项目结构
先来一张项目结构图,因为LZ是用的IDEAL,网上的大部分都是用的eclipse来实现:
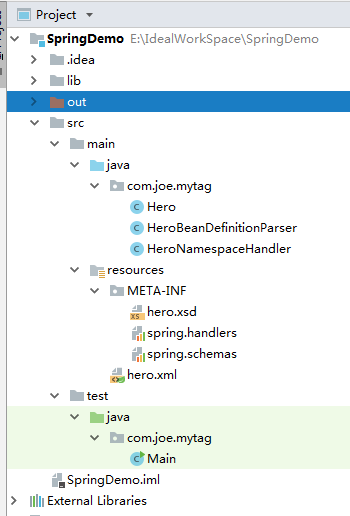
这里也大致说一下项目的新建,考虑到有的读者会想LZ一样对IDEAL的使用不是很熟练。
新建一个spring项目(不会的话网上搜索一下,很简单的),建好之后,再新建这些文件夹,点击File—>Project Structure --->Modules,设置文件夹的意义。LZ设置的java源文件是(Source Folders):srcmainjava;资源文件(Resource Folders):srcmain esources;测试文件(Test Source Folders):src estjava。
设置好这些以后,就可以正式开始自定义Spring标签了。
自定义Spring标签
1.定义一个JavaBean:
package com.joe.mytag; public class Hero { private String name; private int age; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } }
2.hero.xsd文件:
<xsd:schema xmlns="http://joe.com/schema" xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema" targetNamespace="http://joe.com/schema"><!-- 目标命名空间,xmlns要与它一致 --> <xsd:complexType name="myTagcomplexType"> <xsd:attribute name="name" type="xsd:string"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ The myTag name. ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> <xsd:attribute name="age" type="xsd:int"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ The myTag age. ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:attribute> </xsd:complexType> <xsd:element name="myTag" type="myTagcomplexType"> <xsd:annotation> <xsd:documentation><![CDATA[ myTag的文档 ]]></xsd:documentation> </xsd:annotation> </xsd:element> </xsd:schema>
这里需要注意几点:
(1)定义targetNamespace(目标命名空间),xmlns的值要与其一致;
(2)<xsd:element>定义的就是将会在xml文件中使用的元素,例如<hero:myTag>中的myTag;
(3)<xsd:attribute>定义的就是JavaBean中的属性,例如<hero:myTag name="age">中的name,就是bean中的属性name,并且还可以通过type来指定属性类型,进而起到检测的作用(比如我们定义的类型是int,如果xml中的值是非int类型的,就会直接报错)。
3.编写spring.schemas:
http://joe.com/schema/hero.xsd=META-INF/hero.xsd
注意:这里红色加粗的部分要与hero.xsd文件中的targetNamespace一致。
4.编写自定义BeanDefinition解析器
package com.joe.mytag; import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry; import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParser; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.ParserContext; import org.w3c.dom.Element; //自定义BeanDefinition解析器 public class HeroBeanDefinitionParser implements BeanDefinitionParser { private final Class<?> beanClass; public HeroBeanDefinitionParser(Class<?> beanClass) { this.beanClass = beanClass; } public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) { //创建用于属性承载的BeanDefinition RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(); //设置bean的对应class beanDefinition.setBeanClass(beanClass); //设置延迟加载为否 beanDefinition.setLazyInit(false); //获取对应的属性值,并设置到BeanDefinition中 beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("name", element.getAttribute("name")); beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("age", element.getAttribute("age")); //获取BeanDefinition的注册器 BeanDefinitionRegistry beanDefinitionRegistry = parserContext.getRegistry(); //注册bean到BeanDefinitionRegistry中 beanDefinitionRegistry.registerBeanDefinition(beanClass.getName(),beanDefinition); return beanDefinition; } }
5.编写命名空间的处理器
其作用主要是用来注册自定义的BeanDefinition解析器。
package com.joe.mytag; import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport; public class HeroNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport { public void init() { //注册自定义的BeanDefinition解析处理器 registerBeanDefinitionParser("myTag", new HeroBeanDefinitionParser(Hero.class)); } }
说明:通常为每一个xsd:element都要注册一个BeanDefinitionParser。
6.编写spring.handlers文件:
http://joe.com/schema=com.joe.mytag.HeroNamespaceHandler
作用:主要用于关联命名空间处理器和xsd中的targetNamespace。
注意:这里红色加粗的部分要与hero.xsd文件中的targetNamespace一致。
7.编写hero.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:hero="http://joe.com/schema" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://joe.com/schema http://joe.com/schema/hero.xsd"> <hero:myTag name="joe" age="25"/> </beans>
说明:
(1)xmlns:hero的value是xsd文件中的targetNamespace;
(2)xmlns:hero可以写成xmlns:xxx,此时<hero:myTag/>就要写成<xxx:myTag/>;
8.测试自定义标签:
package com.joe.mytag; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("hero.xml"); Hero hero = (Hero) applicationContext.getBean(Hero.class.getName()); System.out.println("name: " + hero.getName() + " age: " + hero.getAge()); } }
输出结果:
十二月 17, 2018 10:49:59 上午 org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext prepareRefresh
信息: Refreshing org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext@5910e440: startup date [Mon Dec 17 10:49:59 CST 2018]; root of context hierarchy
十二月 17, 2018 10:49:59 上午 org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanDefinitionReader loadBeanDefinitions
信息: Loading XML bean definitions from class path resource [hero.xml]
name: joe age: 25
如何在spring中自定义xml标签的方法就结束了。在实际中,随着注解和javaconfg的盛行,xml的方式渐渐的会淡出舞台,但是spring的启动流程还是会的。说一下上述代码涉及到的流程:
(1)使用ResourceLoader将配置文件xml装载为Resource对象;
(2)使用BeanDefinitionReader解析配置信息:将每一个<bean>解析为一个BeanDefinition对象,然后存储到BeanDefinitionRegistry中;
(3)实际上是BeanDefinitionReader调用BeanDefinitionParser进行了解析操作,解析完成后注册到BeanDefinitionRegistry(代码看上边的HeroBeanDefinitionParser);
踩过的坑
(1)项目中spring包错误,在新建项目时,有的包(不止一个)不会加载完全导致项目出错。(解决方式:网上下载新包,替换即可)。
(2)没有加上xsd:前缀,导致解析hero.xsd文件报错。
至此,简单的自定义标签完成。