实验任务详情:
完成火车站售票程序的模拟。
要求:
(1)总票数1000张;
(2)10个窗口同时开始卖票;
(3)卖票过程延时1秒钟;
(4)不能出现一票多卖或卖出负数号票的情况。
实验代码
package test6;
public class MyThread implements Runnable{
private int ticket=999;
public int getTicket() {
return ticket;
}
public void setTicket(int ticket) {
this.ticket = ticket;
}
public void run() {
for(int i=0;i<1000;i++) {
synchronized (this) {
if(ticket>=0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(0);
}catch(InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
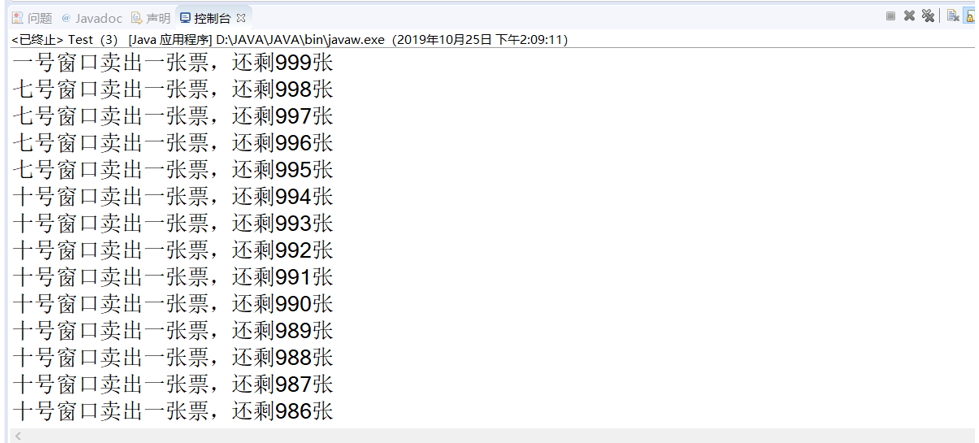
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖出一张票,还剩"+ticket+"张");
ticket--;
}
}
}
}
}
package test6;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread my=new MyThread();
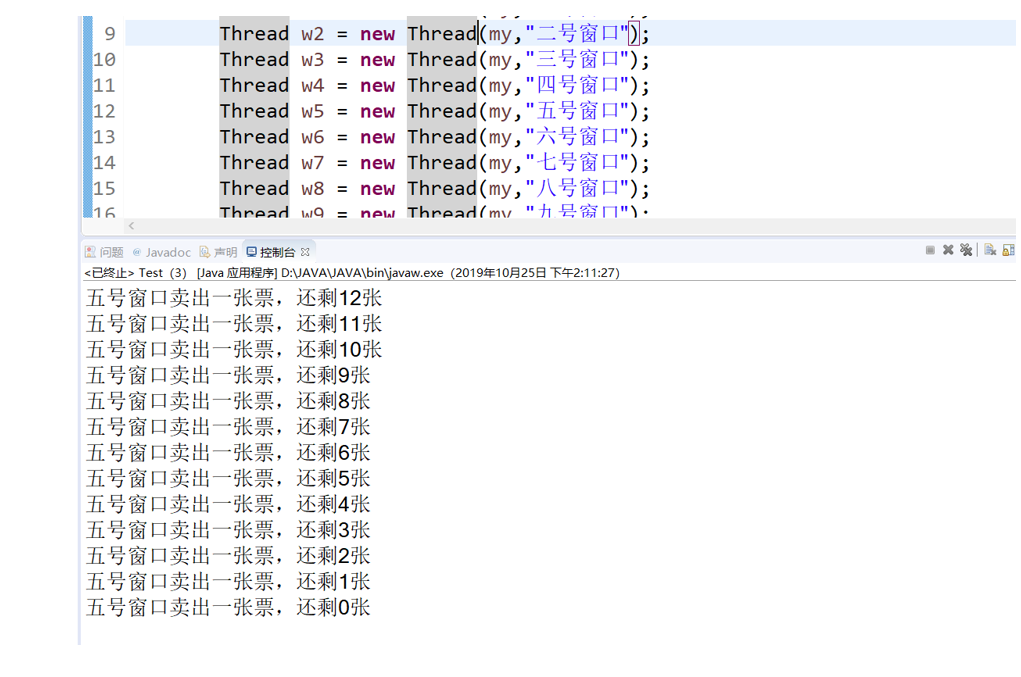
Thread w1 = new Thread(my,"一号窗口");
Thread w2 = new Thread(my,"二号窗口");
Thread w3 = new Thread(my,"三号窗口");
Thread w4 = new Thread(my,"四号窗口");
Thread w5 = new Thread(my,"五号窗口");
Thread w6 = new Thread(my,"六号窗口");
Thread w7 = new Thread(my,"七号窗口");
Thread w8 = new Thread(my,"八号窗口");
Thread w9 = new Thread(my,"九号窗口");
Thread w10 = new Thread(my,"十号窗口");
w1.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
w2.setPriority(Thread.MIN_PRIORITY);
w3.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
w1.start();
w2.start();
w3.start();
w4.start();
w5.start();
w6.start();
w7.start();
w8.start();
w9.start();
w10.start();
}
}
运行截图

学习总结
(一)多线程
1.这一周我们接着上一周的多线程学习了实现Runnable接口,上一周中学习了Thread类,thread类实现的是多线程,但是这个还是很局限的,而Runnable接口是用来实现资源共享同时也可以通过Runnable接口的方式实现多线程。
格式
class 类名称 extends Thread{ //继承Thread类
属性···;
方法···;
public void run(){
线程主体
}
}
通过Runnable接口实现多线程
class 类名称 implements Runnable{ //实现Runnable接口
属性···;
方法···;
public void run(){
线程主体
}
}
(二)Java IO
操作文件的类——File
在整个IO包中,唯一表示与文件本身有关的类就是File类,使用file类可以进行创建或删除文件等常用操作。
File类的构造方法:
public File(String pathname )
文件的删除和创建:
import java.io.File;
public class File{
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path=“d:”+File.separator+”test.txt”;
File f=new File(path);
if(f.exists()){
f.delete();
}else {
try{
createNewFile();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTreace();
}
}
}