Tree Recursion
递归是计算机科学中一个非常重要的概念,对于斐波那契那种比较简单的递归,分析起来比较容易,但是由于二叉树涉及指针操作,所以模拟下遍历过程中系统栈的情况。
以二叉树中序遍历为例演示:
// 二叉树定义
struct TreeNode {
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
int val;
TreeNode(int x) :val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
中序遍历的递归实现:
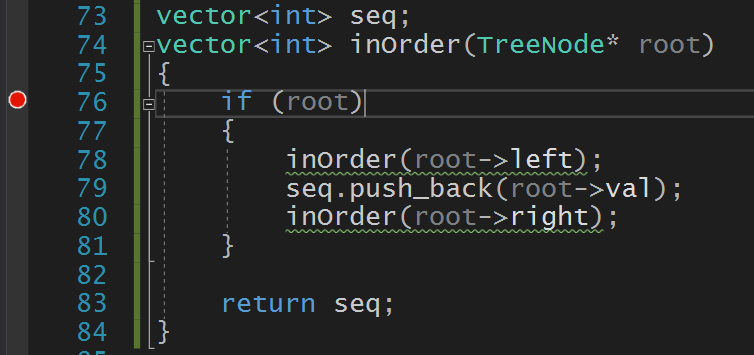
假设二叉树如图所示:
其中序遍历序列为(2413),可以在VS中用单步调试的方法跟踪相应的变量:
当root==NULL(root指向2的左孩子)时,此时的系统栈(将1和2都压栈,因为中序遍历需要先访问左孩子):
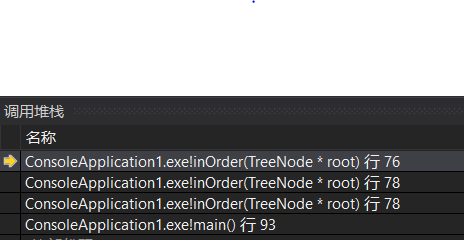
这时if不成立,执行83行的return语句,接着退栈,回到78行,此时的root指向2(因为此时程序已经来到了新的栈顶),并且向这个新栈顶返回了一个空的seq:
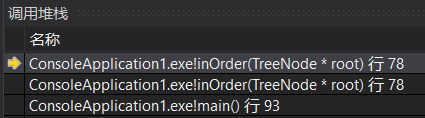
接着执行79行(因为这是上一个函数return的,所以不会再一次执行78行),将2存入seq中;
执行80行(root指向4),进而执行78行,root指向4的左孩子,此时的系统栈(很明显可以看到从栈底到栈顶依次存放根结点到当前root结点的路径上的结点):
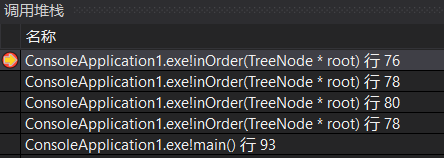
同样,执行return语句,退栈,将seq(里面只有2)返回到这一层,这一层的root指向4,接着将4存入seq;
到80行,调用inOrder()使得root指向4的右孩子,右孩子为空,所以返回并退栈,root重新指向4,此时80行执行完毕,整个if执行完毕,返回seq并退栈,root返回到了2,以2为根结点的子树中序遍历完毕,系统栈:
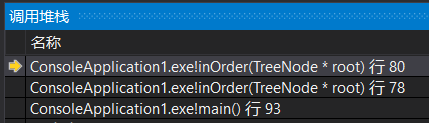
继续执行,return到78行,root指向1,将1存入seq,以此类推,就可以得到整个的遍历序列。
最关键的是:之所以要递归调用inOrder,就是因为现在还不想访问当前的结点(对于中序,要先找到最左边的结点),所以通过递归的方式将当前暂时不想访问的结点压入系统栈,找到了想访问的结点后,访问它并利用退栈操作返回父结点。
有关树的问题,有一些通用的模板:
// one root
func solve(root)
{
if(root == null) return ...
if f(root) return ...
l = solve(root->left);
r = solve(root->right);
return g(root, l , r);
}
// two roots
func solve(p, q)
{
if(p == null && q == null) return ...
