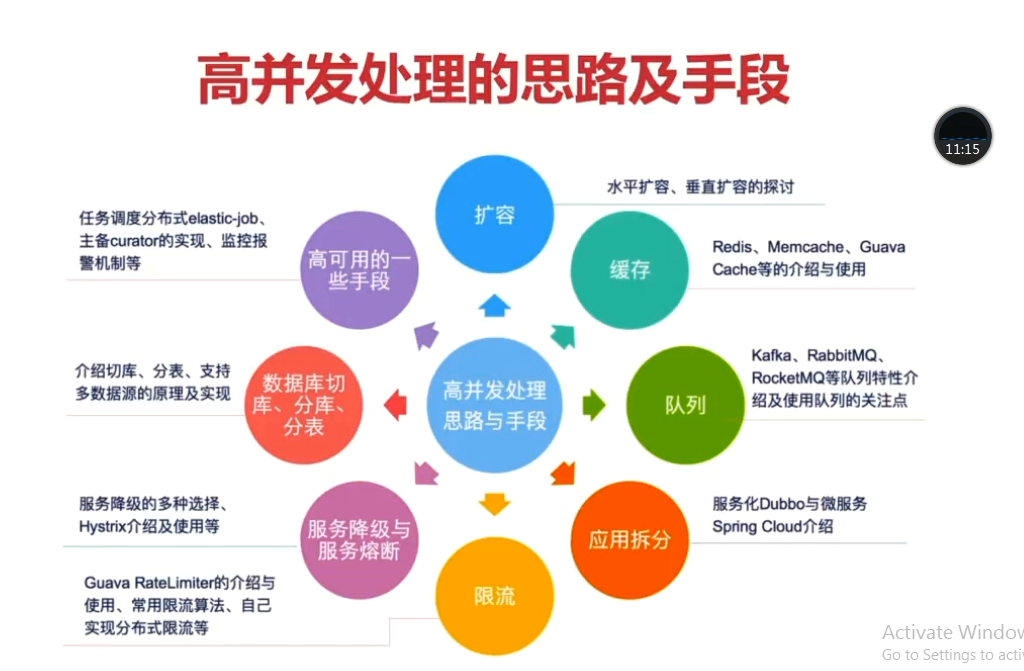
写在前面
一切技术都是纸老虎,技术就是一层膜,捅破了就什么也不是
// 读书推荐
设计模式:
Head First Design Patterns
设计模式之禅
// java 并发编程实战
// 深入理解 java 虚拟机
// effective java
// 代码工程化
代码整洁之道
Java 部分
1.Java NIO 编程
2.Java 并发编程
3.Java 容器类的实现
4.Java 异常、反射与注解、泛型
5.Java 网络编程
6.Java 虚拟机
数据库部分
1.《 MySQL 必知必会》
2.《 Redis 设计与实现》
NIO
Non blocked IO ==> New IO
传统 IO 面向流 是阻塞式的
NIO 面向缓冲区 像是 火车轨道 (Channel) + 火车 (Buffer)
选择器


NIO 复制文件小例子
package com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.nio;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.MappedByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.StandardOpenOption;
/**
* @author :Frank Li
* @date :Created in 2019/7/31 20:20
* @description:${description}
* @modified By:
* @version: $version$
*/
public class ChannelDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
/* FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream("C:\Users\FrankLi\Desktop\AI\timesheet\favicon.ico");
FileChannel inChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("C:\Users\FrankLi\Desktop\AI\timesheet\dist\favicon.ico");
FileChannel outChannel = fos.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len = -1;
while((len=inChannel.read(byteBuffer)) != -1){
byteBuffer.flip();
outChannel.write(byteBuffer);
byteBuffer.clear();
}
outChannel.close();
inChannel.close();
fos.close();
fileInputStream.close();*/
// copyFile("C:\Users\FrankLi\Desktop\AI\timesheet\favicon.ico","C:\Users\FrankLi\Desktop\AI\timesheet\favicon2.ico");
copyFile2("C:\Users\FrankLi\Desktop\AI\timesheet\timesheet.py","C:\Users\FrankLi\Desktop\AI\timesheet\timesheet_copied.py");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(String.format("cost about %d s",end-start));
}
public static void copyFile(String src, String tar){
// 首先获取 读取管道
FileChannel readChannel = null;
// 获取 写入管道
FileChannel writeChannel =null;
try{
readChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(src), StandardOpenOption.READ);
writeChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(tar), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(readChannel.read(buf) != -1){
buf.flip();
writeChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
}catch(IOException ioe){
ioe.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(readChannel!=null){
try{
readChannel.close();
}catch(IOException ioe){
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(writeChannel!=null){
try{
writeChannel.close();
}catch(IOException ioe){
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件) ,这样操作可以省去内核与JVM 内存之间的数据 拷贝
public static void copyFile2(String src, String tar){
FileChannel inFileChannel = null;
FileChannel outFileChannel = null;
try{
inFileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(src), StandardOpenOption.READ);
outFileChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get(tar),StandardOpenOption.READ, StandardOpenOption.WRITE, StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
// 这里 如果 直接通道数据传输会更加方便
/*inFileChannel.transferTo(0,inFileChannel.size(),outFileChannel);
