一、快速排序:qsort
头文件:stdlib.h
函数原型:void qsort(void *base, size_t nitems, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void *, const void*))
参数说明:
base -- 指向要排序的数组的第一个元素的指针。
nitems -- 由 base 指向的数组中元素的个数。
size -- 数组中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位,通常为sizeof(base[0])。
compar -- 用来比较两个元素的函数,需要自己定义,可以实现复杂的比较逻辑;
compar函数的返回值,<0(不进行置换),>0(进行置换),0(不进行置换)。
比较函数说明:
函数原型: int compar(const void *a, const void *b);
如果*a应该排在*b前面,则compar返回负整值;
如果*a与*b排序不分,则compar返回0;
如果*a应该排在*b后面,则compar返回正整值。
无返回值
1、一维数组排序
// 比较函数:升序
int cmpfunc (const void * a, const void * b)
{
return ( *(int*)a - *(int*)b );
}
// double 类型
int inc (const void * a, const void * b)
{
return *(double *)a > *(double *)b ? 1 : -1;
}
完成例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int cmpfunc (const void * a, const void * b)
{
return ( *(int*)a - *(int*)b );
}
int main()
{
int n;
int values[] = { 88, 56, 100, 2, 25 };
printf("before qsort:
");
for( n = 0 ; n < 5; n++ ) {
printf("%d ", values[n]);
}
qsort(values, 5, sizeof(int), cmpfunc);
printf("
after qsort:
");
for( n = 0 ; n < 5; n++ ) {
printf("%d ", values[n]);
}
return(0);
}
2、二维数组排序
// 比较函数
// 对于malloc申请内存的二维数组
int cmp1(const void *a,const void *b)
{
int *ap = *(int **)a;
int *bp = *(int **)b;
if(ap[0] == bp[0])
return ap[1] - bp[1];
else
return ap[0] - bp[0];
}
// 对于变量定义的二维数组
int cmp(const void *a, const void *b)
{
return ((int *)a)[0] - ((int *)b)[0];
}
// 可以将二维数组转换成结构体数组
struct node
{
int x,y;
} a[1000];
int cmp(const void *a,const void *b) //要转化为结构体类型
{
struct node *c = (node*)a;
struct node *d = (node*)b;
return c->y - d->y;
}
3、字符串数组排序
// 字符串数组比较函数
int compare(const void *arg1, const void *arg2) {
char *a = (char*)arg1;
char *b = (char*)arg2;
int result = strcmp(a, b);
if (result > 0) {
return 1;
}
else if (result < 0) {
return -1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
// 字符串指针数组比较函数
int compare(const void *arg1, const void *arg2) {
char *a = *(char**)arg1;
char *b = *(char**)arg2;
int result = strcmp(a, b);
if (result > 0) {
return 1;
}
else if (result < 0) {
return -1;
}
else {
return 0;
}
}
// 完整例子
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
int strCmp(const void *a, const void *b)
{
return strcmp((char * )a, (char *)b);
}
int main ()
{
char array[10][8] = {
"rbsc",
"jcsse",
"afgdsd",
"arbs",
"abs",
"cbfefaa",
"cgafg" ,
"ewqrta",
"ofgd",
"mbcv312",
};
qsort(array, 10, sizeof(array[0]), strCmp);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%s
", array[i]);
}
return 0;
}
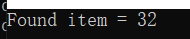
测试结果:
4、结构体数组排序
// 完整例子:包括结构体耳机排序
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define NUM 5
struct Student{
unsigned ID;
char szName[20];
float fGPA;
};
struct Student MyClass[NUM]={
{1234,"Tom",3.78},
{1345,"Sam",2.12},
{1795,"Bob",4.77},
{1456,"Echo",1.34},
{1178,"Amy",3.04},
};
int IDCompare(const void * elem1,const void * elem2)
{
return ((struct Student *)elem1)->ID - ((struct Student *)elem2)->ID;
}
int NameCompare(const void * elem1, const void * elem2)
{
return ((struct Student *)elem1)->szName - ((struct Student *)elem2)->szName;
}
int fGpaCompare(const void * elem1, const void * elem2)
{
// double类型判断
return (((struct Student *)elem1)->fGPA < ((struct Student *)elem2)->fGPA) ? -1 : 1;
}
int idFGpaCompare(const void * elem1, const void * elem2)
{
// double类型判断
if (((struct Student *)elem1)->ID != ((struct Student *)elem2)->ID) {
return ((struct Student *)elem1)->ID - ((struct Student *)elem2)->ID;
} else {
return (((struct Student *)elem1)->fGPA < ((struct Student *)elem2)->fGPA) ? -1 : 1;
}
}
int main()
{
qsort(MyClass, NUM, sizeof(MyClass[0]), IDCompare);
for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++) {
printf("IDCompare: id[%d], name[%s], fpga[%f]
", MyClass[i].ID, MyClass[i].szName, MyClass[i].fGPA);
}
printf("
");
qsort(MyClass, NUM, sizeof(MyClass[0]), NameCompare);
for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++) {
printf("NameCompare: id[%d], name[%s], fpga[%f]
", MyClass[i].ID, MyClass[i].szName, MyClass[i].fGPA);
}
printf("
");
qsort(MyClass, NUM, sizeof(MyClass[0]), fGpaCompare);
for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++) {
printf("fGpaCompare: id[%d], name[%s], fpga[%f]
", MyClass[i].ID, MyClass[i].szName, MyClass[i].fGPA);
}
printf("
");
qsort(MyClass, NUM, sizeof(MyClass[0]), idFGpaCompare);
for(int i=0;i<NUM;i++) {
printf("idfGpaCompare: id[%d], name[%s], fpga[%f]
", MyClass[i].ID, MyClass[i].szName, MyClass[i].fGPA);
}
return 0;
}
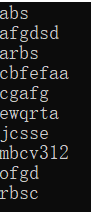
测试结果:
二、查找:bsearch
头文件:stdlib.h
函数原型:void *bsearch(const void *key, const void *base, size_t nitems, size_t size, int (*compar)(const void *, const void *))
参数说明:
key -- 指向要查找的元素的指针,类型转换为 void*;
base -- 指向进行查找的数组的第一个对象的指针,类型转换为 void*;
nitems -- base 所指向的数组中元素的个数, sizeof(base)/sizeof(base[0]);
size -- 数组中每个元素的大小,以字节为单位;
compar -- 用来比较两个元素的函数, compar 函数提供给用户的接口,对所需的内容进行比较。compar会返回一个值,表示比较的结果,如果返回0,bsearch函数立即返回,并且返回在base中找到的位置信息,如果到最后都没有找到,则返回null。
返回值:如果查找成功,该函数返回一个指向数组中匹配元素的指针,否则返回空指针。
注意: 数据必须是经过预先排序的,而排序的规则要和comp所指向比较子函数的规则相同。
// 完整示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int cmpfunc(const void * a, const void * b)
{
return (*(int*)a - *(int*)b);
}
int main()
{
int *item;
int key = 32;
int values[] = { 5, 20, 29, 32, 63 };
/* 使用 bsearch() 在数组中查找值 32 */
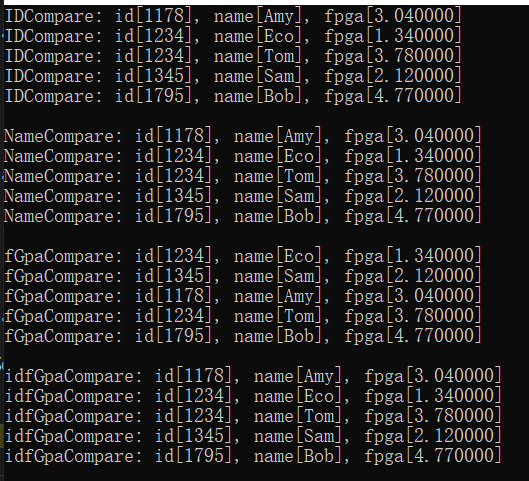
item = (int*) bsearch (&key, values, 5, sizeof (int), cmpfunc);
if (item != NULL) {
printf("Found item = %d
", *item);
} else {
printf("Item = %d could not be found
", *item);
}
return(0);
}
// 测试结果