一、概述
在看JDK源码时,看到关于map相关的,看到HashMap时,一部分源码与红黑树有关。索性就将树这种数据结构从头学一遍,记录下来,给自己还有他人留个参考和学习的资料。
涉及到使用二叉树进行排序、查找节点值、前序遍历、中序遍历、后续遍历(它们的递归实现和非递归实现)、删除节点、查找最大节点、查找最小节点。
二、开讲
下面为代码片段,在文档最后面有完整代码
1. 定义二叉树节点(我是用的是静态内部类)
/**
* 二叉树节点
*/
static class Node {
int value;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Node(int value, Node leftChild, Node rightChild) {
this.value = value;
this.leftChild = leftChild;
this.rightChild = rightChild;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.valueOf(value);
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Node node = (Node) o;
return value == node.value;
}
}2.类的整体结构和定义操作
/**
* 二叉树(根据大小排序)
*/
public class BinaryTree {
private Node root;
private int treeDepth;
private int treeWidth;
public BinaryTree(int value) {
this.root = new Node(value);
}
public boolean insert(int t) // 插入节点
public int getTreeDepth() // 获取树的深度
public int getTreeWidth() // 树的逻辑最大宽度
public void preOrderTtaverse() // 前序遍历
public void preOrderByStack() // 前序遍历非递归实现
public void inOrderTraverse() // 中序遍历
public void inOrderByStack() // 中序遍历非递归实现
public void postOrderTraverse() // 后续遍历
public void postOrderByStack() // 后续遍历非递归实现
public void printBinaryTreeByRow() // 行式打印二叉树
public void printBinaryTreeByColumn() // 列式打印二叉树
public Node findKey(int value) // 查找指定值
public boolean removeNode(int value) // 移除指定节点
public int getMinValue() // 获取最小值
public int getMaxValue() // 获取最大值
}3.插入数据
/**
* 插入新节点
*
* @param t 节点的值域
* @return 操作是否成功
* @throws Exception
*/
public boolean insert(int t) throws Exception {
Node newNode = new Node(t); // 创建新的节点
// 计数器
int count = 0;
if (root == null) { // 如果根节点为空,将新节点赋值给根节点
root = newNode;
count++;
} else {
Node current = root; // 节点指针
Node parent; // 节点指针的父节点
for (; ; ) { // 循环遍历
count++;
if (t < current.value) { // 小于当前节点,插入在左边
parent = current;
current = current.leftChild;
if (current == null) { // 如果节点指针为空,此时父节点为叶子节点,此时该插入元素
parent.leftChild = newNode;
break; // 插入完成,打破循环
}
} else if (t > current.value) { // 大于当前节点,插入在右边
parent = current;
current = current.rightChild;
if (current == null) { // 如果节点指针为空,此时父节点为叶子节点,此时该插入元素
parent.rightChild = newNode;
break; // 插入完成,打破循环
}
} else {
throw new Exception("comparsion Exception for compare value big or small(insert() method!)");
}
}
}
if (treeDepth < count) { // 计算二叉树深度和逻辑逻辑宽度
treeDepth = count;
treeWidth = (int)Math.pow(2, treeDepth);
}
return true;
}4.获取二叉排序树的最大深度、最大逻辑宽度
// 返回深度
public int getTreeDepth() {
return treeDepth;
}
// 返回宽度
public int getTreeWidth() {
return treeWidth;
}5.前序遍历
递归实现:
/**
* 前序遍历二叉树(递归实现)
*/
public void preOrderTtaverse() {
System.out.print("二叉树它的前序遍历: ");
preOrderTtaverse(root);
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 前序遍历:
* 若二叉树为空,则空操作返回;
* 若二叉树不为空,则执行下述操作:
* (1) 访问根节点;
* (2) 前序遍历根节点的左子树
* (3) 前序遍历根节点的右子树
*/
private void preOrderTtaverse(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
preOrderTtaverse(node.leftChild);
preOrderTtaverse(node.rightChild);