outFileChannel.transferFrom(inFileChannel,0,inFileChannel.size());
*/
// 内存映射页
MappedByteBuffer inMappedByteBuffer = inFileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY,0,inFileChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outMappedByteBuffer = outFileChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0 , inFileChannel.size());
// 直接对缓冲区进行数据的读写操作
byte [] dst = new byte[1024];
inMappedByteBuffer.get(dst);
outMappedByteBuffer.put(dst);
}catch(IOException ioe){
ioe.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(inFileChannel != null){
try{
inFileChannel.close();
}catch(IOException ioe){
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(outFileChannel != null){
try{
outFileChannel.close();
}catch(IOException ioe){
ioe.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
分散读取 聚集写入
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
copyFile("C:\Users\FrankLi\Desktop\AI\timesheet\timesheet.py","C:\Users\FrankLi\Desktop\AI\timesheet\timesheet_2.py");
}
public static void copyFile(String src, String dst) throws IOException{
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFileReader = new RandomAccessFile(src,"r");
FileChannel inChannel = randomAccessFileReader.getChannel();
ByteBuffer byteBufferFirst = ByteBuffer.allocate(512);
ByteBuffer byteBufferSecond = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024*6);
ByteBuffer [] bufs = {byteBufferFirst,byteBufferSecond};
inChannel.read(bufs);
for(ByteBuffer buf:bufs){
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,buf.limit()));
System.out.println("---------------=============---------------");
}
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFileWriter = new RandomAccessFile(dst,"rw");
FileChannel outChannel = randomAccessFileWriter.getChannel();
outChannel.write(bufs);
inChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
}
NIO 字符集
Map<String, Charset> charsetMap = Charset.availableCharsets();
for(Map.Entry<String, Charset> entrySet:charsetMap.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entrySet.getKey()+" <----> "+entrySet.getValue());
}
读写 JSON
jackson 的强项是灵活可定制, 并且具有了一个生态, yaml 也能完美驾驭
gson是轻量 简洁
fastjson 似乎没有一个好的生态 , 性能也比较好
多线程两种实现方式

- 继承 Thread 类,实现 run 方法将需要多线程启动的功能代码放在 run 方法内 该方式有 isinterrupted 标志位,
可以根据该标志位在另一个能够获取到该线程的代码块中that.interrupt 实现中断,但是是否真的中断则由that线程决定 - 实现 runnable 接口,覆写 run 方法将需要多线程启动的功能代码放在 run 方法内,注意这里没有 isInterrupted 标志位
实际上在一个线程中停止另一个线程可以用 concurrent 包中的 cancel 方法,这个 跟 python 简直一毛一样啊啊啊
ExecutorService 接口下固定大小线程池 (Fixed),动态变化(Cached) , 以及只有单个(Single)线程的 线程池
// t1.start() 永远使用 start --》 start0 (本地方法) 去启动线程 而非 调用 run 方法
// 这里记得 t1.join() 是等待t1线程执行完成才会继续往下执行
// t1.setDaemon(true) 设置为守护线程,也就是不那么重要的,JVM 在所有非守护线程执行完成后就会退出,垃圾回收就是一个守护线程
// 虽然我们以后使用 concurrent 包来进行并发,但是基础原理一定要掌握牢固
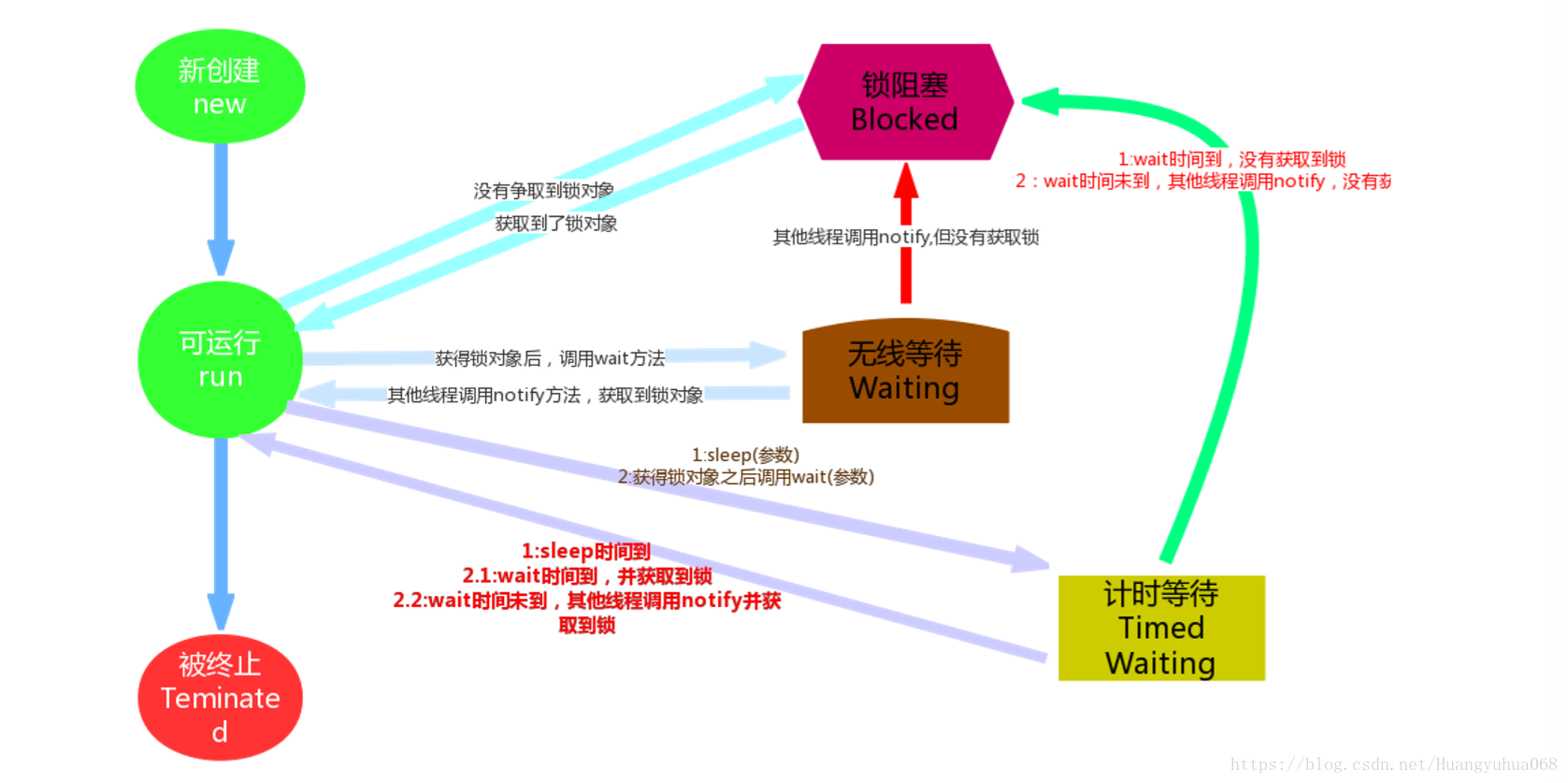
// 进程 六种状态
NEW:新建状态 刚刚创建出来,还没有调用start方法之前的状态。
RUNNABLE:可运行状态,可能正在执行,也可能不是正在执行,只有在该种状态下的线程才有资格抢CPU。
BLOCKED:锁阻塞状态 线程要等待另一个线程释放锁对象。
WAITING:无限等待 线程调用了wait()方法进入的状态,需要其它线程调用notify方法唤醒。
TIMED_WAITING:计时等待状态 线程调用了sleep方法获wait(long time)方法进入的状态。
