- T1 Plus and Square Root
- 题面:
-
A. Plus and Square Roottime limit per test2 secondsmemory limit per test256 megabytesinputstandard inputoutputstandard output
ZS the Coder is playing a game. There is a number displayed on the screen and there are two buttons, ' + ' (plus) and '
 ' (square root). Initially, the number 2 is displayed on the screen. There are n + 1 levels in the game and ZS the Coder start at the level 1.
' (square root). Initially, the number 2 is displayed on the screen. There are n + 1 levels in the game and ZS the Coder start at the level 1.When ZS the Coder is at level k, he can :
- Press the ' + ' button. This increases the number on the screen by exactly k. So, if the number on the screen was x, it becomes x + k.
- Press the '
 ' button. Let the number on the screen be x. After pressing this button, the number becomes
' button. Let the number on the screen be x. After pressing this button, the number becomes 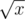 . After that, ZS the Coder levels up, so his current level becomes k + 1. This button can only be pressed when x is a perfect square, i.e. x = m2 for some positive integer m.
. After that, ZS the Coder levels up, so his current level becomes k + 1. This button can only be pressed when x is a perfect square, i.e. x = m2 for some positive integer m.
Additionally, after each move, if ZS the Coder is at level k, and the number on the screen is m, then m must be a multiple of k. Note that this condition is only checked after performing the press. For example, if ZS the Coder is at level 4 and current number is 100, he presses the '
 ' button and the number turns into 10. Note that at this moment, 10 is not divisible by 4, but this press is still valid, because after it, ZS the Coder is at level 5, and 10 is divisible by 5.
' button and the number turns into 10. Note that at this moment, 10 is not divisible by 4, but this press is still valid, because after it, ZS the Coder is at level 5, and 10 is divisible by 5.ZS the Coder needs your help in beating the game — he wants to reach level n + 1. In other words, he needs to press the '
 ' button ntimes. Help him determine the number of times he should press the ' + ' button before pressing the '
' button ntimes. Help him determine the number of times he should press the ' + ' button before pressing the ' ' button at each level.
' button at each level. Please note that ZS the Coder wants to find just any sequence of presses allowing him to reach level n + 1, but not necessarily a sequence minimizing the number of presses.
InputThe first and only line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 100 000), denoting that ZS the Coder wants to reach level n + 1.
OutputPrint n non-negative integers, one per line. i-th of them should be equal to the number of times that ZS the Coder needs to press the ' + ' button before pressing the '
 ' button at level i.
' button at level i. Each number in the output should not exceed 1018. However, the number on the screen can be greater than 1018.
It is guaranteed that at least one solution exists. If there are multiple solutions, print any of them.
Examplesinput3
output14
16
46input2
output999999999999999998
44500000000input4
output2
17
46
97NoteIn the first sample case:
On the first level, ZS the Coder pressed the ' + ' button 14 times (and the number on screen is initially 2), so the number became 2 + 14·1 = 16. Then, ZS the Coder pressed the '
 ' button, and the number became
' button, and the number became 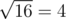 .
. After that, on the second level, ZS pressed the ' + ' button 16 times, so the number becomes 4 + 16·2 = 36. Then, ZS pressed the '
 ' button, levelling up and changing the number into
' button, levelling up and changing the number into 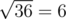 .
.After that, on the third level, ZS pressed the ' + ' button 46 times, so the number becomes 6 + 46·3 = 144. Then, ZS pressed the '
 ' button, levelling up and changing the number into
' button, levelling up and changing the number into 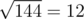 .
. Note that 12 is indeed divisible by 4, so ZS the Coder can reach level 4.
Also, note that pressing the ' + ' button 10 times on the third level before levelling up does not work, because the number becomes 6 + 10·3 = 36, and when the '
 ' button is pressed, the number becomes
' button is pressed, the number becomes 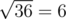 and ZS the Coder is at Level 4. However, 6 is not divisible by 4 now, so this is not a valid solution.
and ZS the Coder is at Level 4. However, 6 is not divisible by 4 now, so this is not a valid solution.In the second sample case:
On the first level, ZS the Coder pressed the ' + ' button 999999999999999998 times (and the number on screen is initially 2), so the number became 2 + 999999999999999998·1 = 1018. Then, ZS the Coder pressed the '
 ' button, and the number became
' button, and the number became 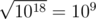 .
. After that, on the second level, ZS pressed the ' + ' button 44500000000 times, so the number becomes 109 + 44500000000·2 = 9·1010. Then, ZS pressed the '
 ' button, levelling up and changing the number into
' button, levelling up and changing the number into 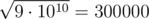 .
. Note that 300000 is a multiple of 3, so ZS the Coder can reach level 3.
- 题意:当前数字a[k](a[k]是k的倍数)要么+k,要么开根得到a[i+1](必须完全平方根),问每次得到下一个数要几次加几次。
- 模拟:开方后满足每次为k与k+1的公倍数,注意爆精度
-
 View Code
View Code1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #define ll long long 4 using namespace std; 5 6 ll n; 7 ll k; 8 int main() { 9 scanf("%lld",&n); 10 for(ll i=1; i<=n; i++) { 11 k=i==1?2:i*(i+1)*(i+1)-i+1; 12 printf("%lld ", k); 13 } 14 }
- T2 Dfscount
- 题面:
-
Problem Statement for DFSCount 

Problem Statement
Fox Ciel has a simple undirected graph with n vertices. The vertices are numbered 0 through n-1. The graph is connected.
You are given a String[] G containing the adjacency matrix of the graph. More precisely, for each i and j, G[i][j] is 'Y' if there is an edge between vertices i and j and it is 'N' if there is no such edge.
Ciel then implemented a depth-first search:
p = [] dfs(current) := p.append(current) Let adjs[] = list of vertices that are adjacent to current. random_shuffle(adjs) for v in adjs: if v is not in p: dfs(v) Let start = random(0, n-1) # a random number between 0 and n-1, inclusive dfs(start) output(p)
Clearly, the output of this algorithm is always a permutation of the numbers from 0 to n-1. However, as the algorithm uses randomness, there may be multiple possible outputs. Please compute and return the number of different permutations the algorithm may return.Definition
Class: DFSCount Method: count Parameters: String[] Returns: long Method signature: long count(String[] G) (be sure your method is public) Constraints
- n will be between 1 and 14, inclusive. - G will contain exactly n elements. - Each element in G will contain exactly n characters. - Each character in G will be 'N' or 'Y'. - For any valid i, G[i][i] = 'N'. - For any valid i and j, G[i][j] = G[j][i]. - The graph described by G will be connected. Examples
0) {"NYY", "YNY", "YYN"}Returns: 6
G describes a complete graph with 3 vertices. There are 3! = 6 permutations of vertices, and we can easily verify that each of these permutations can appear as the output of Ciel's algorithm. 1) {"NYNN", "YNYN", "NYNY", "NNYN"}Returns: 6
This time the graph is a line: 0 - 1 - 2 - 3. These are the possible outputs: - 0,1,2,3
- 1,0,2,3
- 1,2,3,0
- 2,1,0,3
- 2,3,1,0
- 3,2,1,0
2) {"NYYY", "YNYY", "YYNN", "YYNN"}Returns: 16
This graph looks as follows: 2 / 0---1 / 3
There are 16 possible permutations:- 0,1,2,3
- 0,1,3,2
- 0,2,1,3
- 0,3,1,2
- 1,0,2,3
- 1,0,3,2
- 1,2,0,3
- 1,3,0,2
- 2,0,1,3
- 2,0,3,1
- 2,1,0,3
- 2,1,3,0
- 3,0,1,2
- 3,0,2,1
- 3,1,0,2
- 3,1,2,0
3) {"NYYYYYYYYYYYYY", "YNYYYYYYYYYYYY", "YYNYYYYYYYYYYY", "YYYNYYYYYYYYYY", "YYYYNYYYYYYYYY", "YYYYYNYYYYYYYY", "YYYYYYNYYYYYYY", "YYYYYYYNYYYYYY", "YYYYYYYYNYYYYY", "YYYYYYYYYNYYYY", "YYYYYYYYYYNYYY", "YYYYYYYYYYYNYY", "YYYYYYYYYYYYNY", "YYYYYYYYYYYYYN"}Returns: 87178291200
The answer is 14! 4) {"N"}Returns: 1
- 题意:给定一个(n<=14)的简单无向图,问可生成的DFS序有多少。
- 记忆化搜索,状态压缩
- 状态:f[x][s] x:讨论到第x号点 s:已经讨论的点
- 转移:f[x][s]=sum(f[v][s|v]*f[x][s|T]) T:v所在联通块集合
-
 View Code
