1.首先看一下效果
1.1.预览一下真实页面

1.2.分析一下:
要求输入Email或者用户名,点击编辑框,弹出键盘,默认先进入输入Email或用户名编辑框。
点击密码后,密码字样网上浮动一段距离,Email编辑框也是一样的,不过第一次默认是第一个。
没有账号?点击注册后跳转到一个网页,采用手机默认浏览器跳转。
2.LoginActivity布局分析
2.1.首先看一下activity_login源代码

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- ~ Copyright 2017 GcsSloop ~ ~ Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); ~ you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. ~ You may obtain a copy of the License at ~ ~ http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 ~ ~ Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software ~ distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, ~ WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. ~ See the License for the specific language governing permissions and ~ limitations under the License. ~ ~ Last modified 2017-03-19 01:27:22 ~ ~ GitHub: https://github.com/GcsSloop ~ Website: http://www.gcssloop.com ~ Weibo: http://weibo.com/GcsSloop --> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/activity_login" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context="com.gcssloop.diycode.activity.LoginActivity"> <android.support.v7.widget.Toolbar android:id="@+id/toolbar" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" android:paddingLeft="14dp" android:paddingRight="14dp"> <View android:id="@+id/span1" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="10dp" android:visibility="invisible"/> <ImageView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="40dp" android:scaleType="centerInside" android:src="@drawable/ic_logo"/> <View android:id="@+id/span2" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="80dp" android:visibility="invisible"/> <android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/username" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="36dp" android:layout_marginLeft="6dp" android:background="@null" android:hint="Email / 用户名" android:inputType="textEmailAddress|text" android:textSize="16sp"/> <View android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="1dp" android:layout_below="@id/username" android:layout_marginTop="2dp" android:background="@drawable/horizontal_line"/> </android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout> <android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" > <EditText android:id="@+id/password" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="36dp" android:layout_marginLeft="6dp" android:background="@null" android:hint="密码" android:inputType="textPassword" android:textSize="16sp"/> <View android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="1dp" android:layout_below="@id/password" android:layout_marginTop="2dp" android:background="@drawable/horizontal_line"/> </android.support.design.widget.TextInputLayout> <View android:id="@+id/span3" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="20dp" android:visibility="invisible"/> <Button android:id="@+id/login" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="48dp" android:layout_marginTop="6dp" android:background="@drawable/bg_longin_btn" android:text="登 录" android:textColor="@color/diy_white" android:textSize="18sp"/> <TextView android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:padding="12dp" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:id="@+id/sign_up" android:text="没有账号?点击注册" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>
2.2.代码和布局对应关系

2.3.从上之下分析布局
最外层是一个LinearLayout==>一个线性布局,一般登录都是这样做的。
然后是一个toolbar,自带返回按钮的标题栏。
标题栏下面的布局也是一个线性布局,它将标题栏和下方登录界面分隔开了。
下方的线性布局就很简单了。
首先是一个view,就是一个最基本的视图,这里用作类似于占空间控件。
有时候view可以当做一条分割线,这里讲将宽度设置为0,高度不等,巧妙利用了这个特点。
2.4.值得关注的是编辑框外层的一个TextInputLayout布局
这里的编辑框布局都是外层的TextInputLayout,然后里面是一个EditText+View。
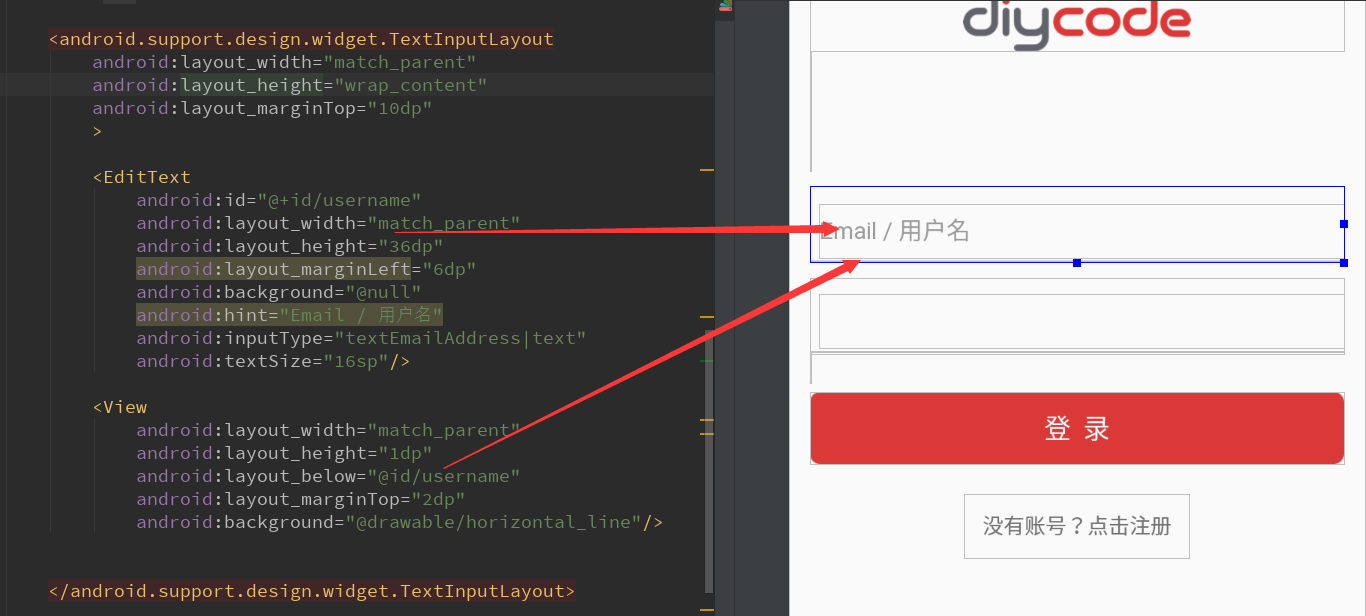
TextInputLayout支持悬浮实现hint效果。给用户体验比较好。
一个TextInputLayout只能包含一个EditText。
3.LoginActivity活动源代码分析
3.1.成员变量分析

