LINQ定义:.NET环境下基于关系型数据的语言集成查询技术,用于以对象形式管理关系型数据。
下面是学习Linq To Sql的预备知识:
1、隐式类型
var a = 1; //int a = 1; var b = "123";//string b = "123"; var myObj = new MyObj();//MyObj myObj = new MyObj()
在使用var定义变量时必须赋值,否则编译器无法推测其类型,隐式类型对性能没有影响
2、匿名类型
new关键字之后就直接为对象定义了属性,并且为这些属性赋值 var obj = new {Guid.Empty, myTitle = "匿名类型", myOtherParam = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 } }; Console.WriteLine(obj.Empty);//另一个对象的属性名字,被原封不动的拷贝到匿名对象中来了。 Console.WriteLine(obj.myTitle); Console.ReadKey();
匿名类型常和var配合使用,var用于声明匿名类型。
3、对象初始化器
//不同于匿名类型的是此处对象属性都是先定义好的
var myObj1 = new MyObj() { id = Guid.NewGuid(), Title = "allen" };
//集合初始化器
var arr = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
4、委托
委托和类是同一级别的,代表某一类型的方法
委托定义:
//名为name的委托代表传入整型参数并返回bool类型的方法 delegate bool name(int i); //委托的使用 var d = new name(method); bool b = d(1); public bool method(int a){ ... }
5、泛型类型
定义方法的传入参数和返回类型为指定的类型
如果没有泛型,你可能把参数和返回值的类型都设定为Object了,这样就避免不了装箱和拆箱带来的性能损失;泛型一般用于集合中,指定集合中元素类型。
.net库预定义好的泛型类型有List<T>、Dictionary<TKey, TValue>等。
泛型定义:
public static class SomeFactory<T> { public static T InitInstance(T inObj) { if (false)//你的判断条件 { //do what you want... return inObj; } return default(T); } }
在消费泛型类型时需要注意:
1、传入参数必须为指定类型
2、如果你想返回T类型的空值,那么请用default(T)这种形式,因为你不知道T是值类型还是引用类型,所以别擅自用null
//约束传入的参数必须为MyObj类型或其基类类型,new()来约束传入的类型必须有一个构造函数
public static class SomethingFactory<T> where T:MyObj,new()
泛型中没有了类型转换,一方面保证了类型安全,另一方面提升了性能
泛型委托:指定委托表示的方法传入的参数类型和返回值类型为泛型中指定的类型
.net中预定义的三种泛型委托:
Predicate:表示方法只能接受一个类型参数,并且必须返回bool类型public delegate bool Predicate<T>(T inObj); var d=new Predicate<int>(methodName); bool b=d(12);
Action:表示方法能接受多个类型参数,但不返回值
public delegate void Action<T1,T2,...>(T1 t1, T2 t2,...); var d = new Action<T1,T2,...>(methodName);d(12);
Func:表示方法能接受多个类型参数,并且可以指定返回值类型(最后一个类型ReturnType指定返回值类型)
public delegate ReturnType Func<T1,T2, ... ,ReturnType>(T1 t1, T2 t2,...);
var d = new Func<T1,T2, ... ,ReturnType>(methodName);
ReturnType val = d(12);
public bool methodName(int a){ ... }
在定义委托实例时除了可以传入方法指针(方法名)外还可以传入一段代码块作为匿名方法:
var arr = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 }; //var d1 = new moreOrlessDelgate(More); //var d1 = new Predicate<int>(More); var d1 = new Predicate<int>(delegate(int item) { //可以访问当前上下文中的变量 Console.WriteLine(arr.Count); if (item > 3) { return true; } return false; }); Print(arr, d1); Console.WriteLine("OK");
6、Lambda表达式
用于替代定义委托实例时传入的匿名方法
var d1 = new Predicate<int>(delegate(int item) { //可以访问当前上下文中的变量 Console.WriteLine(arr.Count); if (item > 3) { return true; } return false; }); 可用lambda表达式替换成:
var d1 = new Predicate<int>(item => item > 3);
//item表示参数
//多个参数可以写成
var d2 = new Action<int, int>((a, b) => a=a+b);
//没有参数可以写成
() => print("xxx")
7、扩展方法:
//定义扩展方法,用this关键字指定要扩展的对象
public static void PrintString(this string a, string b) { Console.Writeline(a); } //消费扩展方法string b = "xxx"; a.PrintString(b);
使用扩展方法先决条件:
<1>扩展方法必须在一个非嵌套、非泛型的静态类中定义
<2>扩展方法必须是一个静态方法
<3>扩展方法至少要有一个参数
<4>第一个参数必须附加this关键字作为前缀
<5>第一个参数不能有其他修饰符(比如ref或者out)
<6>第一个参数不能是指针类型
注意事项
<1>跟前面提到的几个特性一样,扩展方法只会增加编译器的工作,不会影响性能(用继承的方式为一个类型增加特性反而会影响性能)
<2>如果原来的类中有一个方法,跟你的扩展方法一样(至少用起来是一样),那么你的扩展方法奖不会被调用,编译器也不会提示你
<3>扩展方法太强大了,会影响架构、模式、可读性等等等等....
8、迭代器
c#中的所有集合都继承了IEnumerable接口,IEnumerable只定义了一个方法GetEnumertor(),对集合使用foreach操作时会调用GetEnumerable方法对集合中元素进行迭代,而对于数组则会用for代码块循环;
重写迭代器:
//yield用于在迭代器块中返回枚举对象的值或发出迭代结束的信号;
public IEnumerable<int> GetIterator() { Console.WriteLine("迭代器返回了1");
yield return 1; //yield返回int类型枚举对象的值,此时返回的此枚举对象的值才被加载到内存中
Console.WriteLine("迭代器返回了2");
yield return 2;
yield break; //yield终止了此次迭代,后面的枚举对象的值则不会加载到内存中
Console.WriteLine("迭代器返回了3");
yield return 3;
}
foreach(int i GetIterator())
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
输出结果:迭代器返回了11迭代器返回了22
注意事项
<1>做foreach循环时多考虑线程安全性
在foreach时不要试图对被遍历的集合进行remove和add等操作
任何集合,即使被标记为线程安全的,在foreach的时候,增加项和移除项的操作都会导致异常
<2>IEnumerable接口是LINQ特性的核心接口
只有实现了IEnumerable接口的集合
才能执行相关的LINQ操作,比如select,where等
开始Linq To Sql学习:
Linq查询句法解析:
//where方法 static void TestWhere() { List<int> arr = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 }; #region Where作为扩展方法使用 //传入Func委托实例 var sum = arr.Where<int>(new Func<int, bool>(delegate(int a) { return a > 3; })).Sum(); //传入匿名方法 var sum = arr.Where<int>(delegate(int a) { return a > 3; }).Sum(); //传入lambda表达式 var sum = arr.Where(a => a > 3).Sum(); #endregion //where作为查询操作符使用 ,下面的语句为查询表达式(非lambda表达式)
var sum = (from a in arr where a > 3 select a).Sum(); Console.WriteLine("TestWhere:" + sum); Console.ReadKey(); }
DataContent(数据上下文)
位于Global::System.Data.Linq中,实体和数据库之间的桥梁,用于将Linq句法翻译成可执行T_Sql语句并执行,以及将数据从数据库返回给调用者和把实体的修改写入数据库,使用前先定义实体和关系数据之间的映射关系。
Linq To Sql中的大部分功能都在DataContent类中已定义好。
实体类定义
[Table(Name = "Categories")] public class BoardCategory { //Column特性:
//Name属性--指定数据库中要映射的字段名,若没指定则使用属性名称映射,这时属性名称必须和表字段名相同
//DbType属性--字段数据类型
//IsPrimaryKey--是否主键
//IsDbGenerated--列是否包含数据库自动生成的值
//CanBeNull--列是否为空
[Column(Name = "CategoryID", DbType = "int identity", IsPrimaryKey = true, IsDbGenerated = true, CanBeNull = false)] public int CategoryID { get; set; } [Column(Name = "CategoryName", DbType = "varchar(50)", CanBeNull = false)] public string CategoryName { get; set; } }
强类型数据上下文
public class DataCtx:DataContext { //base()调用基类构造函数
public DataCtx(string sConnection) : base(sConnection) { } public DataCtx(IDbConnection connection) : base(connection) { } public Table<Customer> Customers;
}
DataContent部分功能介绍:
日志功能:
NorthwindDataContext ctx = new NorthwindDataContext("server=xxx;database=Northwind;uid=xxx;pwd=xxx"); StreamWriter sw = new StreamWriter(Server.MapPath("log.txt"), true); // Append ctx.Log = sw;
每次执行查询句法都会把生成的sql语句追加到日志文件中。
获取查询句法对应DbCommand:
var select = from c in ctx.Customers where c.CustomerID.StartsWith("A") select new { 顾客ID = c.CustomerID, 顾客名 = c.Name, 城市 = c.City }; DbCommand cmd = ctx.GetCommand(select);
Response.Write(cmd.CommandText + "<br/>");
foreach (DbParameter parm in cmd.Parametrs)
Response.Write(string.Format("参数名:{0},参数值:{1}<br/>", parm.ParameterName, parm.Value));
获取修改后的实体:
IList<object> queryText = ctx.GetChangeSet().Updates;
执行Sql语句:
ctx.ExecuteCommand("update Customers set City={0} where CustomerID like 'A%'", newcity); IEnumerable<Customer> customers = ctx.ExecuteQuery<Customer>("select * from Customers where CustomerID like 'A%'");
创建数据库:
//创建TestDB数据库,并且还会在TestDB下根据DataCtx类中定义的Table<T>类型的属性创建表 DataCtx.CreateDB("server=.;database=TestDB;uid=sa;pwd=1");
将DbDataReader数据源转换为实体集合:
var conn = new SqlConnection("server=xxx;database=Northwind;uid=xxx;pwd=xxx"); var ctx = new DataContext(conn); var cmd = new SqlCommand("select * from customers where CustomerID like 'A%'", conn); conn.Open(); var reader = cmd.ExecuteReader(); GridView1.DataSource = ctx.Translate<Customer>(reader);
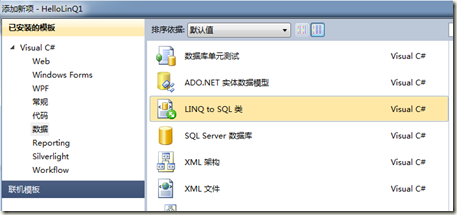
使用设计视图生成映射文件:
2、连接服务器资源管理器,将需要映射的表拖到右边的设计视图中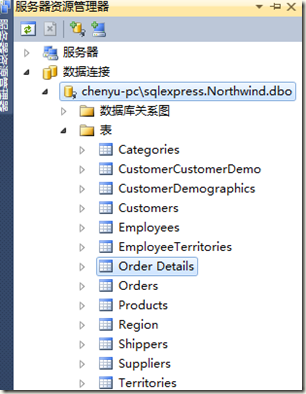
3、然后保存,系统就会自动生成映射文件(.dbml文件)。
note:在生成映射文件时系统会根据各表之间的关系(如主外键)在实体类中生成相应的关系。