TERMINATED:死亡状态 线程任务执行完毕或调用了stop方法。
Thread 常用方法
构造方法 Thread(Runnable target,String name)
静态方法:
Thread.currentThread().getName()
Thread.sleep(1000) // java 中 单位是毫秒 所以 1000ms = 1 s,python 中直接是 秒
线程安全同步机制 synchronized 同步代码快, 同步方法,可重入锁,可重入读写锁
// synchronized 代码块中 可以 wait , notify() , notifyAll()
// lock.newCondition 也可以实现 await() signal() signalAll()
加入 synchronized 同步方法, synchronized 这个方式不如 可重入锁安全,被synchronized修饰的要么获得锁,要么永远等待下去
public class Counter {
private int value;
public synchronized void inc(int m){
this.value+=m;
}
public synchronized void dec(int m){
this.value-=m;
}
}
引入可重入锁即可以在同一个线程内多次获取该锁
package com.ghc.test;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class Counter {
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private int value;
public void inc(int m){
if(lock.tryLock()){
try{
this.value+=m;
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public void dec(int m){
if(lock.tryLock()){
try{
this.value-=m;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public int getValue(){
lock.lock();
try{
return this.value;
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String [] args) throws InterruptedException{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" start...");
new Thread(()->{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" start...");
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end...");
},"download thread").start();
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end...");
}
}
引入 可重入 读写锁,因为 可以同时读 , 不可同时写入 或者说不可同时读写
引入 可重入读写锁在同时写入的时候会加锁进行同步,而在同时读取的时候则不会提高并发性能
package com.ghc.test;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
public class Counter {
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock = lock.readLock();
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock = lock.writeLock();
private int value;
public void inc(int m){
// 写 锁
writeLock.lock();
try{
this.value+=m;
}finally {
writeLock.unlock();
}
}
public void dec(int m){
// 读锁
readLock.lock();
try{
this.value-=m;
}finally {
readLock.unlock();
}
}
}
使用 线程池进行并发
package com.ghc.test;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.time.LocalTime;
/**
* @author :Frank Li
* @date :Created in 2019/7/11 8:49
* @description:${description}
* @modified By:
* @version: $version$
*/
class PrintThread extends Thread{
private String taskName;
PrintThread(String taskName, String threadName){
this.taskName = taskName;
this.setName(threadName);
}
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println(this.getName()+": Hello, "+this.taskName);
try{
Thread.sleep(1000);
int i = 1/0;
}catch (InterruptedException e){}
System.out.println(this.getName()+": Goodbye, "+this.taskName);
}
}
public class ExecutorServiceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 阅读源码可以发现 ThreadPoolExecutor 才是万物之基
// 创建 固定大小的 线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
executor.submit(new PrintThread("Frank", "t1"));
executor.submit(new PrintThread("May", "t2"));
executor.shutdown();
System.out.println("---***华丽的分割线***---");
