初始化流程
Vue的初始化流程,是从 new Vue() 开始的,从以下的图中可以看知道。在 new Vue()后,会执行init,再 $mount实现挂载,再到编译compile,生成render函数,接下来是响应式依赖收集,通过pach实现异步更新 。render function 会被转化为Vnode节点,Virtual DOM 是一棵以JavaScript对象(Vnode节点)为基础的树。是对真实DOM的描述。通过patch() 转化为真的 DOM。在数据有变化时,会通过setter -> Watcher -> update 来更新视图。整个Vue的运行机制大致就是这样。
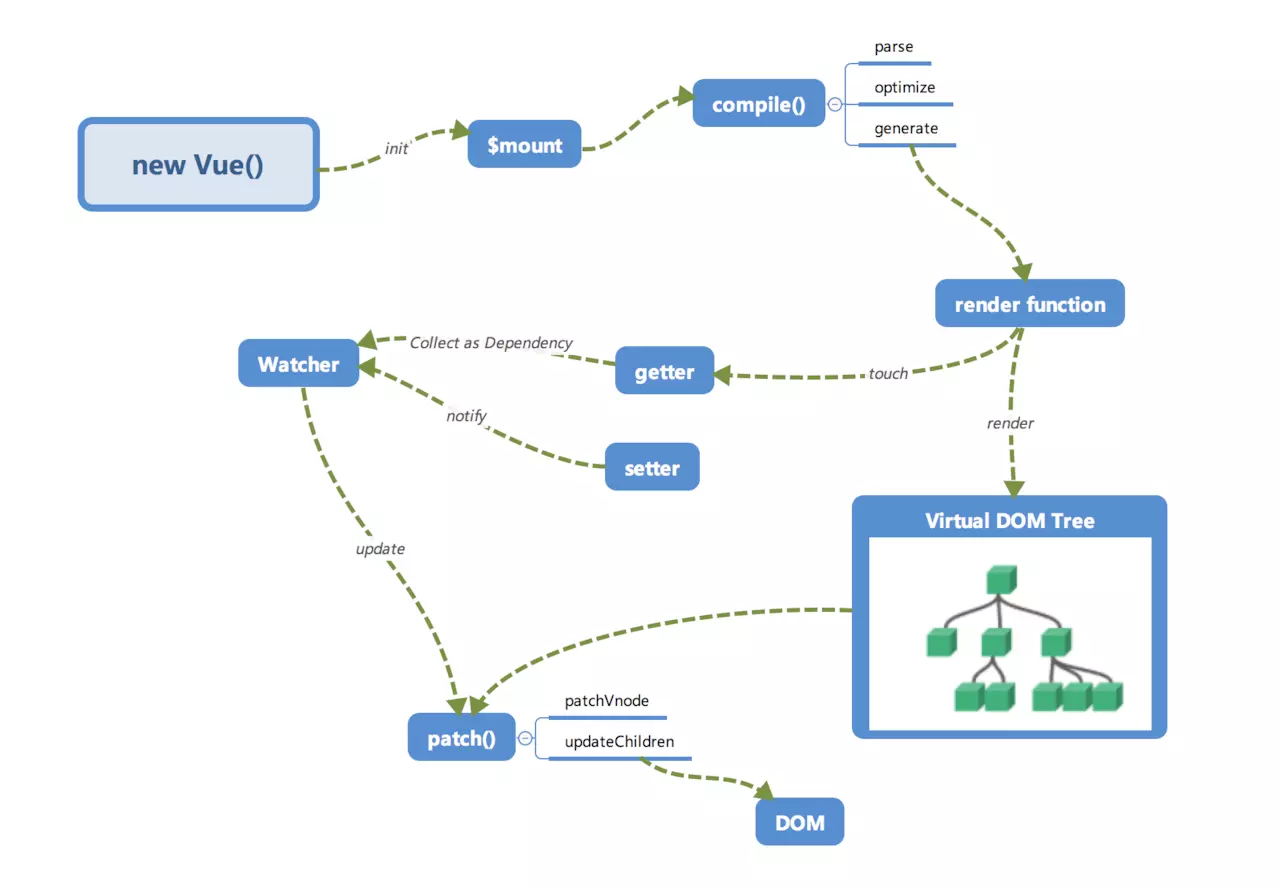
接下来,我们来看在 new Vue() 过后发生了什么。Vue 中我们是通过 $mount 实现方法去挂载 vm 的。我们接下来主要分析带 complier 版本的 $mount 。
带 compiler 版本的 $mount 是在 src/platform/web/entry-runtime-with-compiler.js 中定义的。
const mount = Vue.prototype.$mount // 扩展了$mount 方法 Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( el?: string | Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { el = el && query(el) /* istanbul ignore if */ if (el === document.body || el === document.documentElement) { process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && warn( `Do not mount Vue to <html> or <body> - mount to normal elements instead.` ) return this } // 处理el 和 template 选项 const options = this.$options // resolve template/el and convert to render function // render 不存在时才考虑 el 和 template if (!options.render) { let template = options.template if (template) { if (typeof template === 'string') { // template 是选择器 if (template.charAt(0) === '#') { template = idToTemplate(template) /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !template) { warn( `Template element not found or is empty: ${options.template}`, this ) } } } else if (template.nodeType) { template = template.innerHTML } else { if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { warn('invalid template option:' + template, this) } return this } } else if (el) { // el 作为template template = getOuterHTML(el) } // 编译过程 if (template) { /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { mark('compile') } // 执行编译, 将template字符串 转化为 render 函数 const { render, staticRenderFns } = compileToFunctions(template, { outputSourceRange: process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production', shouldDecodeNewlines, shouldDecodeNewlinesForHref, delimiters: options.delimiters, comments: options.comments }, this) options.render = render options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { mark('compile end') measure(`vue ${this._name} compile`, 'compile', 'compile end') } } } return mount.call(this, el, hydrating) }
可以看到,这里是实现了对 $mount 进行了扩展,处理了template 或 el 选项。尝试编译他们为render函数。
我们在使用Vue 实例的时候,通常会这样写
const app = new Vue({ el: '#app', })
那其实可以写成
const app = new Vue({ render: h => h(App), }) const app = new Vue({ template: '<div>测试</div>', })
根据以上对以上代码的分析,Vue 不能挂载到 body、html 根节点上,然后会去如果没有 render 方法,才会去找 el 和 template,然后转换成render 方法。所以不管是 el 还是 template,最终都会转化成 render。 我们知道优先级的顺序 render > template > el 。 最后调用之前原型上的 $mount 方法挂载。
那么问题来了,现在的 Vue 构造函数从哪里来的呢?
