so that recovery may occur." << endl;
cout << "Alternatively (not recommended), you can backup everything, then delete the journal files, and run --repair" << endl;
cout << "**************" << endl;
uasserted(13597, "can't start without --dur enabled when journal/ files are present");
}
uassert( 13342, "Unable to truncate lock file", ftruncate(lockFile, 0) == 0);
writePid( lockFile );//将进程号写入了mongod.lock文件
fsync( lockFile );
}
对于这段代码的逻辑,我这里就不罗嗦了,我画了一张流程图,我相信图片比代码更容易让人理解。
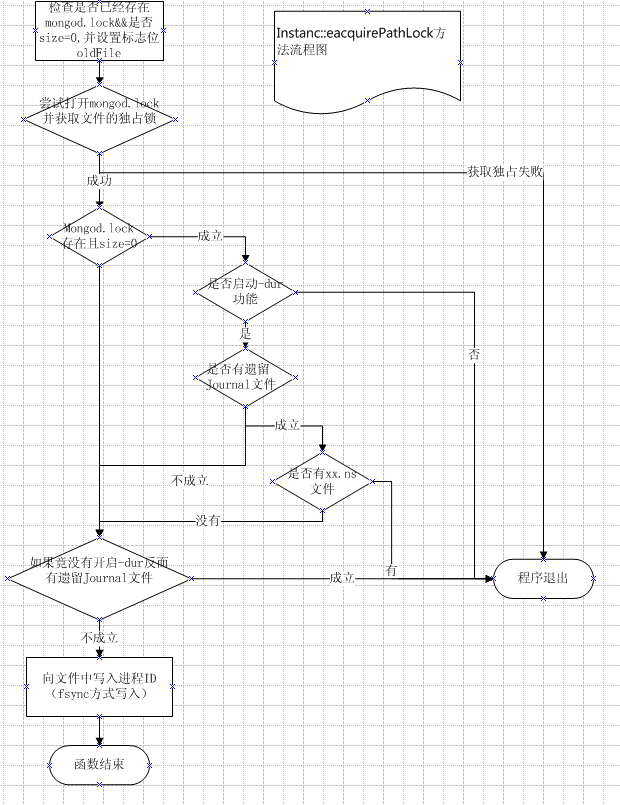
oldFile为true的概念是存在mongod.lock并且它的filesize大于0,对于这一点可能大家不太容易理解filesize在这个特定语境的意思,我们来看在db.cpp里注册的信号处理函数就明白了。
log() << "got kill or ctrl-c signal, will terminate after current cmd ends" << endl;
Client::initThread( "ctrlCTerminate" );
exitCleanly( EXIT_KILL );
}
在exitCleanly中 最后调用了shutdownServer函数,负责所有的扫尾工作,对于我们关注的mongo.lock的处理部分如下:
log() << "shutdown: removing fs lock..." << endl;
if( ftruncate( lockFile , 0 ) ) //man ftruncate 设置文件大小为0
log() << "couldn't remove fs lock " << errnoWithDescription() << endl;
flock( lockFile, LOCK_UN );
}
也就是是,只要是正常退出(包括CTRL+C),mongo.lock的大小就会为0,所以可以通过它来判断上次服务此是怎么结束的。
在_initAndListen 方法中还进行了如下调用:
FileAllocator::get()->start();
一看到这种调用入口,就可以推测出这里肯定使用的是单例模式![]()
在我们调用的start方法中,FileAllocator创建了一个单独的线程来专门运行其run方法
2 boost::thread t( boost::bind( &FileAllocator::run , this ) );
}
当系统的其他运行部分需要使用它的服务的时候,只需要在那个线程调用 FileAllocator::requestAllocation函数
这个函数会把用户想要创建的文件名放入list< string > _pending 中存储,将其文件名和大小对应关系存入mutable map< string, long >中
同时这个函数还是用了boost::condition来进行同步操作(类似于生产者消费者),在run函数中,放文件创建需求列表(_pending)为空时会进行等待
fa->_pendingUpdated.wait( lk.boost() );
这样就防止了无限循环while所带来了损耗CPU时间的弊端
若需求列表中有需要创建的item了就会调用系统API进行文件创建
long fd = open(name.c_str(), O_CREAT | O_RDWR | O_NOATIME, S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR);
通过上面的调用, 文件是被创建了,可是需求却没有得到满足,因为我们创建的文件不是指定大小的,这里有必要解释一下为什么需要先创建指定大小的文件,因为对于数据库文件来说,操作很有可能是非常频繁,这就对我存数据的文件提出了要求,我们总是希望数据库文件在磁盘上能得到一块连续的空间(就像内存分配一样),这样对文件进行读写的时候,文件的fragments比较少,读起来也会比较快(系统API级别的,不可控的),所以一般希望能够Handles allocation of contiguous files on disk
下面来看mongoDB是怎么处理这个问题的:
在调用open创建文件后会进行 ensureLength( fd , size )调用,在ensureLength内部会进行下面的循环
2 memset(buf, 0, z);
3 long left = size;
4 while ( left > 0 ) {
5 long towrite = left;
6 if ( towrite > z )
7 towrite = z;
8
9 int written = write( fd , buf , towrite );
10 uassert( 10443 , errnoWithPrefix("FileAllocator: file write failed" ), written > 0 );
11 left -= written;
}
看完 之后你会不会很惊讶,居然创建指定大小的文件是通过while循环来做的,没错,不管你有没有惊讶,反正我惊讶了。
后来仔细一想,其实这也是一个还不错的方案,毕竟暂时我还没有发现任何可以创建指定大小,空间连续的文件的方法,虽然用上面的方法不能保证空间就一定连续,但是集中在一个时间在占用文件大小,比需要时每次再去写一下,fragments会少很多。
Ok,现在总结一下,FileAllocator的职责就是尽量创建fragments少的指定大小的文件,实现方法为,一个线程专门用于提供创建文件和填充到指定大小的服务,其他的线程调用requestAllocation函数进行需求注册,服务线程获取需求,然后工作,其实也可以理解为一种生产者消费者模式,其他的线程生产出需求(文件名,大小),这可以理解为生产者,而服务线程可以理解为消费者,只有需求到达时才运行,否则等待....