// 创建 弹性动态伸缩线程池
ExecutorService cachedThreadPool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); // 不指定大小
cachedThreadPool.submit(new PrintThread("SCALA", "t3"));
cachedThreadPool.submit(new PrintThread("PYTHON", "t4"));
cachedThreadPool.shutdown();
// 创建弹性动态伸缩线程池 但是指定最大线程 为 10 个, 线程池中保持 corePoolSize 个线程即使是idle 的
int corePoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
ExecutorService cachedThreadMaxSpecifiedPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(corePoolSize, 10,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
Future<PrintThread> future = (Future<PrintThread>) cachedThreadMaxSpecifiedPool.submit(new PrintThread("China", "t5"));
future.cancel(true); // 取消某个线程
cachedThreadMaxSpecifiedPool.submit(new PrintThread("World", "t6"));
cachedThreadMaxSpecifiedPool.shutdown();
// 创建单个线程的线程池
/* Executor singleExecutor = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
singleExecutor.execute(new PrintThread("single", "dog"));
singleExecutor.execute(new PrintThread("all the way", "single"));*/
// 创建一个 定时执行 executor
ScheduledExecutorService scheduledExecutor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
scheduledExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(new PrintThread("scheduled task "+LocalTime.now(),"t7"), 2, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 每间隔 n 秒 执行一次
scheduledExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new PrintThread("scheduled delay task "+LocalTime.now(),"t8"), 2, 2,TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 等待上一次任务运行结束delay 运行下一个
// scheduledExecutor.shutdown();
}
}
获取 返回值的 线程 需要使用 Callable 的 子类 , 否则 可用 Runnable 接口的子类
package com.ghc.test;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @author :Frank Li
* @date :Created in 2019/7/11 15:31
* @description:${description}
* @modified By:
* @version: $version$
*/
class CallableFuture implements Callable<String> {
private String taskName;
CallableFuture(String taskName){
this.taskName = taskName;
}
@Override
public String call() throws InterruptedException{
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--> "+ "start: Hello, "+this.taskName);
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--> "+ "end: Goodbye, "+this.taskName);
return this.taskName;
}
}
public class FutureTest {
public static void main(String [] args){
Callable<String> callableTask = new CallableFuture("Frank");
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);
Future<String> future = executor.submit(callableTask);
String result = null;
try{
result = future.get(2, TimeUnit.SECONDS); // 可能会阻塞 等待 线程完成 获取返回结果 ,设置超时
/*java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:205)
at com.ghc.test.FutureTest.main(FutureTest.java:32)*/
}catch (InterruptedException interException){
interException.printStackTrace();
}catch (ExecutionException ee){
ee.printStackTrace();
}catch (TimeoutException te){
te.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(result);
executor.shutdown();
}
}
ForkJoin 采用分治算法 ,想到快排 分治 + 挖坑 填坑。 思考, 他与 Map Reduce 并行框架的区别
package com.ghc.test;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinTask;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
/**
* @author :Frank Li
* @date :Created in 2019/7/11 16:56
* @description:${description}
* @modified By:
* @version: $version$
*/
public class ForkJoinTest extends RecursiveTask<Long> {
private static final int THRESHOLD = 250;
long [] array;
int start;
int end;
ForkJoinTest(long [] array, int start, int end){
this.array = array;
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
protected Long compute(){
if(end-start <= THRESHOLD){
// 如果任务量足够小,直接计算;
long sum = 0;
for(int i = start; i < end; i++){
sum += this.array[i];
try{
Thread.sleep(2);
}catch (InterruptedException interExcept){
interExcept.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sum;
}else{
// 当任务太大, 我们将大任务进行拆分
int middle = (end + start) / 2;
System.out.println(String.format("split %d~%d ==> %d~%d, %d~%d", start,end,start,middle,middle,end));
ForkJoinTest subTask1 = new ForkJoinTest(this.array, start, middle);
ForkJoinTest subTask2 = new ForkJoinTest(this.array,middle, end);
invokeAll(subTask1, subTask2);
Long subResult1 = subTask1.join();
Long subResult2 = subTask2.join();
Long result = subResult1 + subResult2;
System.out.println(String.format("result = %d + %d ==> %d", subResult1,subResult2, subResult1+subResult2));
return result;
}
}
public static void main(String [] args){
long [] array = new long[1000];
long expectedSum = 0;
for(int i=0; i < array.length; i++){
array[i] = random();
expectedSum+=array[i];
}
System.out.println("Expected sum: "+ expectedSum);
ForkJoinTask<Long> task = new ForkJoinTest(array, 0, array.length);
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Long result = ForkJoinPool.commonPool().invoke(task);
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Fork/join sum: "+ result + " in "+(endTime-startTime)+" ms");
}
static Random random = new Random(0);
static long random(){
return random.nextInt(10000);
}
}
ThreadLocal 用作单个线程内部,传递变量,必须用 try finally 处理 , 可以避免 变量在每一个调用方法处传递
package com.ghc.test;
/**
* @author :Frank Li
* @date :Created in 2019/7/11 18:23
* @description:${description}
* @modified By:
* @version: $version$
*/
class User{
String name;
int level;
User(String name, int level){
this.name = name;
this.level = level;
}
}
class UserContext implements AutoCloseable{
// 全局唯一静态变量
private static final ThreadLocal<User> context = new ThreadLocal<>();
// 获取当前线程的 ThreadLocal User:
public static User getCurrentUser(){
return context.get();
}
// 初始化 ThreadLocal 的 User
public UserContext(User user){
context.set(user);
}
@Override
public void close(){
context.remove();
}
}
class ProcessThread extends Thread{
User user;
ProcessThread(User user){
this.user = user;
}
public void run(){
try(UserContext ctx = new UserContext(user)){
new Greeting().hello();
Level.checkLevel();
}
}
}
class Greeting{
void hello(){
User user = UserContext.getCurrentUser();
System.out.println("hello "+user.name+" !");
}
}
class Level{
static void checkLevel(){