}非递归实现:
/**
* 前序非递归遍历:
* 1)对于任意节点current,若该节点不为空则访问该节点后再将节点压栈,并将左子树节点置为current,重复此操作,直到current为空。
* 2)若左子树为空,栈顶节点出栈,将该节点的右子树置为current
* 3) 重复1、2步操作,直到current为空且栈内节点为空。
*/
public void preOrderByStack() {
System.out.print("前序遍历非递归实现: ");
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>(); //栈,用于保存节点
Node current = root; // 节点指针
while (current != null || !stack.isEmpty()) { // 节点指针不为空或栈不为空时循环
while (current != null) {
stack.push(current);
System.out.print(current.value + " ");
current = current.leftChild;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
current = stack.pop();
current = current.rightChild;
}
}
System.out.println();
}6.中序遍历
递归实现:
/**
* 中序遍历:
* 若二叉树为空,则空操作返回;否者执行下列操作:
* 1.中序遍历访问根节点左子树
* 2.访问根节点
* 3.中序遍历访问根节点右子树
*/
public void inOrderTraverse() {
System.out.print("二叉树它的中序遍历: ");
inOrderTraverse(root);
System.out.println();
}
// 递归实现
private void inOrderTraverse(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
inOrderTraverse(node.leftChild);
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
inOrderTraverse(node.rightChild);
}非递归实现:
/**
* 中序非递归遍历:
* 1)对于任意节点current,若该节点不为空则将该节点压栈,并将左子树节点置为current,重复此操作,直到current为空。
* 2)若左子树为空,栈顶节点出栈,访问节点后将该节点的右子树置为current
* 3) 重复1、2步操作,直到current为空且栈内节点为空。
*/
public void inOrderByStack() {
System.out.print("中序遍历非递归实现: ");
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Node current = root;
while (current != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (current != null) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.leftChild;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
current = stack.pop();
System.out.print(current.value + " ");
current = current.rightChild;
}
}
System.out.println();
}7.后续遍历
递归实现:
/**
* 后序遍历:
* 若二叉树为空,则空操作返回;否则执行下列操作:
* 1.后续遍历根节点的左子树
* 2.后续遍历根节点的右子树
* 3.访问根节点
*/
public void postOrderTraverse() {
System.out.print("二叉树它的后序遍历: ");
postOrderTraverse(root);
System.out.println();
}
// 递归实现
private void postOrderTraverse(Node node) {
if (node == null)
return;
postOrderTraverse(node.leftChild);
postOrderTraverse(node.rightChild);
System.out.print(node.value + " ");
}非递归实现:
/**
* 后序非递归遍历:
* 1)对于任意节点current,若该节点不为空则访问该节点后再将节点压栈,并将左子树节点置为current,重复此操作,直到current为空。
* 2)若左子树为空,取栈顶节点的右子树,如果右子树为空或右子树刚访问过,则访问该节点,并将preNode置为该节点
* 3) 重复1、2步操作,直到current为空且栈内节点为空。
*/
public void postOrderByStack() {
System.out.print("后序遍历非递归实现: ");
Stack<Node> stack = new Stack<>();
Node current = root;
Node preNode = null;
while (current != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
while (current != null) {
stack.push(current);
current = current.leftChild;
}
if (!stack.isEmpty()) {
current = stack.peek().rightChild;
if (current == null || current == preNode) {
current = stack.pop();
System.out.print(current.value + " ");
preNode = current;
current = null;
}
}
}
System.out.println();
}8.删除节点(是这里相对来说比较复杂的内容)
1) 删除节点为叶子节点
// 分情况讨论删除节点的情况:
// 1.需要删除的节点为叶子节点
if (waitRemoveNode.leftChild == null && waitRemoveNode.rightChild == null) {
