看完下面两篇文章:
回忆一下Hash表的概念、构造方法和查找效率。
概念
顺序查找、折半查找、二叉排序树查找和B-树查找,查找的效率依赖于查找过程中比较的次数。理想的情况是不经过任何比较,直接定位要找的元素。定位是根据给定的Key找到记录存储位置的映射。我们一般称这种映射关系为hash函数。按照这个思想建立的表叫hash表。
好的hash函数的标准?简单和均匀。简单,指hash函数简单,计算速度快。均匀,指分布均匀,冲突少。
Hash函数的构造方法有:直接定址法,数字分析法,平方取中法,除留余数法,随机数法。(见《数据结构》严蔚敏)
由于Hash函数是一个压缩映像,不可避免的会产生冲突。所以设计Hash表的时候还要设计一种处理冲突的办法。
处理冲突的方法有:开放定址法,再Hash法,链地址法,公共溢出区。(见《数据结构》严蔚敏)
C#的Dictionary
C#中的Dictionary的hash函数算法是什么?还是用老赵文章中的代码片段,下面这段HashTable代码注释:
1: /*
2: Implementation Notes:
3: The generic Dictionary was copied from Hashtable's source - any bug
4: fixes here probably need to be made to the generic Dictionary as well.
5:
6: This Hashtable uses double hashing. There are hashsize buckets in the
7: table, and each bucket can contain 0 or 1 element. We a bit to mark
8: whether there's been a collision when we inserted multiple elements
9: (ie, an inserted item was hashed at least a second time and we probed
10: this bucket, but it was already in use). Using the collision bit, we
11: can terminate lookups & removes for elements that aren't in the hash
12: table more quickly. We steal the most significant bit from the hash code
13: to store the collision bit.
14:
15: Our hash function is of the following form:
16:
17: h(key, n) = h1(key) + n*h2(key)
18:
19: where n is the number of times we've hit a collided bucket and rehashed
20: (on this particular lookup). Here are our hash functions:
21:
22: h1(key) = GetHash(key); // default implementation calls key.GetHashCode();
23: h2(key) = 1 + (((h1(key) >> 5) + 1) % (hashsize - 1));
24:
25: The h1 can return any number. h2 must return a number between 1 and
26: hashsize - 1 that is relatively prime to hashsize (not a problem if
27: hashsize is prime). (Knuth's Art of Computer Programming, Vol. 3, p. 528-9)
28: If this is true, then we are guaranteed to visit every bucket in exactly
29: hashsize probes, since the least common multiple of hashsize and h2(key)
30: will be hashsize * h2(key). (This is the first number where adding h2 to
31: h1 mod hashsize will be 0 and we will search the same bucket twice).
32:
33: We previously used a different h2(key, n) that was not constant. That is a
34: horrifically bad idea, unless you can prove that series will never produce
35: any identical numbers that overlap when you mod them by hashsize, for all
36: subranges from i to i+hashsize, for all i. It's not worth investigating,
37: since there was no clear benefit from using that hash function, and it was
38: broken.
39:
40: For efficiency reasons, we've implemented this by storing h1 and h2 in a
41: temporary, and setting a variable called seed equal to h1. We do a probe,
42: and if we collided, we simply add h2 to seed each time through the loop.
43:
44: A good test for h2() is to subclass Hashtable, provide your own implementation
45: of GetHash() that returns a constant, then add many items to the hash table.
46: Make sure Count equals the number of items you inserted.
47:
48: Note that when we remove an item from the hash table, we set the key
49: equal to buckets, if there was a collision in this bucket. Otherwise
50: we'd either wipe out the collision bit, or we'd still have an item in
51: the hash table.
52:
53: --
54: */
从下面的Insert方法中,来看看Dictionary中如何处理冲突。
1: private void Insert(TKey key, TValue value, bool add)
2: {
3: if ((object) key == null)
4: ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentNullException(ExceptionArgument.key);
5: if (this.buckets == null)
6: this.Initialize(0);
7: int num = this.comparer.GetHashCode(key) & int.MaxValue;
8: int index1 = num % this.buckets.Length;
9: for (int index2 = this.buckets[index1]; index2 >= 0; index2 = this.entries[index2].next)
10: {
11: if (this.entries[index2].hashCode == num && this.comparer.Equals(this.entries[index2].key, key))
12: {
13: if (add)
14: ThrowHelper.ThrowArgumentException(ExceptionResource.Argument_AddingDuplicate);
15: this.entries[index2].value = value;
16: ++this.version;
17: return;
18: }
19: }
20: int index3;
21: if (this.freeCount > 0)
22: {
23: index3 = this.freeList;
24: this.freeList = this.entries[index3].next;
25: --this.freeCount;
26: }
27: else
28: {
29: if (this.count == this.entries.Length)
30: {
31: this.Resize();
32: index1 = num % this.buckets.Length;
33: }
34: index3 = this.count;
35: ++this.count;
36: }
37: this.entries[index3].hashCode = num;
38: this.entries[index3].next = this.buckets[index1];
39: this.entries[index3].key = key;
40: this.entries[index3].value = value;
41: this.buckets[index1] = index3;
42: ++this.version;
43: }
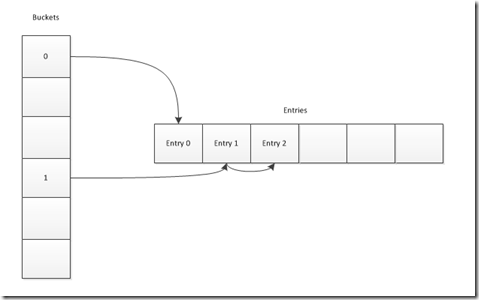
Entries类型是Dictionary<TKey, TValue>.Entry[],Entry的定义如下:
1: private struct Entry
2: {
3: public int hashCode;
4: public int next;
5: public TKey key;
6: public TValue value;
7: }
用于保存插入的每个Key和Value。
bucket类型是int[],用于保存相同hash值的Key和Value Pair构成的链表的第一个元素的在entries中的索引。这和我们在《数据结构》这本书中学的知识不一样,C#的Dictionary的所有的元素都保存在一个个Entry构成的数组中。