User user = UserContext.getCurrentUser();
if(user.level > 100){
System.out.println(user.name+ " is a VIP user");
}else{
System.out.println(user.name + " is a registered user.");
}
}
}
public class ThreadLocalTest {
public static void main(String [] args) throws InterruptedException{
Thread t1 = new ProcessThread(new User("Bob", 120));
Thread t2 = new ProcessThread(new User("Frank", 98));
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println("Main end...");
}
}
深入学习 并发编程以及 高并发
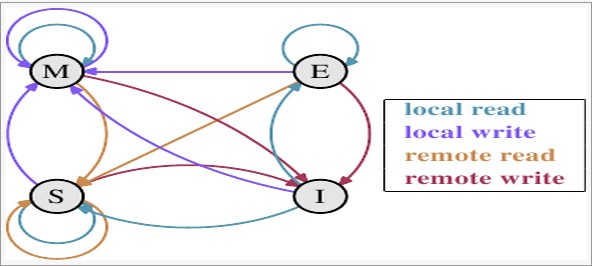
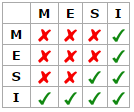
CPU 多级缓存机制 MESI (Modified Exclusive Shared Or Invalid) 四种状态 , Localread local write remote read remote write 四种读写
CPU 对运行代码 进行乱序 优化可能带来 实际结果与 逻辑结果不一致

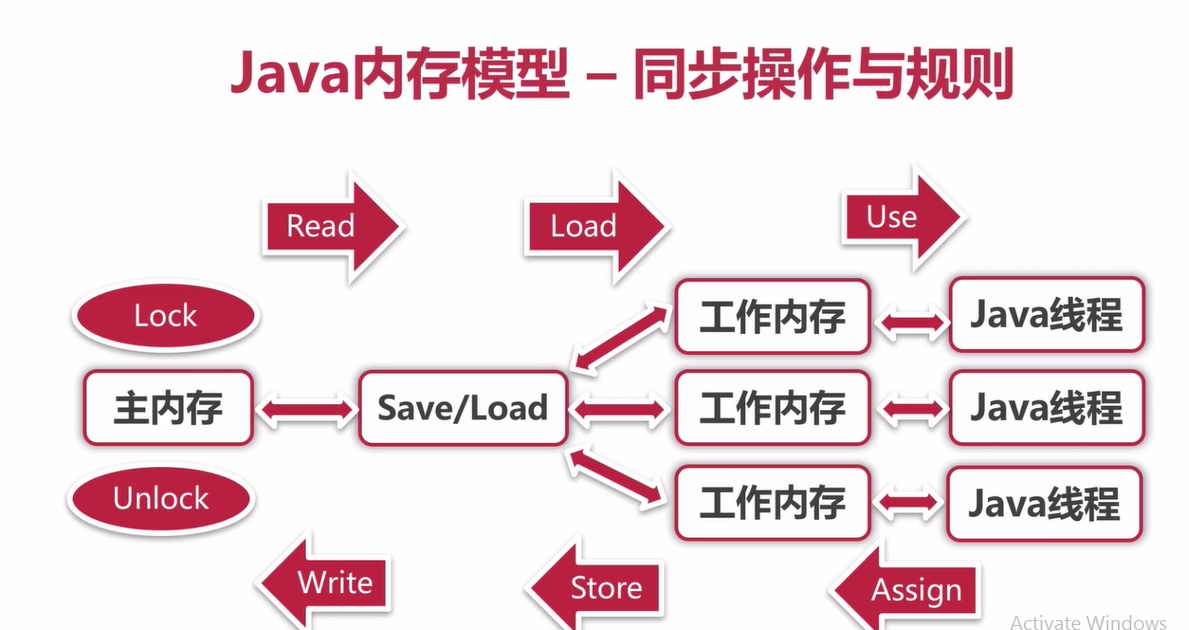
JMM java memory model ==》 java 虚拟机内存模型
JMM 同步操作 八个步骤 lock -> 从主内存 read -> load 到每个线程独享内存-> use --> assign --> store --> write --》unlock
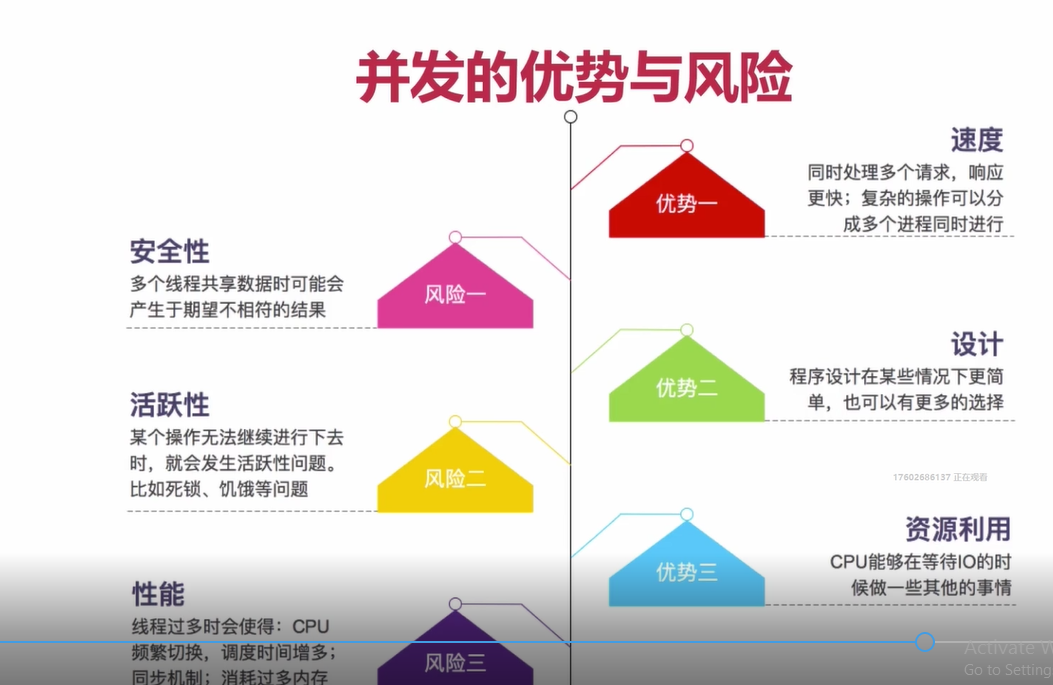
并发的 优缺点
一个 线程不安全的小例子
package com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.test;
import com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.annotations.UnThreadSafe;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @author :Frank Li
* @date :Created in 2019/7/17 16:27
* @description:${description}
* @modified By:
* @version: $version$
*/
@UnThreadSafe
public class ConcurrencyTest {
// 请求总数
public static int clientTotal = 5000;
// 同时并发执行的线程数
public static int threadTotal = 200;
public static int count = 0;
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getGlobal();
private static final Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String [] args) throws InterruptedException {
logger.setLevel(Level.INFO);
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for(int i=0;i<clientTotal;i++){
executor.execute(()->{
try {
semaphore.acquire();
add();
semaphore.release();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
logger.info("count after countDownLatch...:"+count);
}
public synchronized static void add(){
count++;
}
}
使用锁机制,手动加锁也是可以保证线程安全的
package com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.test;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class ThreadSafeDemo {
private static int count = 0;
private final static int clientTotal = 5000;
private final static int threadTotal = 200;
private final static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private final static Logger logger = Logger.getGlobal();
public static void main(String [] args) throws InterruptedException {
logger.setLevel(Level.INFO);
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for(int i=0;i<clientTotal;i++){
executor.execute(()->{
try{
semaphore.acquire();
add();
semaphore.release();
}catch(InterruptedException e){}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executor.shutdown();
logger.info("count: "+count);
}
private static void add() throws InterruptedException{
/*synchronized(ThreadSafeDemo.class){
count++;
}*/
if(lock.tryLock(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)){// (可重入锁是JDK层面实现的锁)可以 有效避免死锁, 使用 上面的 synchronized (基于JVM层面的锁) 可能会 死锁