// 如果为根节点(树中只有做一个节点-节点)
if (waitRemoveNode == root) {
root = null;
} else {
if (isLeftChild) //如果该叶节点是父节点的左子节点,将父节点的左子节点置为null
parent.leftChild = null;
else //如果该叶节点是父节点的右子节点,将父节点的右子节点置为null
parent.rightChild = null;
}
}2)删除的节点只有一个节点:只有一个左子节点、只有一个右子节点
// 2.1 需要删除的节点有一个节点,且该节点为左子节点
else if (waitRemoveNode.rightChild == null) {
// 如果该节点为根节点,将根节点的左子节点变为根节点
if (waitRemoveNode == root) {
root = waitRemoveNode.leftChild;
} else {
// 如果该节点是父节点的左子节点,将待删除节点的左子节点变为父节点的左子节点
if (isLeftChild)
parent.rightChild = waitRemoveNode.leftChild;
else // 如果该节点是父节点的右子节点,将待删除节点的左子节点变为父节点的右子节点
parent.rightChild = waitRemoveNode.leftChild;
}
}
// 2.2 需要删除的节点有一个节点,且该节点为右子节点
else if (waitRemoveNode.leftChild == null) {
// 如果该节点为根节点,将根节点的右子节点变为根节点
if (waitRemoveNode == root) {
root = waitRemoveNode.rightChild;
} else {
// 如果该节点是父节点的左子节点,将待删除节点的右子节点变为父节点的左子节点
if (isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild = waitRemoveNode.rightChild;
else // 如果该节点是父节点的右子节点,将待删除节点的右子节点变为父节点的右子节点
parent.rightChild = waitRemoveNode.rightChild;
}
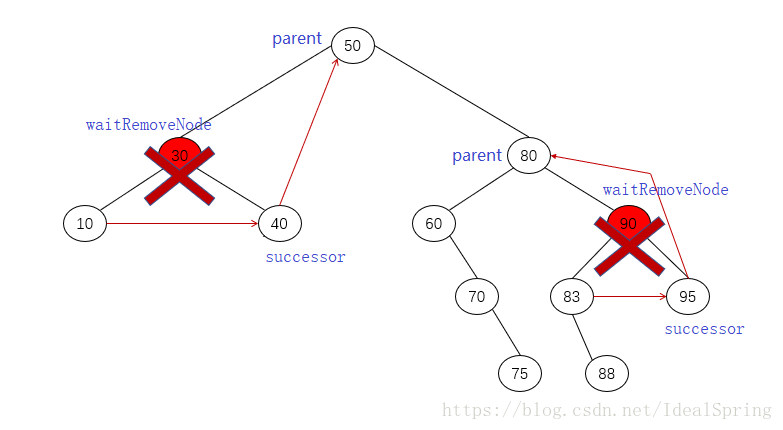
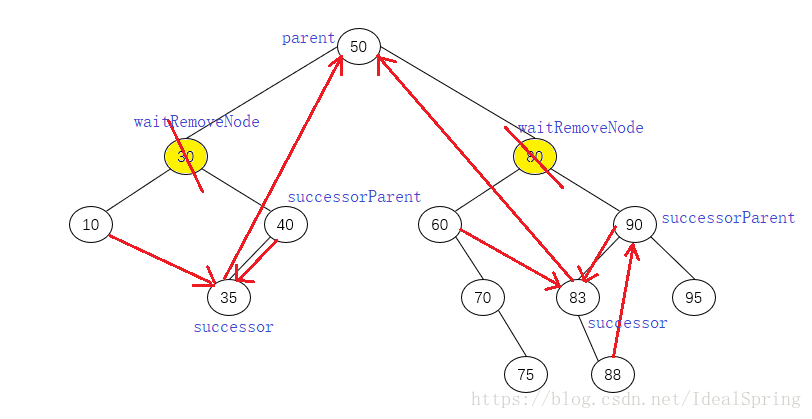
}3)删除的节点有两个子节点:这种情况,需要找到一个节点去替代待删除的节点;在二叉排序树中,替代待删除节点的最好节点是该节点次小于(大小仅次于它)它的节点或者次大于(比它大的所有元素集合中最小的)它的节点。这里,我们选择次大于它的节点,次大于它的节点的专业术语叫后继节点。
后继节点:比要删除的节点的关键值次高的节点是它的后继节点。说得简单一些,后继节点就是比要删除的节点的关键值要大的节点集合中的最小值。
得到后继节点代码如下:
/**
* 获取待删除节点的后继节点
*/
private Node getSuccessorNode(Node waitRemoveNode) {
Node successorParent = null; // 后继节点的父节点
Node successor = waitRemoveNode; // 后继节点
Node current = waitRemoveNode.rightChild; // 现在的节点指针
// 寻找后继节点及其父节点
while (current != null) {
successorParent = successor;
successor = current;
current = current.leftChild;
}
// 如果后继节点不是待删除节点的右子树时
if (successor != waitRemoveNode.rightChild) {
// 将后继节点的右子节点指向后继节点父节点的左子节点
successorParent.leftChild = successor.rightChild;
// 将待删除节点的右子节点指向后继节点的右子节点
successor.rightChild = waitRemoveNode.rightChild;
}
// 任何情况下都需要将待删除节点的左子节点指向后继节点的左子节点
successor.leftChild = waitRemoveNode.leftChild;
return successor;
}a) 如果后继节点是刚好要删除的节点的右子节点(这个右子节点没有左孩子,如果有,它不可能是后继节点)
//删除的节点为父节点的左子节点时:
parent.leftChild = successor;
successor.leftChild = delNode.leftChild;
//删除的节点为父节点的右子节点时:
parent.rightChild = successor;
successor.leftChild = delNode.leftChildb) 如果后继节点为要删除节点的右子节点的左后代:
//删除的节点为父节点的左子节点时:
successorParent.leftChild = successor.rightChild;
successor.rightChild = delNode.rightChild;
parent.leftChild = successor;
successor.leftChild = delNode.leftChild;
//删除的节点为父节点的右子节点时:
successorParent.leftChild = successor.rightChild;
successor.rightChild = delNode.rightChild;
parent.rightChild = successor;
successor.leftChild = delNode.leftChild;综上,完整的删除代码如下:
/**
* 删除节点
*/
public boolean removeNode(int value) {
Node waitRemoveNode = root; // 需要删除的节点
Node parent = null; // 需要删除节点的父节点
boolean isLeftChild = true; // 需要删除的节点是否是父节点的左子树
// 在二叉树中寻找待删除节点和待删除节点的父节点并确定待删除节点是否是左子树
// (简单的来说就是初始化current、parent、isLeftChild)
while (true) {
if (value == waitRemoveNode.value) {
break;
} else if (value < waitRemoveNode.value) {
isLeftChild = true;
parent = waitRemoveNode;
waitRemoveNode = waitRemoveNode.leftChild;
} else {
isLeftChild = false;
parent = waitRemoveNode;
waitRemoveNode = waitRemoveNode.rightChild;
}
// 找不到需要删除的节点,直接返回
if (waitRemoveNode == null)
return false;
}
// 分情况讨论删除节点的情况:
// 1.需要删除的节点为叶子节点
if (waitRemoveNode.leftChild == null && waitRemoveNode.rightChild == null) {
// 如果为根节点(树中只有做一个节点-节点)
if (waitRemoveNode == root) {
root = null;
} else {
if (isLeftChild) //如果该叶节点是父节点的左子节点,将父节点的左子节点置为null
parent.leftChild = null;
else //如果该叶节点是父节点的右子节点,将父节点的右子节点置为null
parent.rightChild = null;
}
}
// 2.1 需要删除的节点有一个节点,且该节点为左子节点
else if (waitRemoveNode.rightChild == null) {
// 如果该节点为根节点,将根节点的左子节点变为根节点
if (waitRemoveNode == root) {
root = waitRemoveNode.leftChild;
} else {
// 如果该节点是父节点的左子节点,将待删除节点的左子节点变为父节点的左子节点
if (isLeftChild)
parent.rightChild = waitRemoveNode.leftChild;
else // 如果该节点是父节点的右子节点,将待删除节点的左子节点变为父节点的右子节点
parent.rightChild = waitRemoveNode.leftChild;
}
}
// 2.2 需要删除的节点有一个节点,且该节点为右子节点
else if (waitRemoveNode.leftChild == null) {
// 如果该节点为根节点,将根节点的右子节点变为根节点
if (waitRemoveNode == root) {
root = waitRemoveNode.rightChild;
} else {
// 如果该节点是父节点的左子节点,将待删除节点的右子节点变为父节点的左子节点
if (isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild = waitRemoveNode.rightChild;
else // 如果该节点是父节点的右子节点,将待删除节点的右子节点变为父节点的右子节点
parent.rightChild = waitRemoveNode.rightChild;
}
}
// 3.待删除节点有两个节点,需要找该节点的后续节点作为替代节点
else {
Node successor = getSuccessorNode(waitRemoveNode);
// 如果待删除节点为根节点,将后继节点变为根节点,并将根节点的左子节点变为后继节点的左子节点
if (waitRemoveNode == root) {
root = successor;
} else {
// 如果待删除节点是父节点的左子节点,将该节点的后继节点变为父节点的左子节点
if (isLeftChild)
parent.leftChild = successor;
else // 如果待删除接点是父节点的右子节点,将该节点的后继节点变成节点的右子节点
parent.rightChild = successor;
}
}
waitRemoveNode = null;
return true;
}上述实现中的删除比较复杂。有一种简单的替代操作,称为懒惰删除(lazy deletion)。在懒惰删除时,我们并不真正从二叉搜索树中删除该节点,而是将该节点标记为“已删除”。这样,我们只用找到元素并标记,就可以完成删除元素了。如果有相同的元素重新插入,我们可以将该节点找到,并取消删除标记。
懒惰删除的实现比较简单,可以尝试一下。树所占据的内存空间不会因为删除节点而减小。懒惰节点实际上是用内存空间换取操作的简便性。
9.查找指定节点
/**
* 查找指定的值
*/
public Node findKey(int value) {
Node current = root;
while (true) {
if (value == current.value)
return current;
else if (value < current.value)
current = current.leftChild;
else if (value > current.value)
current = current.rightChild;
if (current == null)
return null;
}
}10. 获取最大值和最小值
/**
* 获取最小值
*/
public int getMinValue() {
Node current = root;
while (true) {
if (current.leftChild == null)
return current.value;
current = current.leftChild;
}
}
/**
* 获取最大值
*/
public int getMaxValue() {
Node current = root;
while (true) {
if (current.rightChild == null)
return current.value;
current = current.rightChild;
}
}11. 打印二叉排序树
public void printBinaryTreeByRow() {
printBinaryTreeByRow(root);
}
public void printBinaryTreeByColumn() {
printBinaryTreeByColumn(0, root);
}
private void printBinaryTreeByColumn(int space, Node node) {
System.out.println();
for (int i = 0; i < space; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.print("【" + node.value + "】");
if (node.leftChild != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < space + 2; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
printBinaryTreeByColumn(space + 3, node.leftChild);
}
if (node.rightChild != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < space + 2; i++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
printBinaryTreeByColumn(space + 3, node.rightChild);
}
}
private void printBinaryTreeByRow(Node node) {
// 创建一个队列用来存放节点
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
// 当前行最右节点(最右一个元素)
Node lastNode = node;
// 下一行最右节点(最右一个元素)
Node nextLastNode = null;
// 将当节点放入队列中
queue.add(node);
while (queue.size() > 0) {
// 出队列
Node nowNode = queue.poll();
// 如果当前节点有左节点,将左节点压入队列中
if ((nextLastNode = nowNode.leftChild) != null) {
queue.add(nextLastNode);
}
// 如果当前节点有右节点,将左节点压入队列中
if ((nextLastNode = nowNode.rightChild) != null) {
queue.add(nextLastNode);
}
System.out.print(nowNode.value + " ");
if (nowNode.equals(lastNode)) {
System.out.println();
lastNode = nextLastNode;
}
}
}开讲完毕!
三、测试代码
/**
* 二叉树测试类
*/
public class BinaryTreeDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BinaryTree bt = new BinaryTree(50);
bt.insert(30);
bt.insert(80);
bt.insert(10);
bt.insert(40);
bt.insert(35);
bt.insert(60);
bt.insert(90);
bt.insert(70);
bt.insert(83);
bt.insert(95);
bt.insert(75);
bt.insert(88);
bt.preOrderTtaverse();
bt.preOrderByStack();
bt.inOrderTraverse();
bt.inOrderByStack();
bt.postOrderTraverse();
bt.postOrderByStack();
System.out.println("查询的777 : " + bt.findKey(777));
System.out.println("最小值: " + bt.getMinValue());
System.out.println("最大值: " + bt.getMaxValue());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("行式打印:");
bt.printBinaryTreeByRow();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("列式打印:");
bt.printBinaryTreeByColumn();
System.out.println();
bt.removeNode(32); //删除叶子节点//
bt.removeNode(50); //删除只有一个左子节点的节点
bt.removeNode(248); //删除只有一个右子节点的节点
bt.removeNode(248); //删除只有一个右子节点的节点
bt.removeNode(580); //删除有两个子节点的节点,且后继节点为删除节点的右子节点的左后代
bt.removeNode(888); //删除有两个子节点的节点,且后继节点为删除节点的右子节点
bt.removeNode(52); //删除有两个子节点的节点,且删除节点为根节点
System.out.println("行式打印:");
bt.printBinaryTreeByRow();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("列式打印:");
bt.printBinaryTreeByColumn();
}
}运行结果:
二叉树它的前序遍历: 50 30 10 40 35 80 60 70 75 90 83 88 95
前序遍历非递归实现: 50 30 10 40 35 80 60 70 75 90 83 88 95
二叉树它的中序遍历: 10 30 35 40 50 60 70 75 80 83 88 90 95
中序遍历非递归实现: 10 30 35 40 50 60 70 75 80 83 88 90 95
二叉树它的后序遍历: 10 35 40 30 75 70 60 88 83 95 90 80 50
后序遍历非递归实现: 10 35 40 30 75 70 60 88 83 95 90 80 50
查询的777 : null
最小值: 10
最大值: 95
行式打印:
50
30 80
10 40 60 90
35 70 83 95
75 88
列式打印:
【50】
【30】
【10】
【40】
【35】
【80】
【60】
【70】
【75】
【90】
【83】
【88】
【95】
行式打印:
60
30 80
10 40 70 90
35 75 83 95
88
列式打印:
【60】
【30】
【10】
【40】
【35】
【80】
【70】
【75】
【90】
【83】
【88】
【95】