if f(p, q) return ...
l = solve(p.child, q.child);
r = solve(p.child, q.child);
return g(p, q, l, r);
}
经典递归
除了树这种本身就是递归定义的结构外,还有一些search的问题也可以通过递归解决:
bool isPalindrome(string s) {
if (s.length() <= 1)
return true;
return s[0] == s[s.length() - 1] &&
isPalindrome(s.substr(1, s.length() - 2));
}
const int NotFound = -1;
int BSearch(vector<string>& v, int start, int stop, string key) {
if (start > stop) return NotFound;
int mid = (start + stop) / 2;
if (key == v[mid])
return mid;
else if (key > v[mid])
return BSearch(v, mid + 1, stop, key);
else
return BSearch(v, start, mid - 1, key);
}
int C(int n, int k) {
if (n == k || k == 0)
return 1;
else
return C(n - 1, k) + C(n - 1, k - 1);
}
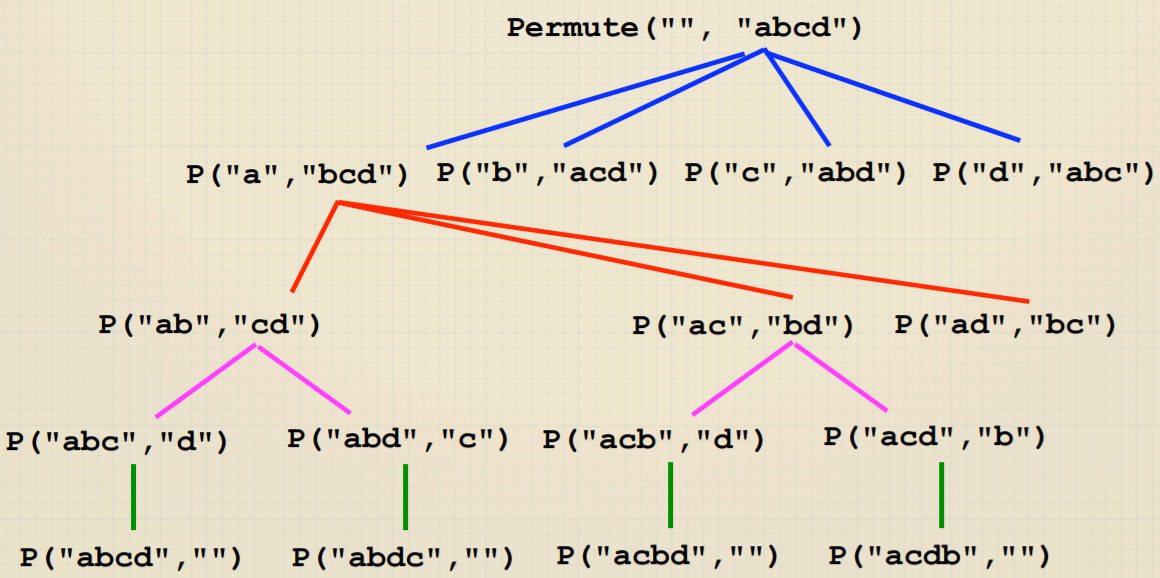
void permute(string soFar, string rest) {
if (rest == "")
cout << soFar << endl;
else {
for (int i = 0; i < rest.length(); ++i) {
string next = soFar + rest[i];
string remaining = rest.substr(0, i) + rest.substr(i + 1);
permute(next, remaining);
}
}
}
// v2
void per(vector<int>& nums, int n, int d, vector<bool>& used, vector<int>& cur, vector<vector<int>>& ans) {
if (n == d) {
ans.push_back(cur);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
if (used[i])
continue;
used[i] = true;
cur.push_back(nums[i]);
per(nums, n, d + 1, used, cur, ans);
cur.pop_back();
used[i] = false;
}
}
void com(vector<int>& nums, int n, int d, int start, vector<int>& cur, vector<vector<int>>& ans) {
if (n == d) {
ans.push_back(cur);
return;
}
for (int i = start; i < nums.size(); ++i) {
cur.push_back(nums[i]);
com(nums, n, d + 1, i + 1, cur, ans);
cur.pop_back();
}
}
void subsets(string soFar,string rest) {
if (rest == "")
cout << soFar << endl;
else {
// add to subset, remove from rest, recur
subsets(soFar + rest[0], rest.substr(1));
// do not add to subset, remove from rest, recur