try{
count++;
}finally{
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
下面这个采用 原子操作 所以是线程 安全的
package com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.test;
import com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.annotations.ThreadSafe;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @author :Frank Li
* @date :Created in 2019/7/17 18:58
* @description:${description}
* @modified By:
* @version: $version$
*/
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class AtomicBooleanTest {
private static AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
private static int clientTotal = 5000;
private static int threadTotal = 200;
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getGlobal();
public static void main(String [] args) throws InterruptedException {
logger.setLevel(Level.INFO);
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for(int i=0;i<clientTotal;i++){
executor.execute(()->{
try{
semaphore.acquire();
incr();
semaphore.release();
} catch(InterruptedException e){
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executor.shutdown();
logger.info("count: "+count);
}
public static void incr(){
count.getAndIncrement();
}
}
// 改用 LongAdder 来 替代 AtomicLong 有时候会更加高效
package com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.test;
import com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.annotations.ThreadSafe;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @author :Frank Li
* @date :Created in 2019/7/17 18:58
* @description:${description}
* @modified By:
* @version: $version$
*/
@Slf4j
@ThreadSafe
public class AtomicBooleanTest {
private static LongAdder count = new LongAdder();
private static int clientTotal = 5000;
private static int threadTotal = 200;
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getGlobal();
public static void main(String [] args) throws InterruptedException {
logger.setLevel(Level.INFO);
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
for(int i=0;i<clientTotal;i++){
executor.execute(()->{
try{
semaphore.acquire();
incr();
semaphore.release();
} catch(InterruptedException e){
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
});
}
countDownLatch.await();
executor.shutdown();
logger.info("count: "+count);
}
public static void incr(){
count.increment();
}
}
安全的线程需要 满足以下特性
- 原子性 , CAS (compareAndSwapxxx , compareAndSet xxx 为 Int Long 等) 底层采用循环不断比较本地内存与主内存中的值是否一样,不一样就一直去取直到一样取出来相加
- 可见性 一个线程 对住内存的修改可以及时地被其他线程观察到
- 有序性
// 特别注意 对于 Long 类型提供了 两个 原子操作的类
AutomicLong , LongAdder (后者更高效但有可能不够精确) // 不妨优先考虑 后者
可见性



安全发布对象

线程安全的 例子, 推荐使用 枚举方法 创建单例
饿汉式单例模式 虽然简单 但是可能造成资源浪费
package com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.singleton;
import com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.annotations.NotRecommend;
import com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.annotations.ThreadSafe;
@ThreadSafe
@NotRecommend
public class Singleton1 {
// 饿汉式 单例模式
// 首先 私有构造方法
private Singleton1(){}
private static Singleton1 singleton = new Singleton1();
