平时偶尔在微信上玩一些小游戏,某天发现一款称之为《最强连一连》的益智游戏,具体玩法概括就是"一笔画"的问题。玩了几关之后随着游戏的格子数量的增加,感觉自己的算力不够用了【汗】于是打算写个脚本用于辅助。
- windows环境下搭建好python编程环境,本人使用python3.8.3版本
- 安装adb(添加到系统环境变量)
- 安卓手机打开usb调试模式,本人手机:小米note3分辨率为1920*1080
- pip 安装好python opencv库
通过对游戏界面截图分析,发现游戏通关过程其实就是从起始点格子(内外层颜色不同的格子)、访问完全部的空白格子。看到这里很容易联想到把所有的格子抽象成N×M的二维数组,我们把不可访问的格子抽象成二维数组中的‘1’,可访问的格子抽象成‘0’,起始点格子抽象成‘S’,然后问题就变成了从二维数组中的‘S’点不重复访问数组中所有的‘0’点。然后通过深度优先算法暴力进行求解、并记录访问顺序。我们把格子相应的坐标与二维数组中的点进行映射,通过遍历保存的路径,然后在屏幕上点击相对应的坐标那么问题就解决了。
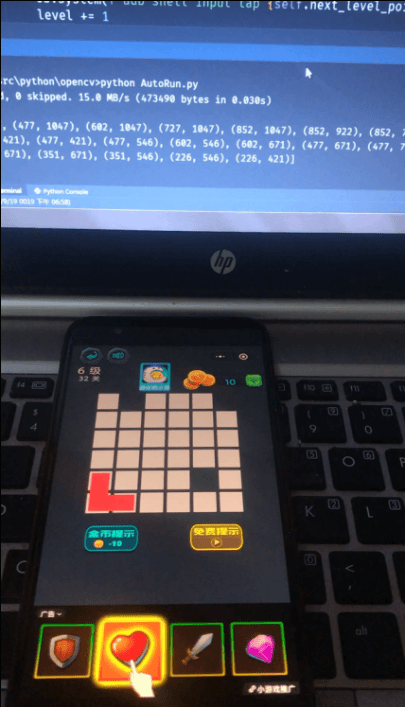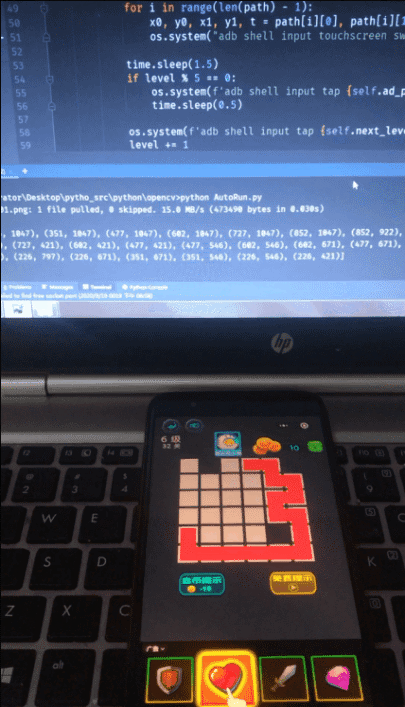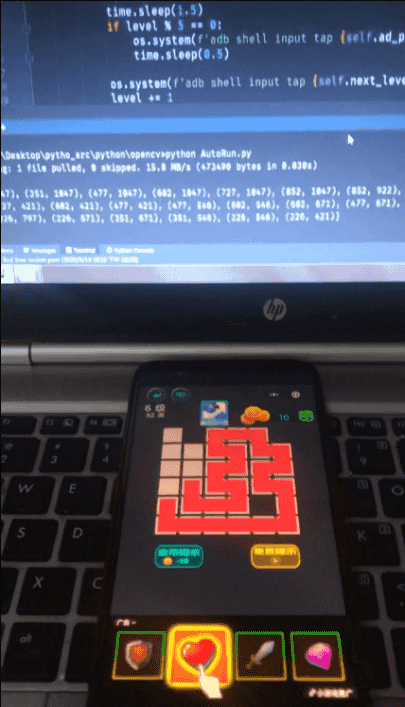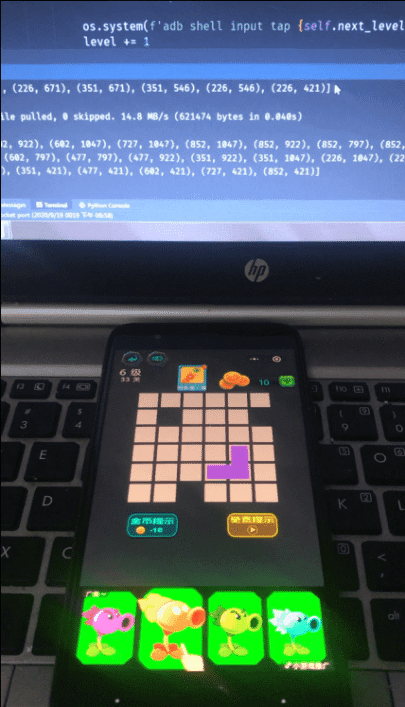
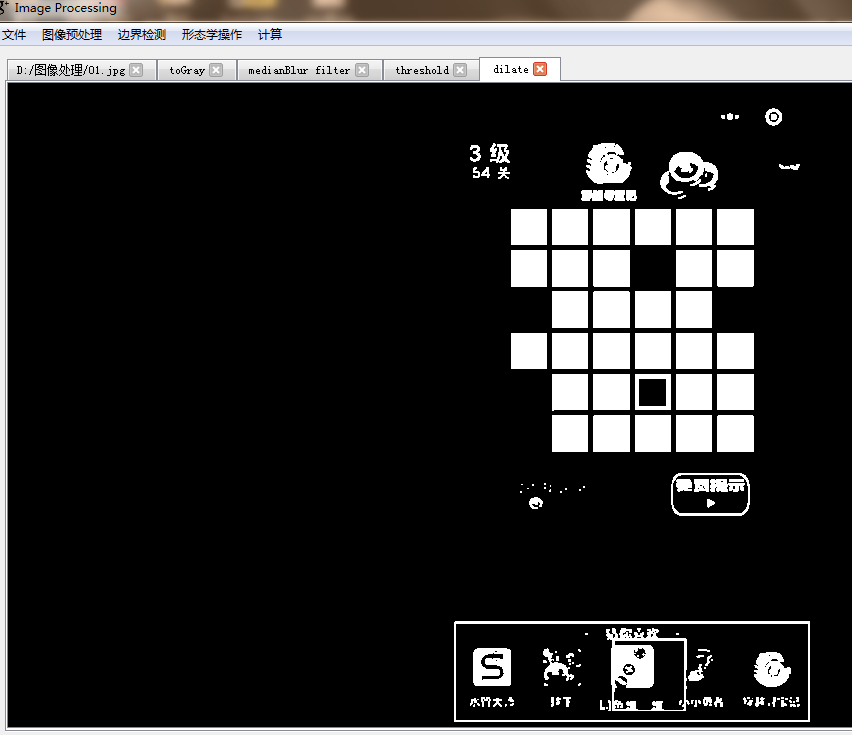
游戏运行界面:

经过上一步的分析我们需要获得游戏截图中所有的格子的坐标,提起图像处理那么现在该轮到opencv上场了,大致思路为:
5. 对游戏截图进行裁剪后,预处理灰度变换、滤波去噪点、二值化、膨胀处理
6. 使用findContours函数提取格子外轮廓,去掉边太短、两边差值过大的轮廓,选择相似面积最多的轮廓
7. 根据找到的轮廓按内颜色值不同,确定起始点格子
8. 找到格子轮廓的长与宽,以及轮廓之间的间距
9. 确定轮廓的左上顶点、然后枚举轮廓顶点坐标开始建图
图像预处理之后:
- 使用adb screencap命令对游戏界面进行截图
- 根据截图构建对应的二维数组
- 使用搜索算法求解、记录路径
- 遍历路径,使用adb tap或者touchscreen swipe命令点击相应的屏幕坐标点
- 游戏每次通关或通过累计5关后会弹出一个界面,使用adb tap命令点击相应坐标进入下一关
建图
"""
===================================
-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
Author :GadyPu
E_mail :Gadypy@gmail.com
Time :2020/9/20 0016 上午 11:44
FileName :create_map.py
===================================
"""
import cv2
import numpy as np
from find_path import FindPath
class CreateMap(object):
def __init__(self, img_path: str = '', cut_size: tuple = (320, 1600)):
self.img_path = img_path
self.cut_size = cut_size
self.points = []
self.start_ptn = None
self.x_min = 0
self.y_min = 0
def get_rect_area(self, point: tuple):
return abs(point[0] - point[2]) * abs(point[1] - point[3])
def img_process(self):
img = cv2.imdecode(np.fromfile(self.img_path, dtype = np.uint8), cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = gray[self.cut_size[0]: self.cut_size[1], :]
media_blur = cv2.medianBlur(gray, 3)
thres = cv2.threshold(media_blur, 180, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