这里仅仅需要两个变量。一个是用户名的编辑框,一个是密码的编辑框。
3.2.实现两个在BaseActivity中定义的抽象方法
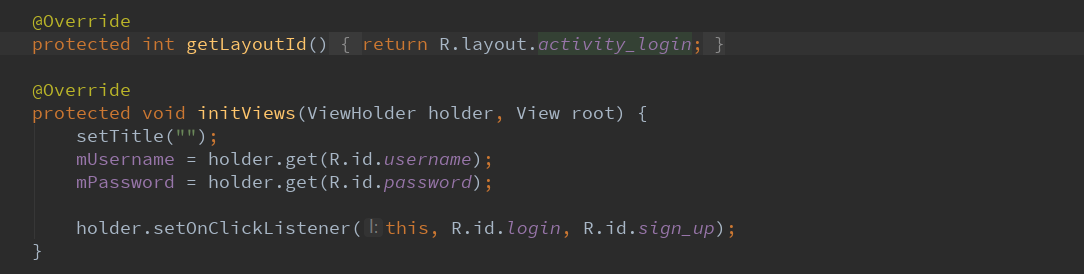
首先确定登录活动的布局==>activity_login.xml
然后将标题栏设空,获得用户名+密码的资源id
最后将这两个资源id添加监听器。
3.3.实现登录接口,利用EventBus实现。

这个onLogin其实是只在点击了登录按钮后才执行。
这里我思考了一下EventBus执行方式。
首先在活动开始即onStart中注册EventBus.getDefault().register(this)即可。
然后在活动的停止或者销毁中反注册EventBus.getDefault().unregister(this)即可。
然后就是写一些只会在UI线程中执行的函数--要用@Subscribe(threadMode=ThreadMode.MAIN)定义。
因为之前也碰到这种类似的方法,我还以为是多余,不会执行呢。
没想到就是要执行的,只是换了一种方式。
安装完Android Studio3.0之后,这个this前面也自动添加了subscriber字样。
这里从SDK的API中获得了个人信息之后,直接finish,交给MainActivity来处理。
3.4.处理软键盘弹起
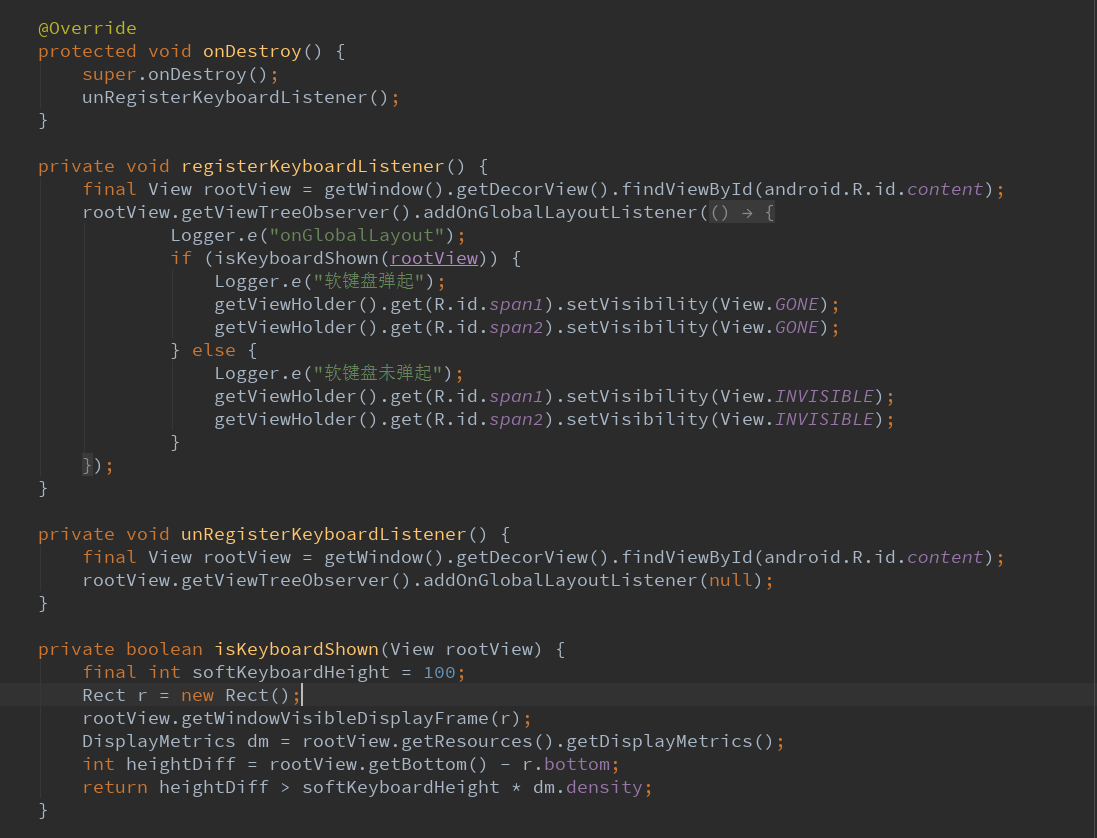
在onStart中,就是默认点开之后,会弹出软键盘,用户即可输入用户名。
注意点:获取当前布局的根布局用下面这种方法。
![]()
如何理解ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener?
参考一下这篇文章:android利用OnGlobalLayoutListener获取视图高度。

作用:当视图树中全局视图发生改变,配合View.GONE和View.INVISIBLE来实现布局上下移动。
本例就是点击了第一个编辑框,整个布局会往上移动,不过这是利用视图的隐藏和显示完成的。
具体的判断软键盘是否显示==>

