前一篇拙文是利用了Jmeter来测试带有CSRF令牌验证的Web API;最近几天趁着项目不忙,练习了用编码的方式实现。
有了之前Jmeter脚本的基础,基本上难点也就在两个地方:获取CSRF令牌、Cookie的传递。
首先添加依赖,在POM.xml中添加以下内容:
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.httpcomponents/httpclient --> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> <version>4.5.6</version> </dependency> <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.jsoup/jsoup --> <dependency> <groupId>org.jsoup</groupId> <artifactId>jsoup</artifactId> <version>1.11.3</version> </dependency>
解释作用:
- httpClient:用来创建httpClient、管理Get和Post的方法、获取请求报文头、应答报文内容、管理CookieStore等等;
- jsoup:用来解析应答报文,获得CSRF令牌的值。
创建一个Web API测试类:
public class LoginEHR { private final static String EHR_ADDRESS = "http://ourTestEHRServer:8083"; static BasicCookieStore cookieStore = new BasicCookieStore(); static CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom().setDefaultCookieStore(cookieStore).build(); }
我选择了CookieStore的方式管理会话;HttpClient现在还有另一种Context的方式实现会话持久,以后再做深入研究。
先写一个打印应答报文的方法,并不做什么处理,纯打印;根据实际需要调用或者注释:
public class LoginEHR {
private static void printResponse(HttpResponse httpResponse)
throws ParseException, IOException { // 获取响应消息实体 HttpEntity entity = httpResponse.getEntity(); // 响应状态 System.out.println("--------Status: " + httpResponse.getStatusLine()); System.out.println("--------Headers: "); HeaderIterator iterator = httpResponse.headerIterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(" " + iterator.next()); } // 判断响应实体是否为空 if (entity != null) { String responseString = EntityUtils.toString(entity); System.out.println("--------Response length: " + responseString.length()); System.out.println("--------Response content: " + responseString.replace(" ", "")); } }
}
现在开始写测试方法,虽然篇幅较长,仍然写在main()方法里,便于展示:
public class LoginEHR { private final static String EHR_ADDRESS = "http://ourTestEHRServer:8083"; static BasicCookieStore cookieStore = new BasicCookieStore(); static CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom().setDefaultCookieStore(cookieStore).build(); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String username = "00022222"; String password = "abc123456"; CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = null; try { HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(EHR_ADDRESS); httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet); System.out.println("--------Cookie store for the 1st GET: " + cookieStore.getCookies()); // 唯一的作用是打印应答报文,没有任何处理;实际测试时,可以不执行 // printResponse(httpResponse); // 取出第一次请求时,服务器端返回的JSESSIONID; // 实际上此处只是取出JSESSIONID用作打印;cookieStore自动保存了本次会话的Cookie信息 // List cookies = cookieStore.getCookies(); // String cookie = cookies.toString(); // String sessionID = cookie.substring("[[version: 0][name: JSESSIONID][value: ".length(), // cookie.indexOf("][domain")); // System.out.println("--------The current JSESSIONID is: " + sessionID);
httpClient.close(); } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } }
private static void printResponse(HttpResponse httpResponse)
throws ParseException, IOException { ...... }
}
根据之前Jmeter测试脚本的经验,先发送一次Get请求,从应答报文中得到CSRF令牌和JSESSIONID。
大家注意我注释掉的那几行打印JSESSIONID的代码,之前在没有引入CookieStore之前,我想的是自己写一个新的Cookie,并把它赋给后面几次请求。
当使用CookieStore之后,就不需要自己封装Cookie、以及添加到Request的Header了,这过程会自动完成。没有删掉也是为了需要的时候打印。
交代完Cookie之后,该轮到处理CSRF令牌了。如果打印出第一次Get的应答,我们能看到令牌的格式是如下呈现的:
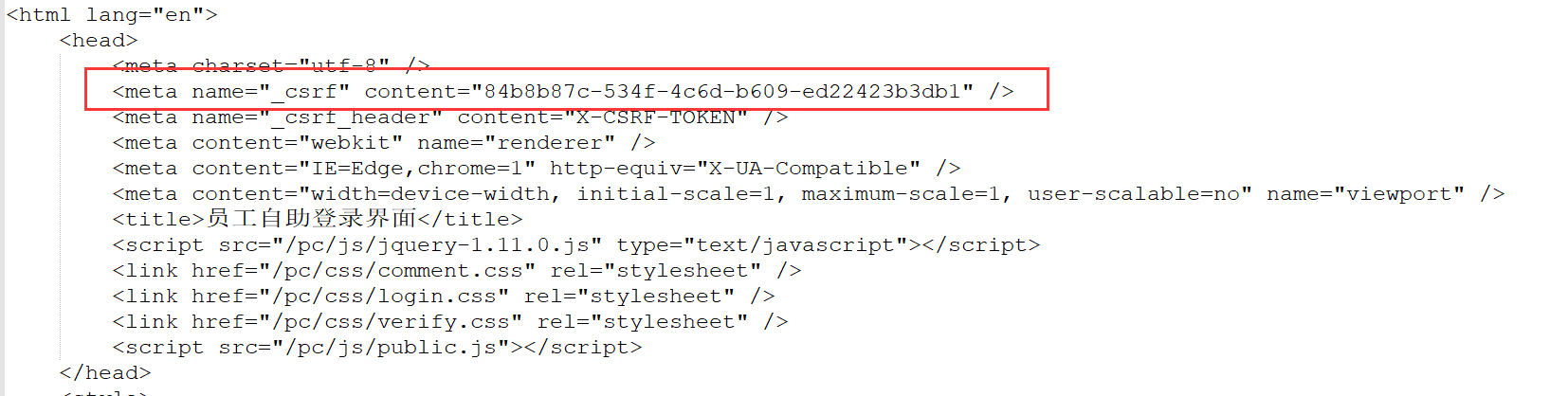
之前在Jmeter脚本中,我是添加了一个正则表达式提取器,把_csrf的content提取出来。
现在我将用jsoup来解析和返回content的内容,代码如下:
private static String getCsrfToken(HttpEntity responseEntity) throws IOException{ //获取网页内容,指定编码 String web = EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity,"utf-8"); Document doc= Jsoup.parse(web); // 选择器,选取特征信息 String token = doc.select("meta[name=_csrf]").get(0).attr("content"); System.out.println( "--------The current CSRF Token is: " + token); return token; }
