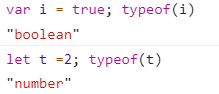
定义数组
const array =[1,2]; const arr = new Array(1,2,3,4); const array1 = new Array(); array1[0]="test";
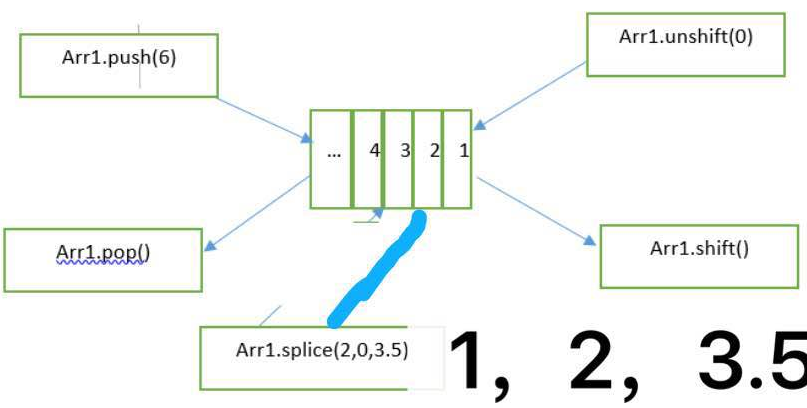
给数组不同位置插值,及头部弹出元素和尾部弹出元素的方法:
常用方法
1. array.concat(array1, array2,...arrayN);
合并多个数组,返回合并后的新数组,原数组没有变化。
const array = [1,2].concat(['a', 'b'], ['name']); // [1, 2, "a", "b", "name"]
2. array.every(callback[, thisArg]);
检测数组中的所有元素是否都满足条件,全部通过返回true,否则返回false。
[5,6,7,8].every(el=>{ return el > 5;//callback函数必须返回true或者false })
// 结果为false
3. array.filter(callback[, thisArg]);
返回符合条件的新数组
const filtered = [1, 2, 3].filter(element => element > 1); // filtered: [2, 3];
4. array.find(callback[, thisArg]);
返回满足条件的第一个元素,否则返回undefined
const finded = [1, 2, 3].find(element => element > 1); // finded: 2
5. array.findIndex(callback[, thisArg]);
返回满足条件的第一个元素的索引,否则返回-1
const findIndex = [1, 2, 3].findIndex(element => element > 1); // findIndex: 1
6. array.includes(searchElement, fromIndex);
includes() 方法用来判断一个数组是否包含一个指定的值,返回 true或 false。searchElement:要查找的元素;fromIndex:开始查找的索引位置。
[1, 2, 3].includes(4, 2); // false [1, 2, 3].includes(1); // true
7. array.indexOf(searchElement[, fromIndex = 0]);
返回在数组中第一个给定元素的索引,如果不存在,则返回-1。searchElement:要查找的元素;fromIndex:开始查找的索引位置。
[2, 9, 7, 8, 9].indexOf(9); // 1
8. array.join(separator=',');
将数组中的元素通过separator连接成字符串,并返回该字符串,separator默认为","。
[1, 2, 3].join(';');
// "1;2;3"
9. array.map(callback[, thisArg]);
返回一个新数组。注意:如果没有return值,则新数组会插入一个undefined值。
array.map由于不具有过滤的功能,因此array调用map函数时,如果array中的数据并不是每一个都会return,则必须先filter,然后再map,即map调用时必须是对数组中的每一个元素都有效。
const maped = [{name: 'aa', age: 18}, {name: 'bb', age: 20}].map(item => item.name + 'c');
// maped: ['aac', 'bbc'];
//对象转为数组
let country = {"beijing": 10, "shanghai": 6, "shenzhen": 9 };
let obj = Object.keys(country).map(key => ({ name: key, value: country[key] }) );
console.log(obj);
10. array.pop() 与 array.shift();
pop为从数组中删除最后一个元素,并返加该值,数组为空时返回undefined。
[1, 2, 3].pop(); // 3
shift删除数组的第一个元素,并返加该值,数组为空返回undefined。
const shifted = ['one', 'two', 'three'].shift(); // shifted: 'one'
11. array.push(element1, element2, ....elementN) 与 array.unshift(element1, element2, ...elementN);
push是将一个或多个元素添加到数组的末尾,并返回新数组的长度;
unshift将一个或多个元素添加到数组的开头,并返回新数组的长度。
const arr = [1, 2, 3]; const length = arr.push(4, 5); // arr: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; length: 5
push和unshift方法具有通用性,通过call()或者apply()方法调用可以完成合并两个数组的操作。
切记与 array.concat区分,它会产生新数组,不影响原数组。
12. array.reduce(callback[, initialValue]);
对数组中的每个元素(从左到右)执行callback,并把每次的返回值传递给下次
const total = [0, 1, 2, 3].reduce((sum, value) => { return sum + value; }, 0); // total is 6 const flattened = [[0, 1], [2, 3], [4, 5]].reduce((a, b) => { return a.concat(b); }, []); // flattened is [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]// initialValue累加器初始值, callback函数定义:
//取最大值 let ages = [1,12,3,5,4,8]; function getMax(val1,val2) { if (val1 > val2) { return val1; } else { return val2; } } let maxAge = ages.reduce((max,age)=>getMax(max,age), 0); console.log(maxAge ); //数组去重 let colors = ['red','green','blue','red','green','blue']; const distinctColor = colors.reduce((distinct, color) => ( (distinct.indexOf(color) !== -1) ? distinct : [...distinct, color] ), [] ); console.log(distinctColor);
function callback(accumulator, currentValue, currentIndex, array) { } accumulator代表累加器的值,初始化时,如果initialValue有值,则accumulator初始化的值为initialValue,整个循环从第一个元素开始;
initialValue无值,则accumulator初始化的值为数组第一个元素的值,currentValue为数组第二个元素的值,整个循环从第二个元素开始。
initialValue的数据类型可以是任意类型,不需要跟原数组内的元素值类型一致。
const newArray = [{ name: 'aa', age: 1 }, { name: 'bb', age: 2 }, { name: 'cc', age: 3 }].reduce((arr, element) => {
if (element.age >= 2) {
arr.push(element.name);
}
return arr; // 必须有return,因为return的返回值会被赋给新的累加器,否则累加器的值会为undefined。
}, []);
// newArray is ["bb", "cc"];
上面代码的同等写法:
const newArray = [{ name: 'aa', age: 1 }, { name: 'bb', age: 2 }, { name: 'cc', age: 3 }]
.filter(element => element.age >= 2)
.map(item => item.name);
// newArray is ["bb", "cc"];
对于reduce的特殊用法,其实类似于省略了一个变量初始化步骤,然后通过每次的callback的返回修改该变量,最后返回最终变量值的过程,类似于一个变量声明 + 一个forEach执行过程。
const newArray = []; [{ name: 'aa', age: 1 }, { name: 'bb', age: 2 }, { name: 'cc', age: 3 }].forEach(item => { if (item.age >=2) { newArray.push(item.name); } });
13. array.reverse();
将数组中元素的位置颠倒。
['one', 'two', 'three'].reverse(); // ['three', 'two', 'one'],原数组被翻转
14. array.slice(begin, end)
返回一个新数组,包含原数组从begin 到 end(不包含end)索引位置的元素。
const newArray = ['zero', 'one', 'two', 'three'].slice(1, 3); // newArray: ['one', 'two'];
15. array.some(callback[, thisArg]);
判断数组中是否含有满足条件的元素。找到第一个满足条件的元素时,立即返回true。
[2, 5, 8, 1, 4].some(item => item > 6); // true
16. array.sort([compareFunction]);
对数组中的元素进行排序,compareFunction不存在时,元素按照转换为的字符串的诸个字符的Unicode位点进行排序,慎用!请使用时一定要加compareFunction函数,而且该排序是不稳定的。
[1, 8, 5].sort((a, b) => { return a-b; // 从小到大排序 }); // [1, 5, 8]
17. array.splice(start[, deleteCount, item1, item2, ...]);
通过删除现有元素和/或添加新元素来更改一个数组的内容。start:指定修改的开始位置;deleteCount:从 start位置开始要删除的元素个数;item...:要添加进数组的元素,从start 位置开始。
返回值是由被删除的元素组成的一个数组。如果只删除了一个元素,则返回只包含一个元素的数组。如果没有删除元素,则返回空数组。
如果 deleteCount 大于start 之后的元素的总数,则从 start 后面的元素都将被删除(含第 start 位)。
const myFish = ['angel', 'clown', 'mandarin', 'sturgeon']; const deleted = myFish.splice(2, 0, 'drum'); // 在索引为2的位置插入'drum' // myFish 变为 ["angel", "clown", "drum", "mandarin", "sturgeon"],deleted为[]
caveat
push、 unshift、 shift、 pop、 reverse、 sort、 splice这七个方法直接修改原数组。其他方法不会改动原数组。校验是不是数组
Array.isArray([]); // true
Array.isArray(undefined); // false;
或者
array instanceof Array; // true 检测对象的原型链是否指向构造函数的prototype对象
或者
array.constructor === Array; // true
注意:typeof []; // "object" 不可以用此方法检查!!!