首先根布局已经获取,且已经作为一个参数了。
这里如何获取根布局可视区域大小,这里采用了一个函数:
rootView.getWindowVisibleDisplayFrame(存放到一个矩形)
打印了一下:
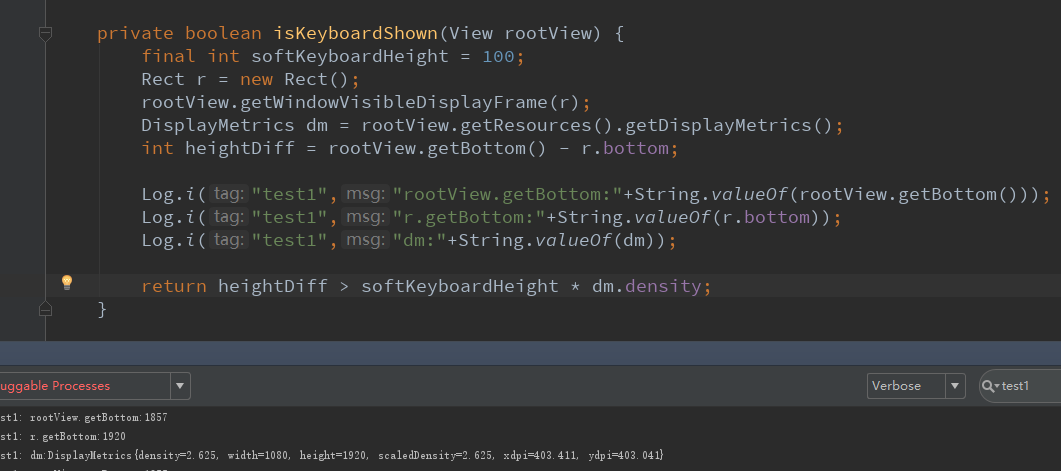
根布局获取到的getBottom:1857
矩形获取到的getBottom:1920
所以两者相减<软键盘高度,所有这里就没有弹出软键盘
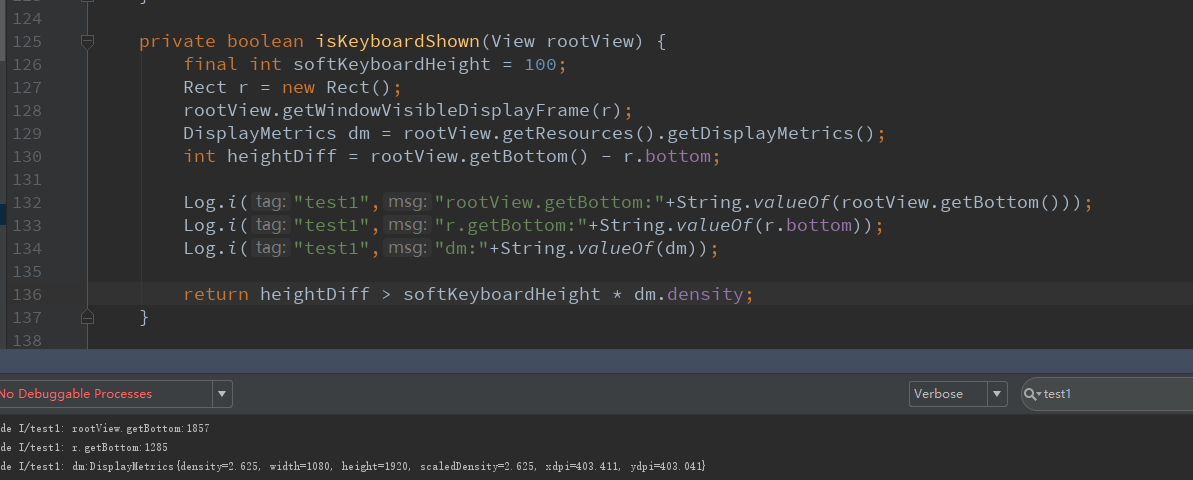
根布局获取到的getBottom:1857
矩形获取到的getBottom:1285
所以两者相减>软键盘高度,所有这里就弹出软键盘
3.5.处理点击事件

这里我发现我上面写错了一点。
就是处理登录接口的函数,就是点击登录之后,会执行这个API函数,而不是上面那个EventBus的onLogin。
上面那个onLogin其实应该类似于回调效果吧。可能EventBus就是处理类似回调的东西吧。
然后另外一个点击事件是注册,打开网页版才能注册,所以这里直接是打开一个链接。
4.总结一下
4.1.终于对EventBus有一定了解了。本篇文章一开始对于EventBus的了解是错误的,之后才发现EventBus就是用于
SDK的API的函数回调效果,比如登录,首先去请求一个接口,API提供的login接口,然后后台通过Event来回调
结果,之前我处理的都是网络请求,但是这个是采用Event事件的方式来回调,更加简单易懂。注意:有那个注
解的地方@Subscribe(threadMode=ThreadMode.MAIN)的地方一定就是用了Event的地方,这里便是回调。
4.2.然后就是对于EventBus一定要先注册,一般在onStart中注册,然后反注册,一般在onStop或者onDestroy中反
注册。
4.3.然后就是对于软键盘的弹起方式有了新的理解,这里采用view的invisible或者gone来实现,当然同时要确定
什么时候invisible,什么时候gone,这里用了一个视图树来配合。如果视图树中某个视图发生改变,采用了
addOnGlobalLayoutListener的方式复写了一个onGlobalLayout的方法来确定什么时候。
4.4.问题在于怎么确定软键盘是否弹起。这里也是采用了根布局rootView和Rect矩形和屏幕分辨率dm来配合,首先
设软键盘高度为100,然后将根视图的可视区域存放到一个Rect中,然后根视图的bottom和矩形的bottom之差
和软键盘高度的大小互相比较,以此为依据确定键盘是否弹出。
4.5.点击事件相对来说,更加容易一些,记得要判断String是否为空,这里直接用.isEmpty即可。然后注册采用了
请求一个网址,用手机默认浏览器打开即进入相应页面。这个IntentUtil基本上每个项目都可以参考。
