一。实现Bezier曲线的升阶,降阶和拖动。
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding: utf-8 -*- 'My Bezier' import numpy as np from scipy.special import comb, perm from matplotlib import pyplot as plt class MyBezier: def __init__(self, line): self.line = line self.index_02 = None #保存拖动的这个点的索引 self.press = None # 状态标识,1为按下,None为没按下 self.pick = None # 状态标识,1为选中点并按下,None为没选中 self.motion = None #状态标识,1为进入拖动,None为不拖动 self.xs = list() # 保存点的x坐标 self.ys = list() # 保存点的y坐标 self.cidpress = line.figure.canvas.mpl_connect('button_press_event', self.on_press) # 鼠标按下事件 self.cidrelease = line.figure.canvas.mpl_connect('button_release_event', self.on_release) # 鼠标放开事件 self.cidmotion = line.figure.canvas.mpl_connect('motion_notify_event', self.on_motion) # 鼠标拖动事件 self.cidpick = line.figure.canvas.mpl_connect('pick_event', self.on_picker) # 鼠标选中事件 def on_press(self, event): # 鼠标按下调用 if event.inaxes!=self.line.axes: return self.press = 1 def on_motion(self, event): # 鼠标拖动调用 if event.inaxes!=self.line.axes: return if self.press is None: return if self.pick is None: return if self.motion is None: # 整个if获取鼠标选中的点是哪个点 self.motion = 1 x = self.xs xdata = event.xdata ydata = event.ydata index_01 = 0 for i in x: if abs(i - xdata) < 0.02: # 0.02 为点的半径 if abs(self.ys[index_01] - ydata) < 0.02:break index_01 = index_01 + 1 self.index_02 = index_01 if self.index_02 is None: return self.xs[self.index_02] = event.xdata # 鼠标的坐标覆盖选中的点的坐标 self.ys[self.index_02] = event.ydata self.draw_01() def on_release(self, event): # 鼠标按下调用 if event.inaxes!=self.line.axes: return if self.pick == None: # 如果不是选中点,那就添加点 self.xs.append(event.xdata) self.ys.append(event.ydata) if self.pick == 1 and self.motion != 1: # 如果是选中点,但不是拖动点,那就降阶 x = self.xs xdata = event.xdata ydata = event.ydata index_01 = 0 for i in x: if abs(i - xdata) < 0.02: if abs(self.ys[index_01] - ydata) < 0.02:break index_01 = index_01 + 1 self.xs.pop(index_01) self.ys.pop(index_01) self.draw_01() self.pick = None # 所有状态恢复,鼠标按下到稀放为一个周期 self.motion = None self.press = None self.index_02 = None def on_picker(self, event): # 选中调用 self.pick = 1 def draw_01(self): # 绘图 self.line.clear() # 不清除的话会保留原有的图 self.line.axis([0,1,0,1]) # x和y范围0到1 self.bezier(self.xs,self.ys) # Bezier曲线 self.line.scatter(self.xs, self.ys,color='b',s=200, marker="o",picker=5) # 画点 self.line.plot(self.xs, self.ys,color='r') # 画线 self.line.figure.canvas.draw() # 重构子图 def bezier(self,*args): # Bezier曲线公式转换,获取x和y t=np.linspace(0,1) # t 范围0到1 le = len(args[0]) - 1 le_1 = 0 b_x,b_y = 0,0 for x in args[0]: b_x = b_x + x*(t**le_1)*((1-t)**le)*comb(len(args[0]) - 1,le_1) # comb 组合,perm 排列 le = le - 1 le_1 = le_1 + 1 le = len(args[0]) - 1 le_1 = 0 for y in args[1]: b_y = b_y + y*(t**le_1)*((1-t)**le)*comb(len(args[0]) - 1,le_1) le = le - 1 le_1 = le_1 + 1 self.line.plot(b_x,b_y) fig = plt.figure(2,figsize=(12,6)) #创建第2个绘图对象,1200*600像素 ax = fig.add_subplot(111) #一行一列第一个子图 ax.set_title('My Bezier') myBezier = MyBezier(ax) plt.xlabel('X') plt.ylabel('Y') plt.show()
二。运行结果
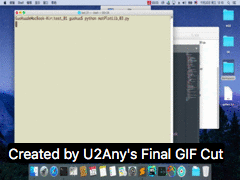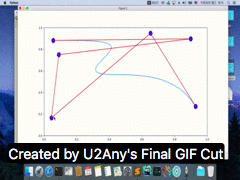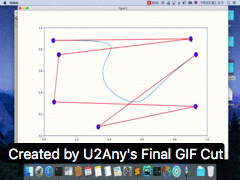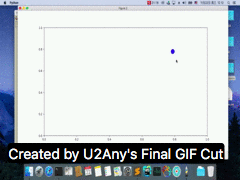
三。参考
http://blog.csdn.net/joogle/article/details/7975118
http://blog.csdn.net/wizardforcel/article/details/54782688