import Vue from './runtime/index'
进入到platforms/web/runtime/index.js里面导出了Vue。
在这里,其实也不是Vue 构造函数的声明。这里主要干了两件事儿:
- 定义 $mount : 挂载根组件到宿主元素上。
- 定义 _patch: 补丁函数,执行patching 算法进行更新
// 实现了patch 方法 Vue.prototype.__patch__ = inBrowser ? patch : noop Vue.prototype.$mount = function ( el?: string | Element, hydrating?: boolean ): Component { el = el && inBrowser ? query(el) : undefined // 执行挂载 return mountComponent(this, el, hydrating) }
这里的 $mount 方法支持传入2个参数,第一个是 el ,表示挂载的元素,可以是字符串,也可以是 DOM 对象,如果是字符串在浏览器环境下调用 query 方法转换成 DOM, 第二次参数是和服务端渲染相关,在浏览器环境下不需要传第二个参数。
$mount 方法会调用 mountComponent 方法,后面再详讲。
接下来我们继续找 Vue 构造函数, 进入到核心代码 core/index 。
import Vue from 'core/index'
在这里我们依然没有找到Vue 构造函数,但是这里有个核心代码。实现了全局 api
initGlobalAPI(Vue)
进入到 initGlobalAPI 函数,具体实现了以下 api
Vue.set = set Vue.delete = del Vue.nextTick = nextTick initUse(Vue) // 实现Vue.use函数 initMixin(Vue) // 实现Vue.mixin函数 initExtend(Vue) // 实现Vue.extend函数 initAssetRegisters(Vue) // 注册实现Vue.component/directive/filter
我们再继续找 Vue 构造函数,进入到 core/instance/index.js 里面。我们终于找到了 Vue 构造函数。
function Vue (options) { ... // 初始化 this._init(options) }
Vue 构造函数内部非常简单,只执行了 this._init(options),实现初始化。 那么这里的 this.init() 又是在哪里定义的呢?
接着往下看
initMixin(Vue) // 实现了_init()函数 stateMixin(Vue) //状态相关api $data,$props,$set,$delete,$watch eventsMixin(Vue) // 事件相关api $on,$once,$off,$emit lifecycleMixin(Vue) // 生命周期api _update,$forceUpdate,$destroy renderMixin(Vue) // 渲染api _render,$nextTick
initMixin(Vue) 实现了_init() 函数,当我们在 new Vue() 时,实际上是执行了 initMixin(Vue) 实现的方法,
core/instance/init.js 进入到 initMixin 方法。
export function initMixin (Vue: Class<Component>) { Vue.prototype._init = function (options?: Object) { const vm: Component = this // a uid vm._uid = uid++ ... vm._self = vm initLifecycle(vm) //生命周期初始化 $parent, $root, $refs, $children initEvents(vm) // 事件初始化 处理父组件传递的监听器 initRender(vm) // $slots,$scopedSlots,_c,$createElement callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate') //生命周期钩子beforeCreate initInjections(vm) // resolve injections before data/props 获取注入数据 initState(vm) // 初始化组件中的props,methods,data,computed,watch initProvide(vm) // resolve provide after data/props 提供数据注入 callHook(vm, 'created') //生命周期钩子created /* istanbul ignore if */ if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && config.performance && mark) { vm._name = formatComponentName(vm, false) mark(endTag) measure(`vue ${vm._name} init`, startTag, endTag) } if (vm.$options.el) { vm.$mount(vm.$options.el) } } }
在 initMixin 方法中,在 Vue 的 原型上挂载了一个 _init。 初始化函数。在 _init() 中主要干了几件事儿:
- initLifecycle: 生命周期初始化 $parent, $root, $refs, $children
- initEvents: 事件初始化 处理父组件传递的监听器
- initRender: $slots,$scopedSlots,_c,$createElement
- callHook(vm, 'beforeCreate'): 生命周期钩子 beforeCreate
- initInjections: 获取注入数据
- initState: 初始化组件中的 props,methods,data,computed,watch
- initProvide: 提供数据注入
- callHook(vm, 'created'):生命周期钩子 created
根据以上的执行顺序,我们知道,在生命周期 beforeCreate 里面我们只可以拿到 $parent, $root, $refs, $children ,如果我们想要获取 props,methods,data,computed,watch,起码要等到created里面。
接着往下走
if (vm.$options.el) { vm.$mount(vm.$options.el) }
如果我们的选项中有 el,那么将会实现 $mount() 挂载。
以上就是整个的初始化流程。
