先附上两张流程图

1.scheduleRootUpdate 这个函数主要执行了两个操作 1个是创建更新createUpdate并放到更新队列enqueueUpdate, 1个是执行sheculeWork函数
function scheduleRootUpdate(current$$1, element, expirationTime, callback) { var update = createUpdate(expirationTime); update.payload = { element: element }; callback = callback === undefined ? null : callback; if (callback !== null) { update.callback = callback; } enqueueUpdate(current$$1, update); scheduleWork(current$$1, expirationTime); return expirationTime; }
先从createUpdate函数分析, 他直接返回了一个包含了更新信息的对象
function createUpdate(expirationTime) { return { // 优先级 expirationTime: expirationTime, // 更新类型 tag: UpdateState, // 更新的对象 payload: null, callback: null, // 指向下一个更新 next: null, // 指向下一个更新effect nextEffect: null }; }
接着更新payload和callback属性, payload即为更新的对象, 然后执行enqueuUpdate, enqueueUpdate相对比较容易理解, 不过里面有一注释挺重要
Both queues are non-empty. The last update is the same in both lists, because of structural sharing. So, only append to one of the lists 意思是alternate的updateQueue和fiber的updateQueue是同一个对象引用,这里会在createWorkInProcess提到
往下走就是重要的scheduleWork, 它是render阶段真正的开始
function scheduleWork(fiber, expirationTime) { // 更新优先级 var root = scheduleWorkToRoot(fiber, expirationTime); ...if (!isWorking && nextRenderExpirationTime !== NoWork && expirationTime < nextRenderExpirationTime) { // This is an interruption. (Used for performance tracking.) 如果这是一个打断原有更新的任务, 先把现有任务记录 interruptedBy = fiber; resetStack(); }
// 设置下一个操作时间nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn markPendingPriorityLevel(root, expirationTime); if ( // If we're in the render phase, we don't need to schedule this root // for an update, because we'll do it before we exit... !isWorking || isCommitting$1 || // ...unless this is a different root than the one we're rendering. nextRoot !== root) { var rootExpirationTime = root.expirationTime; requestWork(root, rootExpirationTime); } ... }
scheduleWork先执行一个scheduleWorkToRoot函数, 该函数主要是更新其expirationTime以及上层fiber的childrenExpirationTime
function scheduleWorkToRoot(fiber, expirationTime) { // Update the source fiber's expiration time if (fiber.expirationTime === NoWork || fiber.expirationTime > expirationTime) { fiber.expirationTime = expirationTime; } var alternate = fiber.alternate; if (alternate !== null && (alternate.expirationTime === NoWork || alternate.expirationTime > expirationTime)) { alternate.expirationTime = expirationTime; } // 如果是HostRoot 即直接返回 var node = fiber.return; if (node === null && fiber.tag === HostRoot) { return fiber.stateNode; }