subsets(soFar, rest.substr(1));
}
}
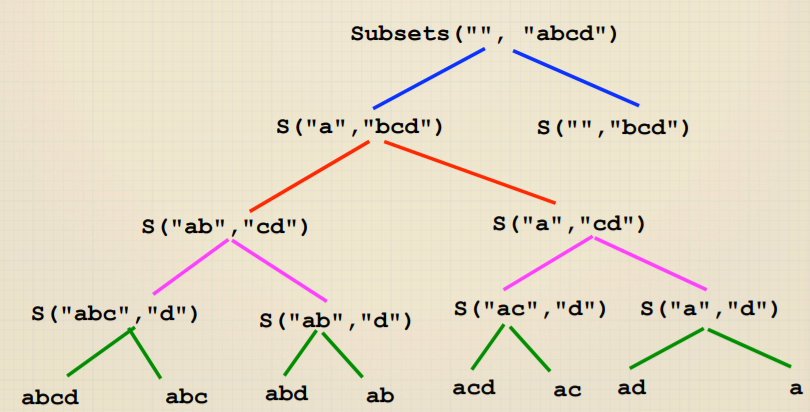
从递归树可以看到:Permutation和Subsets都是关于选择的问题,树的深度代表选择的次数,每层的宽度代表每次决定时的选项。这种都是Exhaustive Recursion,所以复杂度很高。
回溯
回溯用来搜索选择性问题(a series of choices)的所有/部分解,每做一次选择,就递归一次,如果约束条件不满足,需要回退到上一层递归的参数状态。
通过约束条件的剪枝以及启发式搜索更大可能的方案,可以避免对整个搜索空间的穷举,从而提高效率。
三个关键点:
- Choice
明确要做的决定,每次递归代表一次决定,每次的决策结果都保存在这一层的call stack中。
eg. 遍历二叉树时,当处在某一层的某结点时,下一次递归调用是向左还是向右。 - Constraints
怎样剪枝,当前状态已经invalid,不必再从该状态继续搜索,直接返回。 - Goal
找到target后,就要回溯到上一层,进行其它可能性的搜索。
Pattern:
// backtracking
bool/void solve(configuration conf) {
if (no more choices) // base case
return (conf is goal state);
for (all available choices) {
try one choice c:
// solve from here, if works out, you are done
if (solve(conf with choice c made))
return true;
unmake choice c; // explore other solutions
}
return false; // tried all choices, no soln found
}
几个例子:
- N-Queens
对照N皇后问题,明确三个关键点:
1)对于每一列,要做的决定是将Q放在哪一行,每次递归都会进入下一列的决策;
2)约束条件:不能出现在同一行、同一列、同一斜线;
3)目标:当在最后一列成功放置Q后,就可以回溯到上一层去探索其它解。
bool solve(grid<bool>& board, int col) {
if (col >= board.size()) {
return true;
}
for (int rowToTry = 0; rowToTry < board.size(); ++rowToTry) {
if (isSafe(board, rowToTry, col)) {
placeQueen(board, rowToTry, col);
if (solve(board, col + 1)) {
return true;
}
removeQueen(board, rowToTry, col);
}
}
return false;
}
- Sudoku
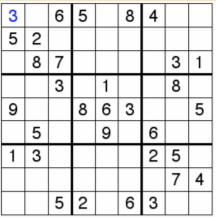
将1-9放入格子,要求每行、每列、每块不能有重复数字。
bool solve(Grid<int>& grid) {
// the gird to check, we should check all the grids
int row, col;
// all grids assigned successfully
if (!findUnassigned(grid, row, col)) {
return true;
}
for (int num = 1; num <= 9; ++num) { // options are 1-9
if (noConflict(grid, row, col, num)) {
grid(row, col) = num; // try assign
if (solve(grid)) {
return true;
}
grid(row, col) = UNASSIGNED; // undo and try again
}
}
return false;
}