下面列举了椭圆曲线GF(p)素数域常用函数:(持续更新)
椭圆曲线GF(p)素数域常用函数:
1.椭圆曲线方程初始化
ecurve_init
Function: void ecurve_init(A,B,p,type)
big A,B,p;
int type;
Module: mrcurve.c
Description: Initialises the internal parameters of the current active GF(p) elliptic curve. The curve is assumed to be of the form y2 =x3 + Ax + B mod p, the so-called Weierstrass model. This routine can be called subsequently with the parameters of a different curve.
Parameters: Three big numbers A, B and p. The type parameter must be either MR_PROJECTIVE or MR_AFFINE, and specifies whether projective or affine co-ordinates should be used internally. Normally the former is faster. (投影坐标、仿射坐标)
Return value: None
2.点乘
ecurve_mult
Function: void ecurve_mult(k,p,pa)
big k;
epoint *p,*pa;
Description: Multiplies a point on a GP(p) elliptic curve by an integer. Uses the addition/subtraction method.
Parameters: A big number k, and two points p and pa. On exit pa=k*p.
Return value: None
Restrictions: The point p must be on the active curve.
3.点乘加快速运算
ecurve_mult2
Function: void ecurve_mult2(k1,p1,k2,p2,pa)
big k1,k2;
epoint *p1,*p2,*pa;
Description: Calculates the point k1.p1+k2.p2 on a GF(p) elliptic curve. This is quicker than doing two separate multiplications and an addition. Useful for certain cryptosystems. (See ecsver.c for example)
Parameters: Two big integers k1 and k2, and three points p1, p2 and pa.
On exit pa = k1.p1+k2.p2
Return value: None
4.点的加法pa=pa+a
ecurve_add
Function: void ecurve_add(p,pa)
epoint *p,*pa;
Description: Adds two points on a GF(p) elliptic curve using the special rule for addition. Note that if pa=p, then a different duplication rule is used. Addition is quicker if p is normalised.
Parameters: Two points on the current active curve, pa and p. On exit pa=pa+p.
Return value: None
Restrictions: The input points must actually be on the current active curve.
5.点的减法pa=pa-a
ecurve_sub
Function: void ecurve_sub(p,pa)
epoint *p,*pa;
Description: Subtracts two points on a GF(p) elliptic curve. Actually negates p and adds it to pa. Subtraction is quicker if p is normalised.
Parameters: Two points on the current active curve, pa and p. On exit pa = pa-p.
Return value: None
Restrictions: The input points must actually be on the current active curve.
6.比较椭圆曲线上两个点是否相同
epoint_comp
Function: BOOL epoint_comp(p1,p2)
epoint *p1,*p2;
Description: Compares two points on the current active GF(p) elliptic curve.
Parameters: Two points p1 and p2.
Return Value: TRUE if the points are the same, otherwise FALSE.
7.点的复制
epoint_copy
Function: void epoint_copy(p1,p2)
epoint *p1,*p2;
Description: Copies one point to another on a GF(p) elliptic curve.
Parameters: Two points p1 and p2. On exit p2=p1.
Return value: None
8.初始化点 返回epoint类型点
epoint_init
Function: epoint* epoint_init()
Description: Assigns memory to a point on a GF(p) elliptic curve, and initialises it to the "point at infinity".(并将其初始化为“无穷远点”)
Parameters: None.
Return value: A point p (in fact a pointer to a structure allocated from the heap).Parameters: A point p.
C程序员有责任确保通过调用此函数初始化的所有椭圆曲线点最终通过调用epoint_free释放;如果没有,将导致内存泄漏。
9.释放点内存
epoint_free
Function: void epoint_free(p)
epoint *p;
Description: Frees memory associated with a point on a GF(p) elliptic curve.
10.设置点坐标,若属于当前方程则返回True,不满足当前方程返回False
值得注意的是:设置后(x!=p->X y!=p->Y)
epoint_set
Function: BOOL epoint_set(x,y,lsb,p)
big x,y;
int lsb;
epoint *p;
Description: Sets a point on the current active GF(p) elliptic curve (if possible).
Parameters: The integer co-ordinates x and y of the point p. If x and y are not distinct variables then x only is passed to the function, and lsb is taken as the least significant bit of y. In this case the full value of y is reconstructed internally. This is known as “point decompression” (and is a bit time-consuming, requiring the extraction of a modular square root). On exit p=(x,y).
Return value: TRUE if the point exists on the current active point, otherwise FALSE.
Restrictions: None
Example: C=epoint_init();
epoint_set(x,x,1,C);
/* decompress C */
11.从epoint结构体中取出点坐标赋给给x、y
值得注意的是:设置后(p->X!=x p->Y!y)
epoint_get
Function: int epoint_get(p,x,y)
epoint *p;
big x,y;
Description: Normalises a point and extracts its (x,y) co-ordinates on the active GF(p) elliptic curve.
