在做 LeetCode 309. 最佳买卖股票时机含冷冻期 时,写完递归超时后,企图用记忆化搜索优化,但是发现原本正确的结果变成错的了
Debug过程:
对于 [2,1,4] 这个用例,列出所有情况后发现最后一步的 not sell 和 buy 两个状态重叠了,导致记忆化错误
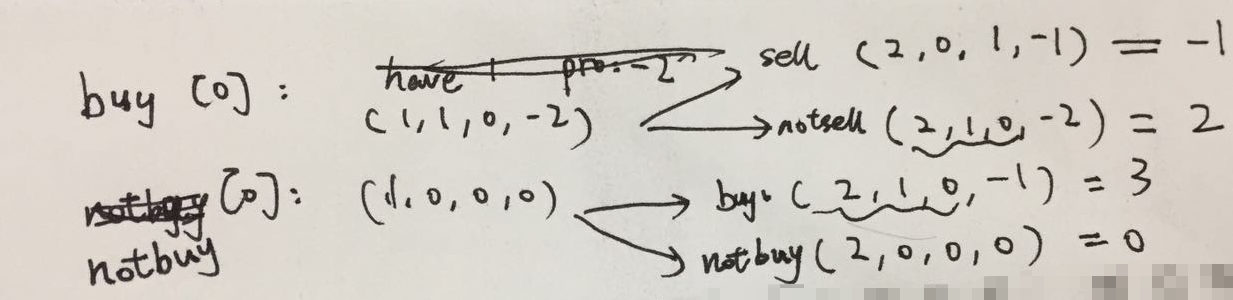
随后改为自顶向下的dp通过
查阅资料发现:https://www.cnblogs.com/zcy0917/p/9316487.html
记忆化搜索的适用范围
根据记忆化搜索的思想,它是解决重复计算,而不是重复生成,也就是说,这些搜索必须是在搜索扩展路径的过程中分步计算的题目,也就是“搜索答案与路径相关”的题目,而不能是搜索一个路径之后才能进行计算的题目,必须要分步计算,并且搜索过程中,一个搜索结果必须可以建立在同类型问题的结果上,也就是类似于动态规划解决的那种。
也就是说,他的问题表达,不是单纯生成一个走步方案,而是生成一个走步方案的代价等,而且每走一步,在搜索树/图中生成一个新状态,都可以精确计算出到此为止的费用,也就是,可以分步计算,这样才可以套用已经得到的答案.
使用条件
- 对于一定状态有唯一相同的解,不应对于一个状态有多个解(解不相同);
- 到达底层时可立即返回解,不应得出路径后才能计算解;
- 状态数量和规模应能够在有限数据结构中存储。
TIP
- 遵循无后效性原则;//某阶段的状态一旦确定,则此后过程的演变不再受此前各种状态及决策的影响。
- 局限性:可十分简洁的优化为递归,即动态规划。
- 往往对于dfs才会使用记忆化,因为bfs并不会重复搜索到某一个状态,而一旦搜索到结果就是最优解,此时立即退出;
递归:
class Solution { int[] prices; public int iter(int idx, boolean have, boolean frozen, int profit){ if (idx == prices.length - 1){ if (have){ profit += prices[prices.length - 1]; } return profit; } if (frozen){ return iter(idx + 1, have, false, profit); } if (have){ int sell = iter(idx+1, false, true, profit + prices[idx]); int notsell = iter(idx+1, true, false, profit); return Math.max(sell, notsell); }else { int buy = iter(idx+1, true, false, profit - prices[idx]); int notbuy = iter(idx+1, false, false, profit); return Math.max(buy, notbuy); } } public int maxProfit(int[] prices){ if (prices == null || prices.length <=0){ return 0; } this.prices = prices; return iter(0, false, false, 0); } }
记忆化搜索:
public class Solution { int[] prices; Integer[][][] dp; int len; public int iter(int idx, int have, int frozen, int profit){ if (dp[idx][have][frozen] != null){ return dp[idx][have][frozen]; } if (idx == prices.length - 1){ if (have == 1){ profit += prices[prices.length - 1]; } dp[idx][have][frozen] = profit; return profit; } int res; if (frozen == 1){ res = iter(idx + 1, 0, 0, profit); dp[idx][have][frozen] = res; return res; } if (have == 1){ int sell = iter(idx+1, 0, 1, profit + prices[idx]); int notsell = iter(idx+1, 1, 0, profit); res = Math.max(sell, notsell); }else { int buy = iter(idx+1, 1, 0, profit - prices[idx]); int notbuy = iter(idx+1, 0, 0, profit); res = Math.max(buy, notbuy); } dp[idx][have][frozen] = res; return res; } public int maxProfit(int[] prices){ if (prices == null || prices.length <=0){ return 0; } this.prices = prices; this.len = prices.length; dp = new Integer[len][2][2]; return iter(0, 0, 0, 0); } }
dp:
class Solution { public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { if (prices == null || prices.length <=0){ return 0; } int len = prices.length; // 这天开始的时候 idx, 有无股票, 是否在冷冻期 Integer[][][] dp = new Integer[len][2][2]; dp[len-1][0][0] = 0; dp[len-1][1][0] = prices[len-1]; dp[len-1][0][1] = 0; // 不可能出现dp[i][1][1] for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; --i) { for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) { for (int k = 0; k < 2; k++) { if (k == 1){ if (j != 1){ // i 0 1 dp[i][j][k] = dp[i+1][0][0]; } } else { if (j == 1){ // sell / not sell dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i+1][0][1] + prices[i], dp[i+1][1][0]); }else { // buy / not buy dp[i][j][k] = Math.max(dp[i+1][1][0] - prices[i], dp[i+1][0][0]); } } } } } return dp[0][0][0]; } }