public static Singleton1 getInstance(){
return singleton;
}
}
懒汉式单例模式 虽然线程安全但是 书写复杂容易造成 线程不安全 所以也不推荐
package com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.singleton;
import com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.annotations.NotRecommend;
import com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.annotations.ThreadSafe;
@ThreadSafe
@NotRecommend
public class Singleton2 {
// 懒汉式 单例模式
// 第一步同样是需要私有化构造方法
private Singleton2(){}
// 1 memory= allocate() 分配对象的内存空间
// 2 ctorInstance() 初始化对象
// 3 instance = memory 设置 instance 指向刚分配的内存
// 第二步 延迟给变量赋值 volatile 确保 JVM CPU 优化指令重排序不会影响线程安全
private static volatile Singleton2 singleton = null;
// volatile + 双重检测机制 --》 禁止对象指令重排
// 静态工厂方法
public static Singleton2 getInstance(){
if(singleton==null){
synchronized (Singleton2.class){
// 双重同步锁 确保线程安全第一点
if(singleton==null){
singleton = new Singleton2();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
}
使用内部枚举类 来利用JVM 控制多线程 运行时侯始终 只有一个实例被创建 推荐使用
package com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.singleton;
import com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.annotations.Recommend;
import com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.annotations.ThreadSafe;
/**
*
*/
@ThreadSafe
@Recommend
public class Singleton3 {
// 使用枚举类确保线程安全
// 第一步 仍然是私有化构造方法
private Singleton3(){}
// 第二步 提供对外访问的静态公用接口
public static Singleton3 getInstance(){
return Singleton.INSTANCE.getInstance();
}
public enum Singleton{
INSTANCE;
private Singleton3 singleton = null;
Singleton(){
singleton = new Singleton3();
}
public Singleton3 getInstance(){
return singleton;
}
}
}
不可变对象 参考 String 类


同步容器

并发容器


ForkJoin
package com.ghc.mmall.concurrency.test;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import java.util.concurrent.ForkJoinPool;
import java.util.concurrent.Future;
import java.util.concurrent.RecursiveTask;
@Slf4j
public class ForkJoinTaskExample extends RecursiveTask<Integer> {
public static final int threshold = 2;
private int start;
private int end;
public ForkJoinTaskExample(int start, int end){
this.start = start;
this.end = end;
}
@Override
protected Integer compute() {
int sum = 0;
// 如果任务足够小 就计算任务
boolean canCompute = (end - start) <= threshold;
if(canCompute){
for(int i = start; i<= end;i++){
sum+=i;
}
}else{
// 如果任务大于阈值 , 就分类成两个子任务计算
int middle = (start + end) / 2;
ForkJoinTaskExample leftTask = new ForkJoinTaskExample(start, middle);
ForkJoinTaskExample rightTask = new ForkJoinTaskExample(middle+1, end);
// 执行子任务
leftTask.fork();
rightTask.fork();
// 等待子任务执行结束合并其结果
int leftResult = leftTask.join();
int rightResult = rightTask.join();
// 合并子任务的结果
sum = leftResult + rightResult;
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ForkJoinPool forkJoinPool = new ForkJoinPool();
// 生成一个计算任务 计算 1+2+3+4
ForkJoinTaskExample task = new ForkJoinTaskExample(1, 100);
Future<Integer> result = forkJoinPool.submit(task);
try{
log.info("result: {}", result.get());
}catch(Exception e){
log.error("exception: ", e);
}
}
}
写在最后