dila = cv2.dilate(thres, (3, 3))
contours = cv2.findContours(dila, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[0]
for c in contours:
#cv2.drawContours(img, [c], -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
x, _x, y, _y = -1, 9999, -1, 9999
for [i] in c:
x = max(x, i[0])
_x = min(_x, i[0])
y = max(y, i[1])
_y = min(_y, i[1])
# 边太短的矩形丢弃
if abs(_x - x) < 40 or abs(_y - y) < 40:
continue
# 两边差值的绝对值控制在5以内
if abs(abs(_x - x) - abs(_y - y)) < 5:
self.points.append((_x, _y + self.cut_size[0], x, y + self.cut_size[0]))
# 寻找相似面积最多的轮廓
freq, freq_area = -1, -1
for i in range(len(self.points)):
area = self.get_rect_area(self.points[i])
count = 1
for j in range(len(self.points)):
if j == i:
continue
_area = self.get_rect_area(self.points[j])
if abs(area - _area) < 500:
count += 1
if count > freq:
freq = count
freq_area = area
point_temp = []
for i in self.points:
area = self.get_rect_area(i)
if abs(freq_area - area) < 500:
point_temp.append(i)
self.points.clear()
self.points = point_temp
self.points.reverse()
# 寻找起始点(内外颜色值不同)
count = { }
temp = None
for i in self.points:
x, y = (i[0] + i[2]) // 2, (i[1] + i[3]) // 2
d = tuple(img[y][x])
if d in count.keys():
count.pop(d)
temp = d
elif d != temp:
count[d] = i
for i in count:
self.start_ptn = count[i]
# cv2.imshow('', img)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
def get_map_size(self):
x, _x, y, _y = 9999, -1, 9999, -1
for i in self.points:
x = min(x, i[0])
y = min(y, i[1])
_x = max(_x, i[2])
_y = max(_y, i[3])
self.x_min = x
self.y_min = y
dif_x, dif_y = 0, 0
H, W = self.points[0][3] - self.points[0][1], self.points[0][2] - self.points[0][0]
n = (_x - x) // W
m = (_y - y) // H
ptn = self.points[0]
for i in range(1, len(self.points)):
if abs(ptn[1] - self.points[i][1]) < 3:
dif_x = self.points[i][0] - ptn[2]
if dif_x > W:
continue
else:
break
else:
ptn = self.points[i]
dif_y = dif_x
if n * W + (n - 1) * dif_x > _x - x + n * 2:
n -= 1
if m * H + (m - 1) * dif_y > _y - y + m * 2:
m -= 1
return m, n, dif_x, dif_y, H, W
def creat_grid(self):
m, n, dif_x, dif_y, H, W = self.get_map_size()
grid = [[('0', (0, 0)) for _ in range(n)] for _ in range(m)]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
_find = False
p1 = self.x_min + (dif_x + W) * j
p2 = self.y_min + (dif_y + H) * i
center_point = (None, None)
for ptn in self.points:
if abs(p1 - ptn[0]) < 5 and
abs(p2 - ptn[1]) < 5:
_find = True
center_point = (ptn[0] + ptn[2]) // 2, (ptn[1] + ptn[3]) // 2
if ptn == self.start_ptn:
grid[i][j] = ('S', center_point)
break
if grid[i][j][1] == (0, 0):
grid[i][j] = ('0' if _find else '1', center_point)
#print(grid)
return grid
def build_map(self, img_path):
self.img_path = img_path
self.points = []
self.start_ptn = None
self.x_min = 0
self.y_min = 0
self.img_process()
return self.creat_grid()
if __name__ == '__main__':
import time
t = time.time()
d = CreateMap()
grid = d.build_map('01.png')
p = FindPath()
print(p.find_path(grid))
print(time.time() - t)
寻找路径
"""
===================================
-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
Author :GadyPu
E_mail :Gadypy@gmail.com
Time :2020/9/20 0013 下午 07:59
FileName :find_path.py
===================================
"""
import copy
class FindPath(object):
def __init__(self):
self.dx = [0, 0, -1, 1]
self.dy = [-1, 1, 0, 0]
self.ret_path = []
self.blank = 0
self.start_x = -1
self.start_y = -1
def find_path(self, grid: list):
H, W = len(grid), len(grid[0])
vis = [[False for _ in range(W)] for _ in range(H)]
self.blank = 0
self.ret_path = []
for i in range(H):
for j in range(W):
if grid[i][j][0] == 'S':
self.start_x, self.start_y = i, j
vis[i][j] = True
elif grid[i][j][0] == '0':
self.blank += 1
self.dfs(self.start_x, self.start_y, grid, vis, H, W, 0, self.blank, [])
self.ret_path.insert(0, grid[self.start_x][self.start_y][1])
return self.ret_path
def dfs(self, x: int, y: int, grid: list, vis: list, H :int, W: int, step: int, tot: int, res: list):
if step == tot:
