转载:https://blog.csdn.net/younghaiqing/article/details/62884658
一. 什么是存储过程
系统存储过程是系统创建的存储过程,目的在于能够方便的从系统表中查询信息或完成与更新数据库表相关的管理任务或其他的系统管理任务。系统存储过程主要存储在master数据库中,以“sp”下划线开头的存储过程。尽管这些系统存储过程在master数据库中,但我们在其他数据库还是可以调用系统存储过程。有一些系统存储过程会在创建新的数据库的时候被自动创建在当前数据库中。
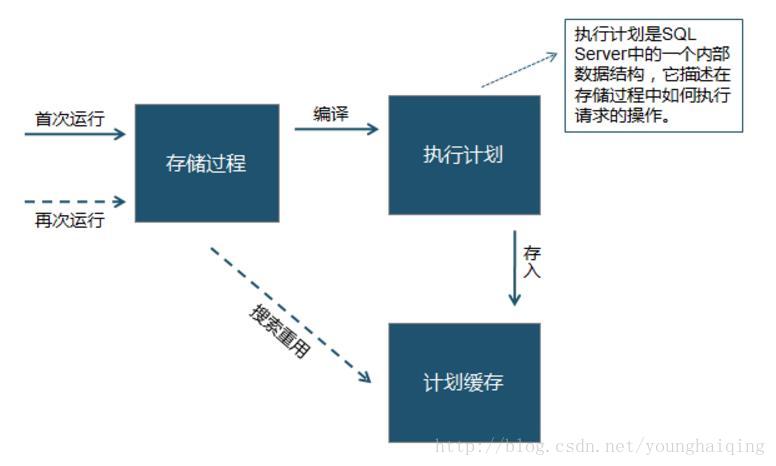
二. 存储过程运行流程
存储过程是由一些SQL语句和控制语句组成的被封装起来的过程,它驻留在数据库中,可以被客户应用程序调用,也可以从另一个过程或触发器调用。它的参数可以被传递和返回。与应用程序中的函数过程类似,存储过程可以通过名字来调用,而且它们同样有输入参数和输出参数。
根据返回值类型的不同,我们可以将存储过程分为三类:
- 返回记录集的存储过程的执行结果是一个记录集,典型的例子是从数据库中检索出符合某一个或几个条件的记录;
- 返回数值的存储过程执行完以后返回一个值,例如在数据库中执行一个有返回值的函数或命令;
- 行为存储过程仅仅是用来实现数据库的某个功能,而没有返回值,例如在数据库中的更新和删除操作。
个人认为,存储过程说白了就是一堆 SQL 的合并。中间加了点逻辑控制。
- 但是存储过程处理比较复杂的业务时比较实用。比如说,
一个复杂的数据操作。如果你在前台处理的话。可能会涉及到多次数据库连接。但如果你用存储过程的话。就只有一次。从响应时间上来说有优势。
- 也就是说存储过程可以给我们带来运行效率提高的好处。
另外,程序容易出现 BUG 不稳定,而存储过程,只要数据库不出现问题,基本上是不会出现什么问题的。也就是说从安全上讲,使用了存储过程的系统更加稳定。
那么问题来了,什么时候才可以用存储?对于数据量不是很大以及业务处理不是很复杂的小项目就无需要了么?
答:错。存储过程不仅仅适用于大型项目,对于中小型项目,使用存储过程也是非常有必要的。其威力和优势主要体现在:
- 存储过程只在创造时进行编译,以后每次执行存储过程都不需再重新编译,而一般 SQL 语句每执行一次就编译一次,所以使用存储过程可提高数据库执行速度。
- 当对数据库进行复杂操作时(如对多个表进行 Update,Insert,Query,Delete 时),可将此复杂操作用存储过程封装起来与数据库提供的事务处理结合一起使用。这些操作,如果用程序来完成,就变成了一条条的 SQL 语句,可能要多次连接数据库。而换成存储,只需要连接一次数据库就可以了。
- 存储过程可以重复使用,可减少数据库开发人员的工作量。
- 安全性高,可设定只有某此用户才具有对指定存储过程的使用权。
- 减少网络通信量。调用一个行数不多的存储过程与直接调用SQL语句的网络通信量可能不会有很大的差别,可是如果存储过程包含上百行SQL语句,那么其性能绝对比一条一条的调用SQL语句要高得多。
- 执行速度更快。有两个原因:首先,在存储过程创建的时候,数据库已经对其进行了一次解析和优化。其次,存储过程一旦执行,在内存中就会保留一份这个存储过程,这样下次再执行同样的存储过程时,可以从内存中直接调用。
- 更强的适应性:由于存储过程对数据库的访问是通过存储过程来进行的,因此数据库开发人员可以在不改动存储过程接口的情况下对数据库进行任何改动,而这些改动不会对应用程序造成影响。
- 布式工作:应用程序和数据库的编码工作可以分别独立进行,而不会相互压制。
存储过程的使用,好像一直是一个争论。
我不倾向于尽可能使用存储过程,是这么认为的:
- 运行速度: 大多数高级的数据库系统都有statement cache的,所以编译sql的花费没什么影响。但是执行存储过程要比直接执行sql花费更多(检查权限等),所以对于很简单的sql,存储过程没有什么优势。
- 网络负荷:如果在存储过程中没有多次数据交互,那么实际上网络传输量和直接sql是一样的。
- 团队开发:很遗憾,比起成熟的IDE,没有什么很好存储过程的IDE工具来支持,也就是说,这些必须手工完成。
- 安全机制:对于传统的C/S结构,连接数据库的用户可以不同,所以安全机制有用;但是在web的三层架构中,数据库用户不是给用户用的,所以基本上,只有一个用户,拥有所有权限(最多还有一个开发用户)。这个时候,安全机制有点多余。
- 用户满意:实际上这个只是要将访问数据库的接口统一,是用存储过程,还是EJB,没太大关系,也就是说,在三层结构中,单独设计出一个数据访问层,同样能实现这个目标。
- 开发调试:一样由于IDE的问题,存储过程的开发调试要比一般程序困难(老版本DB2还只能用C写存储过程,更是一个灾难)。
- 移植性:算了,这个不用提,反正一般的应用总是绑定某个数据库的,不然就无法靠优化数据库访问来提高性能了。
- 维护性:的确,存储过程有些时候比程序容易维护,这是因为可以实时更新DB端的存储过程,但是在3层结构下,更新server端的数据访问层一样能实现这个目标,可惜现在很多平台不支持实时更新而已。
常用系统存储过程有:
exec sp_databases; --查看数据库
exec sp_tables; --查看表
exec sp_columns student;--查看列
exec sp_helpIndex student;--查看索引
exec sp_helpConstraint student;--约束
exec sp_stored_procedures;
exec sp_helptext 'sp_stored_procedures';--查看存储过程创建、定义语句
exec sp_rename student, stuInfo;--修改表、索引、列的名称
exec sp_renamedb myTempDB, myDB;--更改数据库名称
exec sp_defaultdb 'master', 'myDB';--更改登录名的默认数据库
exec sp_helpdb;--数据库帮助,查询数据库信息
exec sp_helpdb master;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
系统存储过程示例:
--表重命名
exec sp_rename 'stu', 'stud';
select * from stud;
--列重命名
exec sp_rename 'stud.name', 'sName', 'column';
exec sp_help 'stud';
--重命名索引
exec sp_rename N'student.idx_cid', N'idx_cidd', N'index';
exec sp_help 'student';
--查询所有存储过程
select * from sys.objects where type = 'P';
select * from sys.objects where type_desc like '%pro%' and name like 'sp%';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
用户自定义存储过程
create proc | procedure pro_name
[{@参数数据类型} [=默认值] [output],
{@参数数据类型} [=默认值] [output],
....
]
as
SQL_statements- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
2、 创建不带参数存储过程
--创建存储过程
if (exists (select * from sys.objects where name = 'proc_get_student'))
drop proc proc_get_student
go
create proc proc_get_student
as
select * from student;
--调用、执行存储过程
exec proc_get_student;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
3、 修改存储过程
--修改存储过程
alter proc proc_get_student
as
select * from student;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
4、 带参存储过程
--带参存储过程
if (object_id('proc_find_stu', 'P') is not null)
drop proc proc_find_stu
go
create proc proc_find_stu(@startId int, @endId int)
as
select * from student where id between @startId and @endId
go
exec proc_find_stu 2, 4;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
5、 带通配符参数存储过程
--带通配符参数存储过程
if (object_id('proc_findStudentByName', 'P') is not null)
drop proc proc_findStudentByName
go
create proc proc_findStudentByName(@name varchar(20) = '%j%', @nextName varchar(20) = '%')
as
select * from student where name like @name and name like @nextName;
go
exec proc_findStudentByName;
exec proc_findStudentByName '%o%', 't%';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
6、 带输出参数存储过程
if (object_id('proc_getStudentRecord', 'P') is not null)
drop proc proc_getStudentRecord
go
create proc proc_getStudentRecord(
@id int, --默认输入参数
@name varchar(20) out, --输出参数
@age varchar(20) output--输入输出参数
)
as
select @name = name, @age = age from student where id = @id and sex = @age;
go
--
declare @id int,
@name varchar(20),
@temp varchar(20);
set @id = 7;
set @temp = 1;
exec proc_getStudentRecord @id, @name out, @temp output;
select @name, @temp;
print @name + '#' + @temp;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
7、 不缓存存储过程
--WITH RECOMPILE 不缓存
if (object_id('proc_temp', 'P') is not null)
drop proc proc_temp
go
create proc proc_temp
with recompile
as
select * from student;
go
exec proc_temp;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
8、 加密存储过程
--加密WITH ENCRYPTION
if (object_id('proc_temp_encryption', 'P') is not null)
drop proc proc_temp_encryption
go
create proc proc_temp_encryption
with encryption
as
select * from student;
go
exec proc_temp_encryption;
exec sp_helptext 'proc_temp';
exec sp_helptext 'proc_temp_encryption';- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
9、 带游标参数存储过程
if (object_id('proc_cursor', 'P') is not null)
drop proc proc_cursor
go
create proc proc_cursor
@cur cursor varying output
as
set @cur = cursor forward_only static for
select id, name, age from student;
open @cur;
go
--调用
declare @exec_cur cursor;
declare @id int,
@name varchar(20),
@age int;
exec proc_cursor @cur = @exec_cur output;--调用存储过程
fetch next from @exec_cur into @id, @name, @age;
while (@@fetch_status = 0)
begin
fetch next from @exec_cur into @id, @name, @age;
print 'id: ' + convert(varchar, @id) + ', name: ' + @name + ', age: ' + convert(char, @age);
end
close @exec_cur;
deallocate @exec_cur;--删除游标- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
10、 分页存储过程
---存储过程、row_number完成分页
if (object_id('pro_page', 'P') is not null)
drop proc proc_cursor
go
create proc pro_page
@startIndex int,
@endIndex int
as
select count(*) from product
;
select * from (
select row_number() over(order by pid) as rowId, * from product
) temp
where temp.rowId between @startIndex and @endIndex
go
--drop proc pro_page
exec pro_page 1, 4
--
--分页存储过程
if (object_id('pro_page', 'P') is not null)
drop proc pro_stu
go
create procedure pro_stu(
@pageIndex int,
@pageSize int
)
as
declare @startRow int, @endRow int
set @startRow = (@pageIndex - 1) * @pageSize +1
set @endRow = @startRow + @pageSize -1
select * from (
select *, row_number() over (order by id asc) as number from student
) t
where t.number between @startRow and @endRow;
exec pro_stu 2, 2;- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
Raiserror返回用户定义的错误信息,可以指定严重级别,设置系统变量记录所发生的错误。
Raiserror({msg_id | msg_str | @local_variable}
{, severity, state}
[,argument[,…n]]
[with option[,…n]]
)- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
# msg_id:在sysmessages系统表中指定的用户定义错误信息
# msg_str:用户定义的信息,信息最大长度在2047个字符。
# severity:用户定义与该消息关联的严重级别。当使用msg_id引发使用sp_addmessage创建的用户定义消息时,raiserror上指定严重性将覆盖sp_addmessage中定义的严重性。
任何用户可以指定0-18直接的严重级别。只有sysadmin固定服务器角色常用或具有alter trace权限的用户才能指定19-25直接的严重级别。19-25之间的安全级别需要使用with log选项。
- 1
- 2
# state:介于1至127直接的任何整数。State默认值是1。
raiserror('is error', 16, 1);
select * from sys.messages;
--使用sysmessages中定义的消息
raiserror(33003, 16, 1);
raiserror(33006, 16, 1);- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
http://www.cnblogs.com/hoojo/archive/2011/07/19/2110862.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/teroy/archive/2013/05/09/3045236.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/selene/p/4483612.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaozhuoyun/archive/2008/06/11/1217415.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/ashleyboy/p/3731550.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/kerrycode/archive/2010/08/14/1799392.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/shpchan/archive/2009/09/23/1572915.html
http://blog.csdn.net/smeyou/article/details/7580862
http://www.jianshu.com/p/d0ec20874f40
http://www.cnblogs.com/zhanht/p/5424469.html