View Code1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<algorithm> 3 #define ll long long 4 using namespace std; 5 6 ll ans,n; 7 ll f[16][1<<15]; 8 ll t; 9 ll a[16][16]; 10 11 void block(ll x) { 12 t|=1<<(x-1); 13 for(ll i=1; i<=n; i++) 14 if(a[x][i]&&(t&(1<<(i-1)))==0)block(i); 15 } 16 17 ll dfs(ll x,ll s) { 18 if(f[x][s]) return f[x][s]; 19 for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) 20 if(a[x][i]&&(s&(1<<(i-1)))==0) { 21 t=s; 22 block(i); 23 f[x][s]+=dfs(x,t)*dfs(i,s^(1<<(i-1))); 24 } 25 f[x][s]=max(f[x][s],1LL); 26 return f[x][s]; 27 } 28 29 int main() { 30 scanf("%lld",&n); 31 for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) { 32 scanf(" "); 33 for(int j=1; j<=n; j++) { 34 char ch; 35 scanf("%c",&ch); 36 if(ch=='Y') a[i][j]=1; 37 } 38 } 39 for(ll i=1; i<=n; i++) ans+=dfs(i,1<<(i-1)); 40 printf("%lld",ans); 41 }
- T3 Gene
- 题面:待补
- AC自动机,矩阵快速幂(这道题完全不会……还得学一波后填坑……先上学长的代码)
-
 View Code
View Code1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<string.h> 3 #include<queue> 4 #include<assert.h> 5 #include<algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 const int N=128,mod=10007,i4v=mod+1>>2; 8 char MAP[256]; 9 int n,m,tot=2,tr[N][4],fail[N]; 10 int M[30][N][N]; 11 typedef int Mat[N][N]; 12 int mul(int a,int b){return a*b%mod;} 13 // root=2, null=1 14 void ins(char *s) { 15 int x,p=2; 16 while(1) { 17 if(p==1) return; 18 x=MAP[*s++]; 19 int &t=tr[p][x]; 20 if(*s) { 21 if(!t) t=++tot; 22 } else t=1; p=t; 23 } 24 } 25 #define reg register 26 #define rint register int 27 void Mul(Mat &A,Mat &S,Mat &C) { 28 static Mat B; 29 for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++) 30 for(int j=1;j<=tot;j++) 31 B[i][j]=S[j][i]; 32 for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++) { 33 for(int j=1;j<=tot;j++) { 34 register long long tmp=0; 35 for(rint *x=A[i]+1,*y=B[j]+1,k=1;k<=tot;k++,x++,y++) 36 tmp+=*x**y; 37 C[i][j]=tmp%mod; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 void build() { 42 int p,i,j,k,hd=0,tl=0; 43 static int Q[N]; 44 for(i=0;i<4;i++) { 45 int &x=tr[2][i]; 46 if(!x) x=2; 47 else if(x!=1) fail[Q[tl++]=x]=2; 48 } 49 while(hd<tl) { 50 p=Q[hd++]; 51 for(i=0;i<4;i++) { 52 int &x=tr[p][i]; 53 if(!x) x=tr[fail[p]][i]; // for root 54 else if(x!=1) 55 fail[Q[tl++]=x]=tr[fail[p]][i]; 56 } 57 } 58 Mat &S=M[0]; 59 for(i=1;i<=tot;i++) { 60 for(j=0;j<4;j++) { 61 assert(tr[i][j]); 62 S[tr[i][j]][i]+=i4v; 63 } 64 } 65 for(i=1;i<30;i++) 66 Mul(M[i-1],M[i-1],M[i]); 67 } 68 void Mul(Mat Y,int X[N]) { 69 static int O[N]; 70 for(rint i=1;i<=tot;i++) { 71 reg long long tmp=0; 72 for(rint *x=X+1,*y=Y[i]+1,j=1;j<=tot;x++,y++,j++) 73 tmp+=*x**y; 74 O[i]=tmp%mod; 75 } 76 copy(O,O+tot+1,X); 77 } 78 int Work(int n) { 79 int i,j,k; 80 static int X[N]; 81 memset(X,0,sizeof X);X[2]=1; 82 for(i=0;i<30;i++) { 83 if(n>>i&1) Mul(M[i],X); 84 } 85 return (mod+1-X[1])%mod; 86 } 87 char buf[N]; 88 int main() { 89 // freopen("gene.in","r",stdin); 90 // freopen("gene.out","w",stdout); 91 92 MAP['A']=0;MAP['T']=1; 93 MAP['C']=2;MAP['G']=3; 94 tr[1][0]=tr[1][1]=tr[1][2]=tr[1][3]=1; 95 96 scanf("%d",&m); 97 while(m--) { 98 scanf("%s",buf); 99 ins(buf); 100 } 101 build();int T; 102 scanf("%d",&T); 103 while(T--) { 104 scanf("%d",&n); 105 printf("%d ",Work(n)); 106 } 107 }