在main()中调用此方法:
// 利用Jsoup从应答报文中读取CSRF Token
HttpEntity responseEntity = httpResponse.getEntity();
String token = getCsrfToken(responseEntity);
然后再封装POST的请求内容:
// 获取到CSRF Token后,用Post方式登录 HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(EHR_ADDRESS); // 拼接Post的消息体 List<NameValuePair> nvps = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>(); nvps.add(new BasicNameValuePair("username", username)); nvps.add(new BasicNameValuePair("password", password)); nvps.add(new BasicNameValuePair("_csrf", token)); HttpEntity loginParams = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(nvps, "utf-8"); httpPost.setEntity(loginParams); // 第二次请求,带有CSRF Token httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpPost); // System.out.println("--------Cookie store for the POST: " + cookieStore.getCookies()); printResponse(httpResponse);
然后。。。这里发生了一点小意外:
按照设想,应该能跳转到登录成功、或者验证失败的页面;而Post方法执行后,从服务器返回的状态码是302,被跳转到另一个网址。
如果放任不管,直接提交后面的业务查询,是不会得到成功的;执行的结果是又回到了登录页面。
我在网上爬了一会,发现提问Post得到301、302的人还不在少数,说明这个坑还是给很多人造成了困扰。
简单的说,如果得到了服务器重定向到新的地址,我们也要跟着执行一次新地址的访问;否则服务器会认为这次请求没有得到正确处理,即便我之后的请求带着全套的验证令牌和Cookie,也会被拦截在系统外。
有了这个认识,下面我需要完成的就是对Code:302的处理;添加代码如下:
// 取POST方法返回的HTTP状态码;不出意外的话是302 int code = httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); if (code == 302) { Header header = httpResponse.getFirstHeader("location"); // 跳转的目标地址是在 HTTP-HEAD 中的 String newUri = header.getValue(); // 这就是跳转后的地址,再向这个地址发出新申请,以便得到跳转后的信息是啥。 // 实际打印出来的是接口服务地址,不包括IP Address部分 System.out.println("--------Redirect to new location: " + newUri); httpGet = new HttpGet(EHR_ADDRESS + newUri); httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet); // printResponse(httpResponse); }
这里需要注意的地方是跳转的location内容。在我这里,服务器给的只是一个单词【/work】,最好加一个打印的步骤。
确认不是一个完整的URL之后,需要把链接拼完整,然后进行一次httpGet请求。
这个httpGet执行之后,我可以确认已经登录成功(或者,又被送回登录页面,当然我这里是成功了)。
接下来是提交一次业务查询的Get,确认能够在系统中进行业务操作:
// 请求一次绩效;确认登录成功 String queryUrl = EHR_ADDRESS + "/emp/performance/mt/query"; httpGet = new HttpGet(queryUrl); httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet); System.out.println("--------Result of the Cardpunch Query: "); printResponse(httpResponse);
最后确认查询的结果无误后,整个脚本完成;只需要修改最后的业务查询,就可以生成其他的测试脚本了。
完整的源码如下:
package com.jason.apitest; import org.apache.http.Header; import org.apache.http.HeaderIterator; import org.apache.http.HttpEntity; import org.apache.http.HttpResponse; import org.apache.http.NameValuePair; import org.apache.http.ParseException; import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost; import org.apache.http.impl.client.BasicCookieStore; import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient; import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients; import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair; import org.apache.http.protocol.HTTP; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; import org.jsoup.Jsoup; import org.jsoup.nodes.Document; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class LoginEHR { private final static String EHR_ADDRESS = "http://ourTestEHRServer:8083"; static BasicCookieStore cookieStore = new BasicCookieStore(); static CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom().setDefaultCookieStore(cookieStore).build(); public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { String username = "00022222"; String password = "abc123456"; HttpResponse httpResponse = null; try { HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(EHR_ADDRESS); httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet); System.out.println("--------Cookie store for the 1st GET: " + cookieStore.getCookies()); // 唯一的作用是打印应答报文,没有任何处理;实际测试时,可以不执行 // printResponse(httpResponse); // 取出第一次请求时,服务器端返回的JSESSIONID; // 实际上此处只是取出JSESSIONID用作打印;cookieStore自动保存了本次会话的Cookie信息 // List cookies = cookieStore.getCookies(); // String cookie = cookies.toString(); // String sessionID = cookie.substring("[[version: 0][name: JSESSIONID][value: ".length(), // cookie.indexOf("][domain")); // System.out.println("--------The current JSESSIONID is: " + sessionID); // 利用Jsoup从应答报文中读取CSRF Token HttpEntity responseEntity = httpResponse.getEntity(); String token = getCsrfToken(responseEntity); // 获取到CSRF Token后,用Post方式登录 HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(EHR_ADDRESS); // 拼接Post的消息体 List<NameValuePair> nvps = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>(); nvps.add(new BasicNameValuePair("username", username)); nvps.add(new BasicNameValuePair("password", password)); nvps.add(new BasicNameValuePair("_csrf", token)); HttpEntity loginParams = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(nvps, "utf-8"); httpPost.setEntity(loginParams); // 第二次请求,带有CSRF Token httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpPost); // System.out.println("--------Cookie store for the POST: " + cookieStore.getCookies()); printResponse(httpResponse); // 取POST方法返回的HTTP状态码;不出意外的话是302 int code = httpResponse.getStatusLine().getStatusCode(); if (code == 302) { Header header = httpResponse.getFirstHeader("location"); // 跳转的目标地址是在 HTTP-HEAD 中的 String newUri = header.getValue(); // 这就是跳转后的地址,再向这个地址发出新申请,以便得到跳转后的信息是啥。 // 实际打印出来的是接口服务地址,不包括IP Address部分 System.out.println("--------Redirect to new location: " + newUri); httpGet = new HttpGet(EHR_ADDRESS + newUri); httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet); // printResponse(httpResponse); } // 请求一次绩效;确认登录成功 String queryUrl = EHR_ADDRESS + "/emp/performance/mt/query"; httpGet = new HttpGet(queryUrl); httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet); System.out.println("--------Result of the Cardpunch Query: "); printResponse(httpResponse); httpClient.close(); } catch (Exception ex) { ex.printStackTrace(); } } private static void printResponse(HttpResponse httpResponse) throws ParseException, IOException { // 获取响应消息实体 HttpEntity entity = httpResponse.getEntity(); // 响应状态 System.out.println("--------Status: " + httpResponse.getStatusLine()); System.out.println("--------Headers: "); HeaderIterator iterator = httpResponse.headerIterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { System.out.println(" " + iterator.next()); } // 判断响应实体是否为空 if (entity != null) { String responseString = EntityUtils.toString(entity); System.out.println("--------Response length: " + responseString.length()); System.out.println("--------Response content: " + responseString.replace(" ", "")); } } private static String getCsrfToken(HttpEntity responseEntity) throws IOException{ //获取网页内容,指定编码 String web = EntityUtils.toString(responseEntity,"utf-8"); Document doc= Jsoup.parse(web); // 选择器,选取特征信息 String token = doc.select("meta[name=_csrf]").get(0).attr("content"); System.out.println( "--------The current CSRF Token is: " + token); return token; } }
补充:如果使用HttpClientContext方式来维持会话,与CookieStore很接近;直接帖上需要修改的部分内容:
// 创建httpClient和context static CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault(); static HttpClientContext context = HttpClientContext.create(); // 下面的代码写在main()方法中 CloseableHttpResponse httpResponse = null; // 先发起一个Get请求,获取CSRF令牌和Cookie HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(EHR_ADDRESS); // 保存context上下文 httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet, context); ... // 处理完CSRF令牌后,准备发起POST请求 HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(EHR_ADDRESS); ... // 封装POST报文 // 发起POST请求 httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpPost, context); // 处理HTTP 302和业务查询操作的GET,也要携带着context httpResponse = httpClient.execute(httpGet, context);