self.ret_path = copy.deepcopy(res)
print('find a answer!')
return None
for i in range(4):
_x, _y = x + self.dx[i], y + self.dy[i]
if _x < 0 or _y < 0 or _x >= H or _y >= W:
continue
if grid[_x][_y][0] == '0' and not vis[_x][_y]:
vis[_x][_y] = True
res.append(grid[_x][_y][1])
self.dfs(_x, _y, grid, vis, H, W, step + 1, tot, res)
vis[_x][_y] = False
res.pop()
if __name__ == '__main__':
pass
主程序
"""
===================================
-*- coding:utf-8 -*-
Author :GadyPu
E_mail :Gadypy@gmail.com
Time :2020/9/20 0016 上午 11:51
FileName :AutoRun.py
===================================
"""
import time
import signal
import os
from create_map import CreateMap
from find_path import FindPath
g_exit = True
class AutoRun():
def __init__(self):
self.get_map = CreateMap()
self.get_path = FindPath()
self.next_level_point = (536, 1417)
self.ad_point = (930, 660)
def handler(self, signum, frame):
global g_exit
g_exit = False
print('接收到ctrl c信号程序退出')
def run(self):
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, self.handler)
signal.signal(signal.SIGTERM, self.handler)
level = 1
while g_exit:
os.system('adb shell screencap -p /sdcard/Download/01.png')
os.system('adb pull /sdcard/Download/01.png')
time.sleep(1)
grid = self.get_map.build_map('01.png')
path = self.get_path.find_path(grid)
print(path)
if not path or len(path) == 1:
time.sleep(0.2)
continue
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
x0, y0, x1, y1, t = path[i][0], path[i][1], path[i + 1][0], path[i + 1][1], 50
os.system("adb shell input touchscreen swipe %d %d %d %d %d" % (x0, y0, x1, y1, t))
time.sleep(1.5)
if level % 5 == 0:
os.system(f'adb shell input tap {self.ad_point[0]} {self.ad_point[1]}')
time.sleep(0.5)
os.system(f'adb shell input tap {self.next_level_point[0]} {self.next_level_point[1]}')
level += 1
os.system(f'adb shell input tap 0 0')
print('程序运行中...')
if __name__ == '__main__':
d = AutoRun()
d.run()
每台手机分辨率不一样,若要在其他机型上运行需要修改相应的坐标点。
adb tap命令执行太慢了每通关一关差不多要20s左右,到现在也没有啥好的办法。