Parameters: A point p, and two big integers x and y. If x and y are not distinct variables on entry then only the value of x is returned.
Return value: The least significant bit of y. Note that it is possible to reconstruct a point from its x co-ordinate and just the least significant bit of y. Often such a “compressed” description of a point is useful.
Restrictions: The point p must be on the active curve.
Example: i=epoint_get(p,x,x);
/* extract x co-ordinate and lsb of y */
12.检验x坐标是否在椭圆曲线下存在点(合法)
epoint_x
Function: BOOL epoint_x(x)
big x;
Description: Tests to see if the parameter x is a valid co-ordinate of a point on the curve. It is faster to test an x co-ordinate first in this way, rather than trying to directly set it on the curve by calling epoint_set, as it avoids an expensive modular square root.
Parameters: The integer coordinate x.
Return value: TRUE if x is the coordinate of a curve point, otherwise FALSE
13.是否为无穷远点
point_at_infinity
Function: BOOL point_at_infinity(p)
epoint *p;
Description: Tests if an elliptic curve point is the "point at infinity".
Parameters: An elliptic curve point p.
Return value: TRUE if p is the point-at-infinity, otherwise FALSE.
Restrictions: The point must be initialised.
这里建立的曲线方程参数是SM2国密算法官方文档给的比较安全的推荐参数:
推荐使用素数域256位椭圆曲线
椭圆曲线方程: y2 = x3 + ax + b
曲线参数:
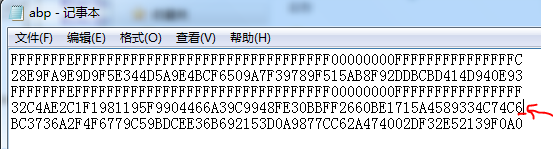
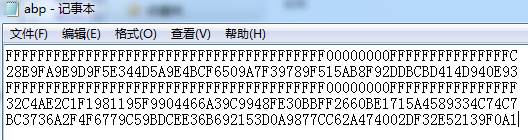
p=FFFFFFFE FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF 00000000 FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF
a=FFFFFFFE FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF 00000000 FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFC
b=28E9FA9E 9D9F5E34 4D5A9E4B CF6509A7 F39789F5 15AB8F92 DDBCBD41 4D940E93
n=FFFFFFFE FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF FFFFFFFF 7203DF6B 21C6052B 53BBF409 39D54123
Gx=32C4AE2C 1F198119 5F990446 6A39C994 8FE30BBF F2660BE1 715A4589 334C74C7
Gy=BC3736A2 F4F6779C 59BDCEE3 6B692153 D0A9877C C62A4740 02DF32E5 2139F0A0
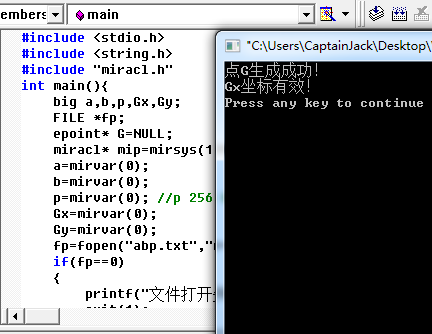
下面给出一段代码实例(把参数a、b、p、Gx、Gy依次放到txt文档内)

#include <stdio.h> #include "miracl.h" int main(){ big a,b,p,Gx,Gy; FILE *fp; epoint* G=NULL; miracl* mip=mirsys(1000,16); a=mirvar(0); b=mirvar(0); p=mirvar(0); //p 256 bits Gx=mirvar(0); Gy=mirvar(0); fp=fopen("abp.txt","r+"); //fp指向同目录下存放大数的文件 if(fp==0) { printf("文件打开失败!"); exit(1); } mip->IOBASE=16; cinnum(a,fp); cinnum(b,fp); cinnum(p,fp); cinnum(Gx,fp); cinnum(Gy,fp); fclose(fp); /* printf("a="); cotnum(a,stdout); printf("b="); cotnum(b,stdout); printf("p="); cotnum(p,stdout);*/ ecurve_init(a,b,p,MR_PROJECTIVE); G=epoint_init(); if(epoint_set(Gx,Gy,0,G)) printf("点G生成成功!\n"); else printf("点G生成失败!\n"); if(epoint_x(Gx)) printf("Gx坐标有效!\n"); else printf("Gx坐标无效!\n"); mirkill(a); mirkill(b); mirkill(p); mirkill(Gx); mirkill(Gy); epoint_free(G); mirexit(); return 0; }
执行查看点坐标G是否合法、存在
若修改一下Gx内容:
再次执行:
也可以只修改Gy的值:
执行: