第一部分:理论知识。
第四章:对象与类
4.1:类与对象的概念。
类:是构造对象的模板或蓝图。由类构造对象的过程称为创建类的实例。
对象:想要使用oop,一定要清楚对象的三个特性:
1)对象的行为:对象的行为使用可调用的方法定义的。
·2)对象的状态:每个对象都保存着描述当前特征的信息。
3)对象标识:如何辨明具有相同行为的相似性。
4.2:类之间的关系。
常见关系有:依赖、聚合、继承。
4.3:使用预定义类。
已学过的预定义类如math,Math,String,Scanner等。
1)对象与对象变量。
在Java语言中,使用构造器构造新实例。构造器是类中一个特殊的方法,生成并初始化对象,它的方法名与类名相同。
想要构造一个Data对象(定义在java.util中),需要在构造器前加上new操作符:new Data()
Data deadline;该语句错误。
可将一个对象变量设置为null,表示该对象变量未引用任何变量,如deadlin=null。
4.4:更改器与访问器。
更改器:修改实例域。前缀set,更改当前类中的属性。
访问器:更改实例域。前缀get。
第二部分:实验部分。
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 理解用户自定义类的定义;
(2) 掌握对象的声明;
(3) 学会使用构造函数初始化对象;
(4) 使用类属性与方法的使用掌握使用;
(5) 掌握package和import语句的用途。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1:测试以下程序,掌握文件输入输出程序设计技术(文件输入输出,教材61-62).
代码如下:
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; public class FileWriteReadTest { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { // 写入文件演示 PrintWriter out = new PrintWriter("myfile.txt"); out.println("姓名 高数 Java 数据结构 平均成绩 总成绩"); out.println("张三 20 30 40 0 0"); out.println("李四 50 60 70 0 0"); out.close();// 输出完毕,需要close // 读入文件演示 Scanner in = new Scanner(new File("myfile.txt"));// 为myfile.txt这个File创建一个扫描器in int number = 1;// 行号 System.out.println(in.nextLine()); while (in.hasNextLine()) {// 判断扫描器是否还有下一行未读取,该循环把文件的每一行都读出 String line = in.nextLine();// 读出myfile.txt的下一行 System.out.print("第" + (++number) + "行的内容: "); Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(line);// 行内容建立扫描器 linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");// 使用空格作为分隔符 String name = linescanner.next(); String math = linescanner.next(); String java = linescanner.next(); String ds = linescanner.next(); String avg = linescanner.next(); String total = linescanner.next(); System.out.println("name=" + name + " math=" + math + " java=" + java + " ds=" + ds + " avg=" + avg + " total=" + total); } in.close();// 读入完毕,最后需要对其进行close。 } }
程序运行结果如下:

实验2 导入第4章示例程序并测试。
测试程序1:
编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-2(教材104页);
结合程序运行结果,掌握类的定义与类对象的用法,并在程序代码中添加类与对象知识应用的注释;
尝试在项目中编辑两个类文件(Employee.java、 EmployeeTest.java ),编译并运行程序。
程序如下:(1)EmployeeTest.java
import java.time.*; /** * This program tests the Employee class. * * @version 1.12 2015-05-08 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class EmployeeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // 用三个Employee对象填充staff数组 Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; staff[0] = new Employee("Carl Cracker", 75000, 1987, 12, 15); staff[1] = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); staff[2] = new Employee("Tony Tester", 40000, 1990, 3, 15); //将每个人的工资提高5% for (Employee e : staff) e.raiseSalary(5); //打印出员工反对的信息 for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary() + ",hireDay=" + e.getHireDay()); } } class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String n, double s, int year, int month, int day) { name = n; salary = s; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
程序运行结果如下所示:

(2)Employee.java
/** * @version 1.10 1999-11-13 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; public native void raiseSalary(double byPercent); public Employee(String n, double s) { name = n; salary = s; } public void print() { System.out.println(name + " " + salary); } static { System.loadLibrary("Employee"); } }
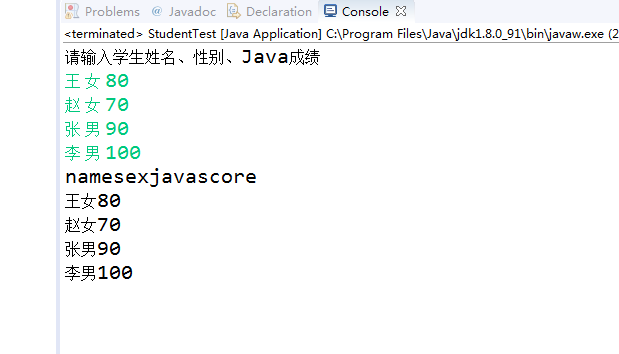
参考教材104页EmployeeTest.java,设计StudentTest.java,定义Student类,包含name(姓名)、sex(性别)、javascore(java成绩)三个字段,编写程序,从键盘输入学生人数,输入学生信息,并按以下表头输出学生信息表:姓名、性别、java成绩。
程序如下:
import java.util.*; public class StudentTest { public static void main(String[] args) { Student[] staff = new Student[4]; System.out.println("请输入学生姓名、性别、Java成绩"); Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in); for(int i=0;i<staff.length;i++) { staff[i]=new Student(in.next(),in.next(),in.nextInt()); } System.out.println("name"+"sex"+"javascore"); for (Student e: staff) System.out.println(e.getName()+e.getSex()+e.getjavaScore()); } } class Student { private String name; private String sex; private int javascore; public Student(String n, String s, int j) { name = n; sex = s; javascore =j; } public String getName() { return name; } public String getSex() { return sex; } public int getjavaScore() { return javascore; } }
程序运行结果如下:
测试程序2:
编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-3(教材116);
结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握静态域(netxtId)与静态方法(getNextId)的用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
理解Java单元(类)测试的技巧。
程序如下:
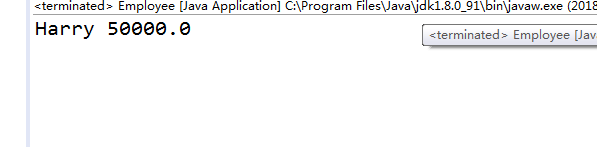
/** /** * This program demonstrates static methods. * @version 1.01 2004-02-19 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class StaticTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //用三个Employee对象填充staff数组 Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; staff[0] = new Employee("Tom", 40000); staff[1] = new Employee("Dick", 60000); staff[2] = new Employee("Harry", 65000); //打印出员工反对的信息 for (Employee e : staff) { e.setId(); System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",id=" + e.getId() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary()); } int n = Employee.getNextId(); // calls static method System.out.println("Next available id=" + n); } } class Employee { private static int nextId = 1; private String name; private double salary; private int id; public Employee(String n, double s) { name = n; salary = s; id = 0; } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId() { id = nextId; //将此ID设置为下一个可用ID nextId++; } public static int getNextId() { return nextId; //返回static域 } public static void main(String[] args) // unit test { Employee e = new Employee("Harry", 50000); System.out.println(e.getName() + " " + e.getSalary()); } }
程序运行结果如下:
测试程序3:
编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-4(教材121);
结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握掌握Java方法参数的用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
程序如下:
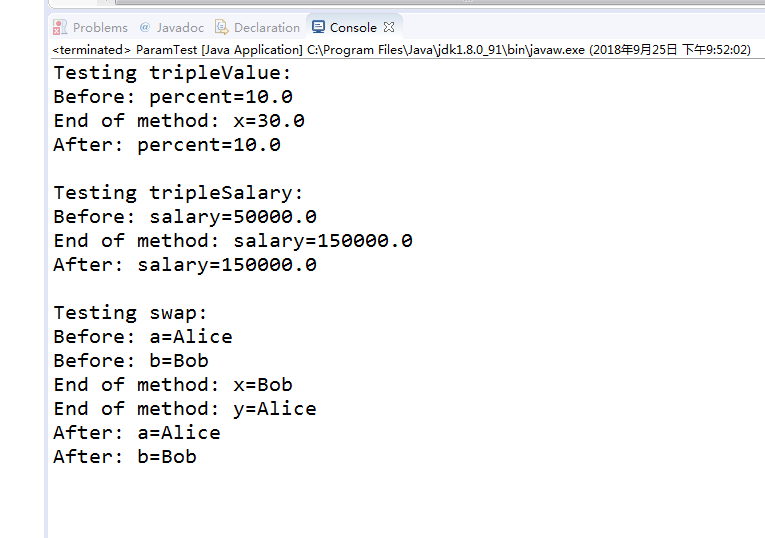
/** * This program demonstrates parameter passing in Java. * @version 1.00 2000-01-27 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ParamTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //该方法不能修改数值参数 System.out.println("Testing tripleValue:"); double percent = 10; System.out.println("Before: percent=" + percent); tripleValue(percent); System.out.println("After: percent=" + percent); //该方法可以改变对象参数的状态 System.out.println(" Testing tripleSalary:"); Employee harry = new Employee("Harry", 50000); System.out.println("Before: salary=" + harry.getSalary()); tripleSalary(harry); System.out.println("After: salary=" + harry.getSalary()); //该方法可以将新对象附加到对象参数 System.out.println(" Testing swap:"); Employee a = new Employee("Alice", 70000); Employee b = new Employee("Bob", 60000); System.out.println("Before: a=" + a.getName()); System.out.println("Before: b=" + b.getName()); swap(a, b); System.out.println("After: a=" + a.getName()); System.out.println("After: b=" + b.getName()); } public static void tripleValue(double x) // doesn't work { x = 3 * x; System.out.println("End of method: x=" + x); } public static void tripleSalary(Employee x) // works { x.raiseSalary(200); System.out.println("End of method: salary=" + x.getSalary()); } public static void swap(Employee x, Employee y) { Employee temp = x; x = y; y = temp; System.out.println("End of method: x=" + x.getName()); System.out.println("End of method: y=" + y.getName()); } } class Employee { private String name; private double salary; public Employee(String n, double s) { name = n; salary = s; } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
程序运行结果如下:
测试程序4:
编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-5(教材129);
结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java用户自定义类的用法,掌握对象构造方法及对象使用方法,在相关代码后添加注释。
程序如下:
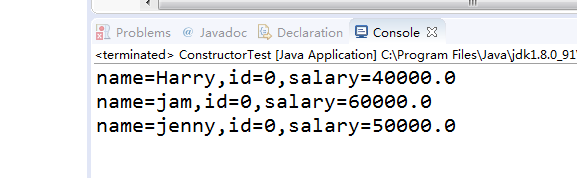
import java.util.*; /** * This program demonstrates object construction. * @version 1.01 2004-02-19 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class ConstructorTest { public static void main(String[] args) { //用单个Employee对象填充staff数组 Employee[] staff = new Employee[3]; staff[0] = new Employee("Harry", 40000); staff[1] = new Employee(60000); staff[2] = new Employee(); //打印出员工反对信息 for (Employee e : staff) System.out.println("name=" + e.getName() + ",id=" + e.getId() + ",salary=" + e.getSalary()); } } class Employee { private static int nextId; private int id; private String name = ""; //实例字段初始化 private double salary; // static initialization block static { Random generator = new Random(); //从0-9999随机分配下一ID的地址 nextId = generator.nextInt(10000); } { id = nextId; nextId++; } public Employee(String n, double s) { name = n; salary = s; } public Employee(double s) { //调用雇员构造函数 this("Employee #" + nextId, s); } //默认构造函数 public Employee() {// salary not explicitly set--initialized to 0 // id initialized in initialization block } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public int getId() { return id; } }
程序运行结果如下:
测试程序5:
l 编辑、编译、调试运行程序4-6、4-7(教材135);
l 结合程序运行结果,理解程序代码,掌握Java包的定义及用法,在相关代码后添加注释;
程序4-6如下:
import com.horstmann.corejava.*; import static java.lang.System.*; /** * This program demonstrates the use of packages. * @version 1.11 2004-02-19 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class PackageTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // because of the import statement, we don't have to use // com.horstmann.corejava.Employee here Employee harry = new Employee("Harry Hacker", 50000, 1989, 10, 1); harry.raiseSalary(5); // because of the static import statement, we don't have to use System.out here out.println("name=" + harry.getName() + ",salary=" + harry.getSalary()); } }
程序运行结果如下:

程序4-7如下:
package com.horstmann.corejava; //这个文件中的类是这个包的一部分 import java.time.*; //导入语句位于PACKAGE语句之后 /** * @version 1.11 2015-05-08 * @author Cay Horstmann */ public class Employee { private String name; private double salary; private LocalDate hireDay; public Employee(String name, double salary, int year, int month, int day) { this.name = name; this.salary = salary; hireDay = LocalDate.of(year, month, day); } public String getName() { return name; } public double getSalary() { return salary; } public LocalDate getHireDay() { return hireDay; } public void raiseSalary(double byPercent) { double raise = salary * byPercent / 100; salary += raise; } }
实验3 编写长方形类Rectangle与圆形类Circle,其中Rectangle类设置私有属性:width,length;Circle类设置私有属性radius。编写Rectangle类的带参构造函数Rectangle(int width,int length), Circle类的带参构造函数Circle(int radius),编写两个类的toString方法(Eclipse可自动生成)。上述2个类均定义以下方法:
求周长的方法public int getPerimeter()
求面积的方法public int getArea()
在main方法中完成以下任务:
(1) 输入1行长与宽,创建一个Rectangle对象;
(2) 输入1行半径,创建一个Circle对象;
(3) 将两个对象的周长加总输出,将两个对象的面积加总输出。
程序如下:
import java.util.*;
public class Rectangle {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("输入长方形的长:");
Float length = in.nextFloat();
System.out.println("输入长方形的宽:");
Float width = in.nextFloat();
System.out.println("输入圆的半径:");
Float radius = in.nextFloat();
Rec l = new Rec(width, length);
Cir r = new Cir(radius);
System.out.println("矩形周长=" + l.getPerimeter() + "矩形面积=" + l.getArea());
System.out.println("圆周长=" + r.getPerimeter() + "圆面积=" + r.getArea());
float c = l.getPerimeter() + r.getPerimeter();
double s = l.getArea() + r.getArea();
System.out.println("矩形和圆的周长之和:" + c + "矩形和圆的面积之和:" + s);
}
}
class Rec {
private Float width;
private double length;
public Rec(Float w, Float l) {
width = w;
length = l;
}
public Float getPerimeter() {
Float Perimeter = (float) ((width + length) * 2);
return Perimeter;
}
public Float getArea() {
Float Area = (float) (width * length);
return Area;
}
}
class Cir {
private double radius;
double PI = 3.14;
public Cir(Float r) {
radius = r;
}
public Float getPerimeter() {
Float Perimeter = (float) (2 * PI * radius);
return Perimeter;
}
public Float getArea() {
Float Area = (float) (PI * radius * radius);
return Area;
}
}
程序运行结果如下:
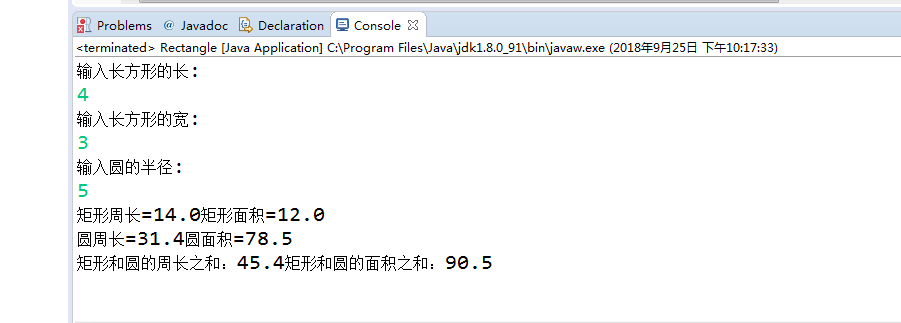
实验总结:本次实验首先是编译运行程序了解文件的输入输出,在实验三的基础上,进一步使用student类编写了一个Java程序。通过本次实验,我进一步了解到对象与类的定义以及各自的特点。在之前的学习中,已经了解了几种预定义类,在这周的学习中,掌握了预定义类的使用。在实验过程中,还是遇到了很多问题,比如误将float型相加,而float型加在一起要用强制转换类型,这是因为基础知识学习不够的原因。而对于新学习的知识,有很多地方还是不明白,做实验时,也是在同学和学长的帮助下,最终才完成了实验。在以后的学习过程中,自己一一定要多练习写代码,提高自己的学习能力。