// 若子fiber中有更新, 即更新其childrenExpirationTime while (node !== null) { ... } return null; }
接着会执行一个markPendingPriorityLevel函数, 这个函数主要是更新root的最高优先级和最低优先级(earliestPendingTime和lastestPendingTime;), 同时设置下一个执行操作的时间nextExpirationTimeToWorkOn(即root中具有最高优先级的fiber的expirationTime),关于这个函数的 latestSuspendedTime;以后再说
最后scheduleWork会执行requestWork
function requestWork(root, expirationTime) { addRootToSchedule(root, expirationTime); if (isRendering) { // rendering状态,直接返回 return; } if (isBatchingUpdates) { // isBatchingUpdates, 直接返回。 react的state更新是会合并的 ...return; } // TODO: Get rid of Sync and use current time? if (expirationTime === Sync) {
// 执行同步 performSyncWork(); } else {
// 异步, 暂不分析 scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(root, expirationTime); } }
requestWork 会先执行addRootToSchedule,由函数名称可知其作用,将root加到schedule, 即设置firstScheduledRoot, lastScheduledRoot以及他们的nextScheduleRoot属性, 说白了就是一个闭环链式结构 first => next => next => last(next => first), 同时更新root的expirationTime属性
function addRootToSchedule(root, expirationTime) { // root尚未开始过任务 将root加到schedule if (root.nextScheduledRoot === null) { ... } else { // root已经开始执行过任务, 更新root的expirationTime var remainingExpirationTime = root.expirationTime; if (remainingExpirationTime === NoWork || expirationTime < remainingExpirationTime) { root.expirationTime = expirationTime; } } }
接着requestWork会判断是否正在渲染中,防止重入。剩余的工作将安排在当前渲染批次的末尾
如果正在渲染直接返回后, 因为已经把root加上到Schedule里面了,依然会把该root执行
同时判断是否正在batch update, 这里留到分析setState的时候说, 最后根据异步或者同步执行不同函数, 此处执行同步performSyncWork(),performSyncWork直接执行performWork(Sync, null);
function performWork(minExpirationTime, dl) { deadline = dl; // 找出优先级最高的root findHighestPriorityRoot(); if (deadline !== null) { // ...异步 } else {
// 循环执行root任务 while (nextFlushedRoot !== null && nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork && (minExpirationTime === NoWork || minExpirationTime >= nextFlushedExpirationTime)) { performWorkOnRoot(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime, true); findHighestPriorityRoot(); } } ... // If there's work left over, schedule a new callback. if (nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork) { scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime); } ... }
performWork首先执行findHighestPriorityRoot函数。findHighestPriorityRoot函数主要执行两个操作, 一个是判断当前root是否还有任务,如果没有, 则从firstScheuleRoot链中移除。 一个是找出优先级最高的root和其对应的优先级并赋值给
nextFlushedRoot
extFlushedExpirationTime
function findHighestPriorityRoot() { var highestPriorityWork = NoWork; var highestPriorityRoot = null; if (lastScheduledRoot !== null) { var previousScheduledRoot = lastScheduledRoot; var root = firstScheduledRoot; while (root !== null) { var remainingExpirationTime = root.expirationTime; if (remainingExpirationTime === NoWork) { // 判断是否还有任务并移除 } else { // 找出最高的优先级root和其对应的优先级 } } } // 赋值 nextFlushedRoot = highestPriorityRoot; nextFlushedExpirationTime = highestPriorityWork; }
紧着, performWork会根据传入的参数dl来判断进行同步或者异步操作, 这里暂不讨论异步,
while (nextFlushedRoot !== null && nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork && (minExpirationTime === NoWork || minExpirationTime >= nextFlushedExpirationTime)) { performWorkOnRoot(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime, true); findHighestPriorityRoot(); }
接着, 会进行performWorkOnRoot函数, 并传入优先级最高的root和其对应的expirationTime以及一个true作为参数,
performWorkOnRoot函数的第三个参数isExpired主要是用来判断是否已超过执行时间, 由于进行的是同步操作, 所以默认超过
performWorkOnRoot函数会先将rendering状态设为true, 然后判断是否异步或者超时进行操作
function performWorkOnRoot(root, expirationTime, isExpired) { // 将rendering状态设为true isRendering = true; // Check if this is async work or sync/expired work. if (deadline === null || isExpired) { // Flush work without yielding. // 同步 var finishedWork = root.finishedWork; if (finishedWork !== null) { // This root is already complete. We can commit it. completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime); } else { root.finishedWork = null; // If this root previously suspended, clear its existing timeout, since // we're about to try rendering again. var timeoutHandle = root.timeoutHandle; if (enableSuspense && timeoutHandle !== noTimeout) { root.timeoutHandle = noTimeout; // $FlowFixMe Complains noTimeout is not a TimeoutID, despite the check above cancelTimeout(timeoutHandle); } var isYieldy = false; renderRoot(root, isYieldy, isExpired); finishedWork = root.finishedWork; if (finishedWork !== null) { // We've completed the root. Commit it. completeRoot(root, finishedWork, expirationTime); } } } else { // Flush async work.异步操作 ...... } } isRendering = false; }
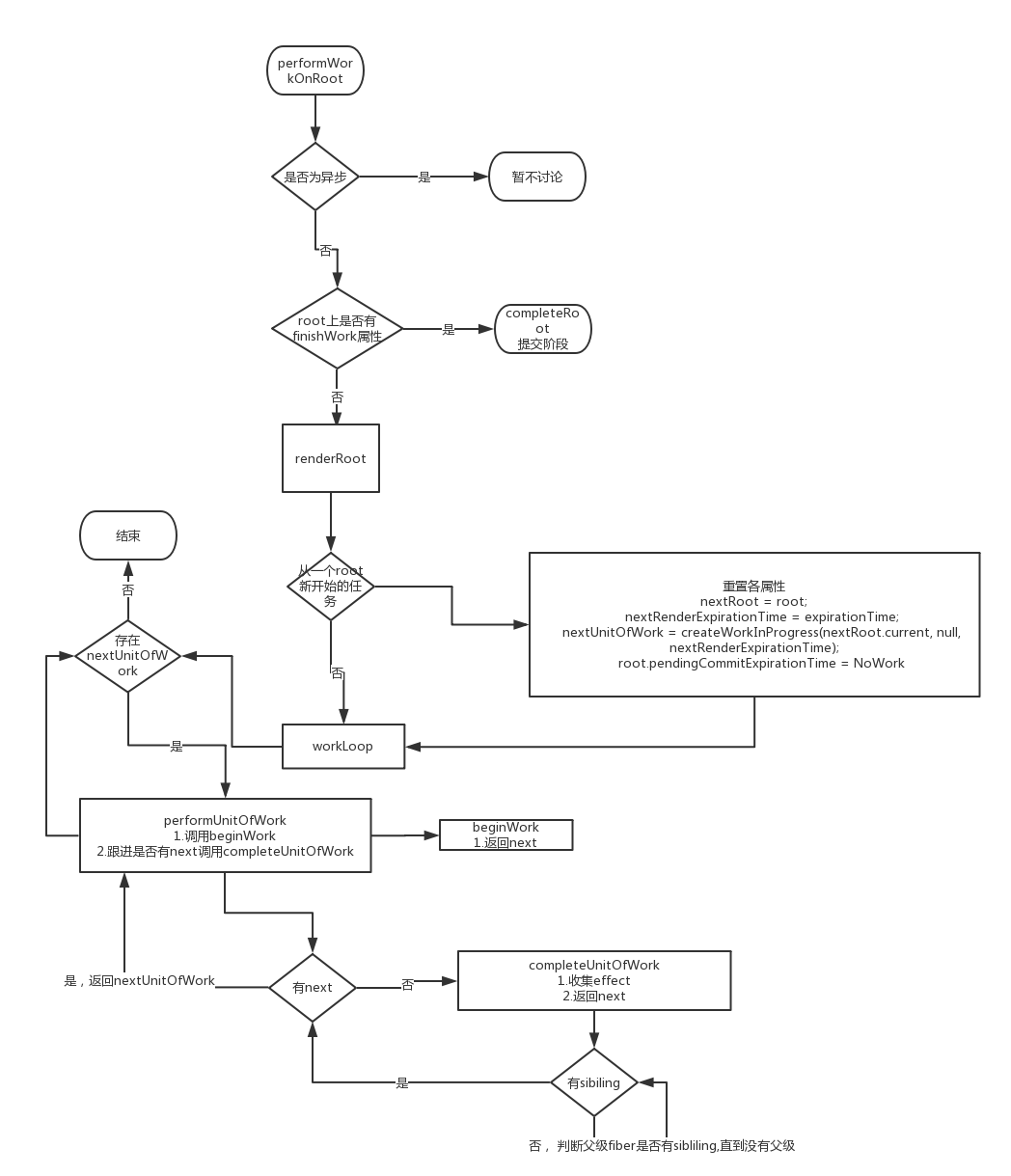
renderRoot的产物会挂载到root的finishWork属性上, 首先performWorkOnRoot会先判断root的finishWork是否不为空, 如果存在的话则直接进入commit的阶段, 否则进入到renderRoot函数, 设置finishWork属性
renderRoot有三个参数, renderRoot(root, isYieldy, isExpired), 同步状态下isYield的值是false,
renderRoot 先将 isWorking设为true,
renderRoot会先判断是否是一个从新开始的root, 是的话会重置各个属性
首先是resetStach()函数, 对原有的进行中的root任务中断, 进行存储
紧接着将nextRoot
extRendeExpirationTime重置, 同时创建第一个nextUnitOfWork, 也就是一个工作单元
这个nextUnitOfWork也是一个workProgress, 也是root.current的alternater属性, 而它的alternate属性则指向了root.current, 形成了一个双缓冲池
if (expirationTime !== nextRenderExpirationTime || root !== nextRoot || nextUnitOfWork === null) { // 判断是否是一个从新开始的root resetStack(); nextRoot = root; nextRenderExpirationTime = expirationTime; nextUnitOfWork = createWorkInProgress(nextRoot.current, null, nextRenderExpirationTime); root.pendingCommitExpirationTime = NoWork; .... .... }
接着执行wookLoop(isYield)函数, 该函数通过循环执行, 遍历每一个nextUniOfWork,
function workLoop(isYieldy) { if (!isYieldy) { // Flush work without yielding while (nextUnitOfWork !== null) { nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork); } } else { // Flush asynchronous work until the deadline runs out of time. while (nextUnitOfWork !== null && !shouldYield()) { nextUnitOfWork = performUnitOfWork(nextUnitOfWork); } } }
performUnitOfWork 先 获取 参数的alaernate属性, 赋值给current,
根据注释的意思, workInProgress是作为一个代替品存在来操作, 然后会执行下面这个语句
next = beginWork(current$$1, workInProgress, nextRenderExpirationTime);
beginWork主要根据workInprogress的tag来做不同的处理, 并返回其child, 也就是下一个工作单元 如<div><p></p><div>, div作为一个工作单元, 处理完后就返回工作单元p, 同时收集他们的effect
若next存在, 则返回到workLoop函数继续循环, 若不存在, 则执行completeUnitOfWork(workInProgress)函数
completeUnitOfWork函数, 会判断是否有sibiling, 有则直接返回赋值给next, 否则判断父fiber是否有sibiling, 一直循环到最上层 父fiber为null, 执行的同时会把effect逐级传给父fiber
这个时候函数执行完毕, 会返回到renderRoot函数, renderRoot函数继续往下走
首先将isWorking = false;执行, 然后会判断nextUnitWork是否为空, 否的话则将root.finishWork设为空(异步, 该任务未执行完)并结束函数
isWorking = false;
if (nextUnitOfWork !== null) { onYield(root); return; }
重置nextRoot等
nextRoot = null; interruptedBy = null;
赋值finishWork
var rootWorkInProgress = root.current.alternate; onComplete(root, rootWorkInProgress, expirationTime); function onComplete(root, finishedWork, expirationTime) { root.pendingCommitExpirationTime = expirationTime; root.finishedWork = finishedWork; }
返回到performWorkOnRoot函数, 进入commit阶段, 将rending状态设为false,返回到performWork函数, 继续进入循环执行root, 直到所有root完成
重置各个状态量, 如果还存在nextFlushedExpirationTime不为空, 则进行scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime函数异步操作
if (deadline !== null) { callbackExpirationTime = NoWork; callbackID = null; } // If there's work left over, schedule a new callback. if (nextFlushedExpirationTime !== NoWork) { scheduleCallbackWithExpirationTime(nextFlushedRoot, nextFlushedExpirationTime); } // Clean-up. deadline = null; deadlineDidExpire = false;