1、case语句的用法:
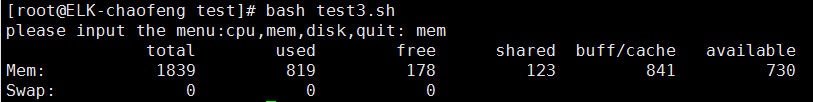
[root@ELK-chaofeng test]# cat test3.sh #!/bin/bash while true ;do read -p "please input the menu:cpu,mem,disk,quit: " variable case $variable in cpu) lscpu break ;; mem) free -m break ;; disk) fdisk -l /dev/[shv]d[a-z][0-9] break ;; *) echo "error,again" ;; esac done
看一下效果
现在我们来编写一个服务框架:
[root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# cat testservice #!/bin/bash # #chkconfig: 2345 60 60 #description: test service script # prog=$(basename $0) lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/${prog} case $1 in start) if [ -f $lockfile ];then echo "service $prog is running" else touch $lockfile echo "service $prog start" fi ;; stop) if [ -f $lockfile ];then rm -rf $lockfile echo "service $prog stop" else echo "service $prog stop" fi ;; restart) if [ -f $lockfile ];then rm -rf $lockfile && touch $lockfile echo "service $prog restart" else touch $lockfile echo "service $prog start" fi ;; status) if [ -f $lockfile ];then echo "service $prog is running" else echo "service $prog is not running" fi ;; *) echo "usage: $prog {start|restart|stop|status}" ;; esac
然后chkconfig添加至service服务管理。现在看一下效果:
[root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# chkconfig --add testservice [root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# chkconfig --list testservice Note: This output shows SysV services only and does not include native systemd services. SysV configuration data might be overridden by native systemd configuration. If you want to list systemd services use 'systemctl list-unit-files'. To see services enabled on particular target use 'systemctl list-dependencies [target]'. testservice 0:off 1:off 2:on 3:on 4:on 5:on 6:off [root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# service testservice status service testservice is running [root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# service testservice stop service testservice stop [root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# service testservice start service testservice start [root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# service testservice status service testservice is running [root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# service testservice stop service testservice stop [root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# service testservice status service testservice is not running [root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# service testservice restart service testservice start [root@ELK-chaofeng init.d]# service testservice status service testservice is running
case总结:
case支持glob风格的通配符:、
*:任意长度的任意字符;
?:任意单个字符;
[ ]:范围内任意单个字符;
a|b:a或b
现在我们使用函数来改写上面的脚本:
#!/bin/bash # #chkconfig: 2345 60 60 #description: test service script # prog=$(basename $0) lockfile=/var/lock/subsys/${prog} start(){ if [ -f $lockfile ];then echo "service $prog is running" else touch $lockfile echo "service $prog start" fi } stop() { if [ -f $lockfile ];then rm -rf $lockfile echo "service $prog stop" else echo "service $prog stop" fi } else touch $lockfile echo "service $prog start" fi } stop() { if [ -f $lockfile ];then rm -rf $lockfile echo "service $prog stop" else echo "service $prog stop" fi } status() { if [ -f $lockfile ];then echo "service $prog is running" else echo "service $prog is not running" fi } usage () { echo "usage: $prog {start|restart|stop|status}" } case $1 in start) start ;; stop) stop ;; restart) stop start ;; status) status ;; *) usage ;; esac
2、for语句的高级用法:
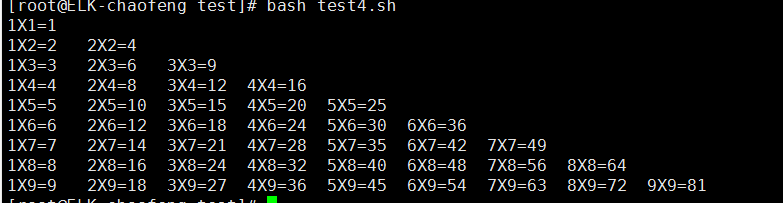
#!/bin/bash # print 9*9 for ((k=1;k<=9;k++));do for ((i=1;i<=k;i++));do echo -e -n "${i}X${k}=$[${i}*${k}] " done echo "" #huan hang done
看一下效果:
3、while语句的高级用法
#!/bin/bash while read VARIABLE;do userID=`echo $VARIABLE | cut -d':' -f 3` userUS=`echo $VARIABLE | cut -d':' -f 1` usershell=`echo $VARIABLE | cut -d':' -f 7` if [ $[$userID%2] -eq 0 ];then echo "$userID,$userUS,$usershell" fi done < /etc/passwd
看一下效果: